
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
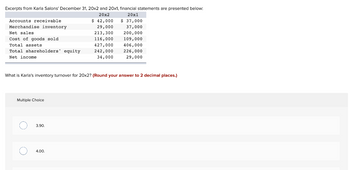
Transcribed Image Text:Excerpts from Karla Salons' December 31, 20x2 and 20x1, financial statements are presented below:
20x2
Accounts receivable
Merchandise inventory
Net sales
Cost of goods sold.
Total assets
Total shareholders' equity
Net income
Multiple Choice
What is Karla's inventory turnover for 20x2? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
O
O
3.90.
$ 42,000
29,000
213,300
116,000
427,000
242,000
34,000
4.00.
20x1
$ 37,000
37,000
200,000
109,000
406,000
226,000
29,000
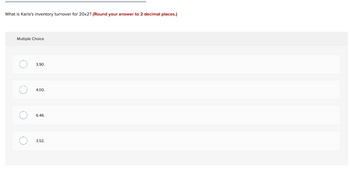
Transcribed Image Text:What is Karla's inventory turnover for 20x2? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
Multiple Choice
O
O
O
3.90.
4.00.
6.46.
3.52.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cost of goods sold computations for Bridgeport Company and Sarasota Company are as follows. Bridgeport Company Sarasota Company Beginning inventory $ 46,500 $ 74,000 Cost of goods purchased 199,000 290,075 Cost of goods available for sale 245,500 364,075 Ending inventory 54,680 74,500 Cost of goods sold $190,820 $289,575 (a1) Compute inventory turnover for each company. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25.) Bridgeport Company Sarasota Company Inventory turnover enter inventory turnover rounded to 2 decimal places enter inventory turnover rounded to 2 decimal placesarrow_forwardPresented below is information related to Kingbird Company. Cost Retail Beginning inventory $59,780 $98.000 Purchases (net) 132.070 196,100 Net markups 11,067 Net markdowns 23,589 Sales revenue 176,870 (a) Compute the ending inventory at retail. Ending inventoryarrow_forward(do not provide image in solution) Suppose that the following information is available for Nike Inc. for the current year. Beginning inventory Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Net sales Inventory turnover Days in inventory $11,570 Gross profit rate 14,360 Calculate the inventory turnover, days in inventory, and gross profit rate for Nike Inc. for the current year. (Round gross profit rate to 2 decimal places, eg. 12.51 and other answers to 1 decimal place, e.g. 15.2. Use 365 days for calculation.) 103,720 145,200 times days %arrow_forward
- Using the following information, what is the amount of net income? Purchases $32,000 Selling expenses $ 960 Merchandise inventory, September 1 5,700 Merchandise inventory,September 30 6,370 Administrative expenses 910 Sales 63,000 Rent revenue 1,200 Interest expense 1,040 a. $28,760 b. $29,960 c. $31,670 d. $29,800arrow_forwardPresented below is information related to Blue Company. cost Retail Begininng Inventory $59,780 $98,000 Purchases (net) $132,070 196,100 Net markups 11,067 Net markdowns 23,589 Sales Revenue 176,870 Compute the ending inventory at retail.arrow_forwardSavitaarrow_forward
- The following is information for Palmer Co. Year 3 Year 2 Year 1 Cost of goods sold $ 643,825 $ 426,650 $ 391,300 Ending inventory 97,400 87,750 92,500 Use the above information to compute inventory turnover for Year 3 and Year 2, and its days' sales in inventory at December 31, Year 3 and Year 2.arrow_forwardUsing the following information, what is the cost of goods sold? Purchases $32,282 Selling expense $955 Inventory, September 1 7,698 Inventory, September 30 2,640 Administrative expense 525 Sales 52,858 Rent revenue 1,044 Interest expense 893 a.$893 b.$31,176 c.$37,340 d.$14,993arrow_forwardGiven the information below, what is the gross profit? Sales revenue Accounts receivable Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Sales returns Multiple Choice $76,000 $197,000 $79,000 $106,000 $ 345,000 60,000 118,000 239,000 30,000arrow_forward
- Using the following information, what is the amount of gross profit? Purchases $ 25,449 Selling expense $ 970 Inventory, September 1 5,138 Inventory, September 30 8,660 Administrative expense 545 Sales 55,013 Rent revenue 844 Interest expense 907 A. $907 B. $21,927 C. $24,542 D. $33,086arrow_forwardDo not provide image in solution.arrow_forwardSolve for the missing information designated by "?" in the following table. (Use 365 days in a year. Round the inventory turnover ratio to one decimal place before computing days to sell. Round days to sell to one decimal place.) Case Beginning Inventory Purchases Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory Inventory Turnover Ratio Days to Sell a. $ 130 $ 730 $ 690 b $ 230 $ 1,320 C $ 1,120 $ 135 6.6 32.6arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education