
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
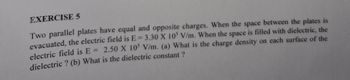
Transcribed Image Text:EXERCISE 5
Two parallel plates have equal and opposite charges. When the space between the plates is
evacuated, the electric field is E=3.30 X 105 V/m. When the space is filled with dielectric, the
electric field is E= 2.50 X 105 V/m. (a) What is the charge density on each surface of the
dielectric ? (b) What is the dielectric constant ?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- X FEED QUESTION 4 A particle of charge +6.1 µC is released from rest at the point x = 98 cm on an x axis. The particle begins to move due to the presence of a charge Q=+89 µC that remains fixed at the origin. What is the kinetic energy of the particle at the instant it has moved 40 cm? OA. 1.443 J OB. 0.334 J OC.0.155 J OD.3.434 J OE. 1.983 J BE ents the magnitude of the electric field as a function of the distance from the center of a solid charged conductingarrow_forwardI Review | Constants The ammonia molecule (NH3) has a dipole moment of 5.0 x 10-30 C.m. Ammonia molecules in the gas phase are placed in a uniform electric field E with magnitude 1.4x106 N/C. Part A What is the change in electric potential energy when the dipole moment of a molecule changes its orientation with respect to E from parallel to perpendicular? Express your answer using two significant figures. ΑΣφ ? AU = Jarrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER ALL PARTS ASAP!!!!!!!arrow_forward
- Problem 1 Two metal spheres A and B with radii RA and RB rest far away from one another but are connected by a long wire with a switch. With the switch disconnected, only sphere A is charged, with an initial charge Q1. a) What is the initial magnitude of the electric field |E₁| at the surface of sphere A? b) What is the initial electric potential V, at the surface of sphere A, assuming V → 0 an infinite distance away? c) The switch is now connected and the spheres reach electrostatic equilibrium. In terms of the radii, electric constant, and initial charge, what are the final charges QA and QB on each sphere? Assume the wire can transfer charge but only hold a negligible amount. d) What are the final potentials V₁ and VB at the surfaces of each sphere? e) What are the final electric field magnitudes |Ē₁] and |ĒB] at the surfaces of each sphere?arrow_forwardPART B ONLY PLEASEarrow_forwardQuestion 14 of 35 A particle that carries a net charge of-41.8 uC is held in a constant electric field that is uniform over the entire region. The electric field vector is oriented 25.2° clockwise from the vertical axis, as shown in the figure. If the magnitude of the electric field is 4.32 N/C, how much work is done by the electric field as the particle is made to E move a distance of d = 0.556 m straight up? d. 25.2° work: J What is the potential difference AV between the particle's initial and final positions? AV =arrow_forward
- I am stuck on this physics homework, any help would be great!arrow_forward1arrow_forwardPart A Two stationary positive point charges, charge 1 of magnitude 3.85 nC and charge 2 of magnitude 1.70 nC are separated by a distance of 39.0 cm An electron is released from rest at the point midway between the two charges, and it moves along the line connecting the two charges. What is the speed vfinal of the electron when it is 10.0 cm from charge 1? Express your answer in meters per second. > View Available Hint(s) ΑΣφ Ufinal m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON