
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A rubber stopper weighing 8.554 g displaces 7.0 mL of water in a graduated cylinder. Refer to Example Excercise 2 and calculate the density of the solid rubber stopper.
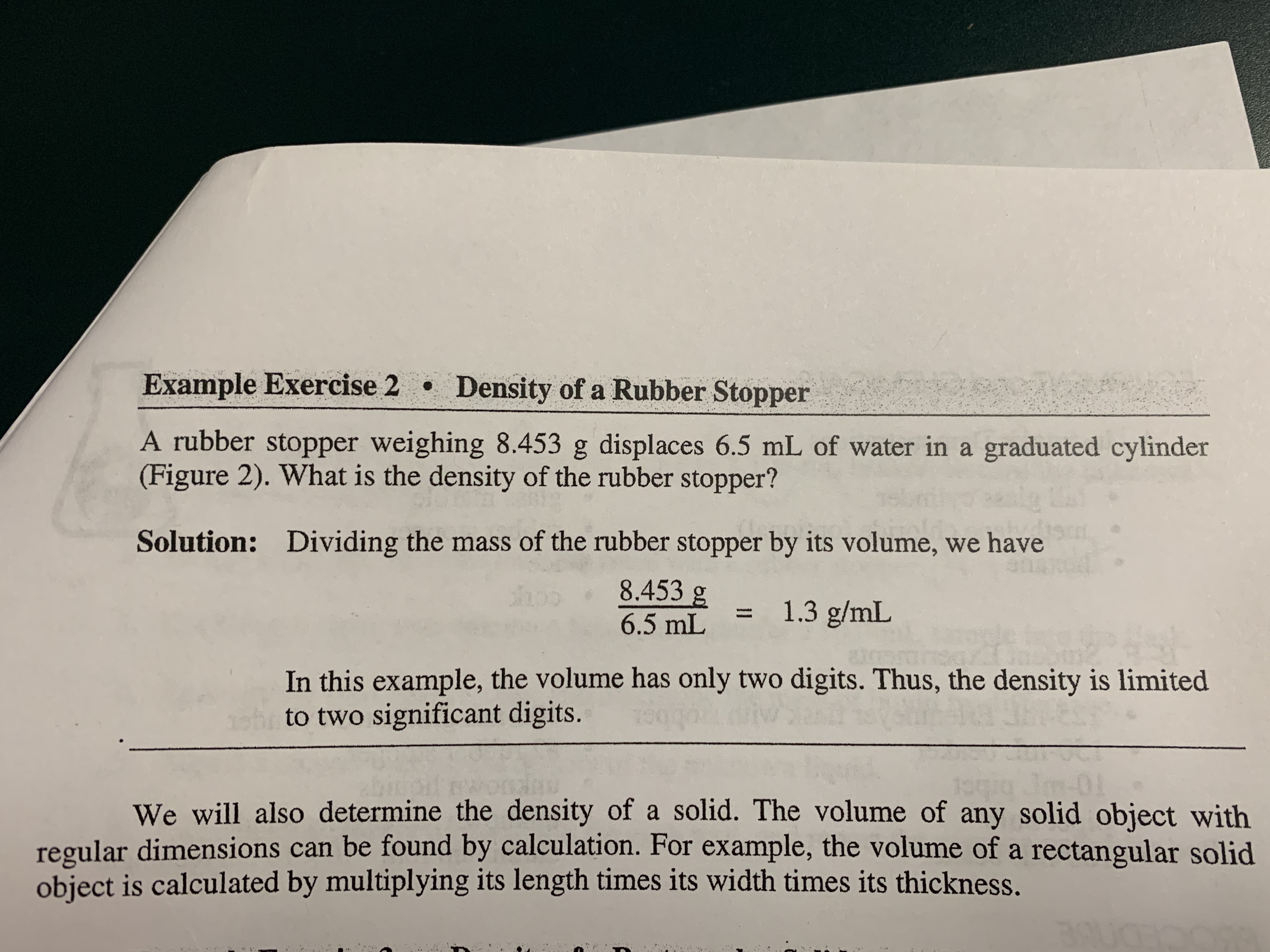
Transcribed Image Text:Example Exercise 2 Density of a Rubber Stopper
A rubber stopper weighing 8.453 g displaces 6.5 mL of water in a graduated cylinder
(Figure 2). What is the density of the rubber stopper?
Solution: Dividing the mass of the rubber stopper by its volume, we have
8.453 g
1.3 g/mL
6.5 mL
In this example, the volume has only two digits. Thus, the density is limited
to two significant digits.
We will also determine the density of a solid. The volume of any solid object with
regular dimensions can be found by calculation. For example, the volume of a rectangular solid
object is calculated by multiplying its length times its width times its thickness.
BRUCE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An 11 lb bowling ball has a circumference of 27 inches. Calculate the density of the bowling ball and determine whether it will float or sink if placed in water. Ignore the holes in the bowling ball.arrow_forwardA bone fragment displaces 4.27 ml of water and is found to have a mass of 4.646 g. What is the density of the bone fragment? (do not include units in your answer, just the numeric part and round off to the correct number of singificant digits)arrow_forwardCarbon disulfide gas and oxygen gas react to form sulfur dioxide gas and carbon dioxide gas. What volume of carbon dioxide would be produced by this reaction if 1.22cm^3 of oxygen were consumed? Also, be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and is rounded to the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
- A rubber stopper has a mass of 5.8 g. When placed in a graduated cylinder filled with water, the water level rises from 15mL to 20.4mL. Calculate the density of the rubber stopper.arrow_forwardFind the radius (in centimeters) of a water droplet with a volume of 0.058 mL. You can assume the droplet is a sphere.arrow_forwardHow many days are in 41,700 minutes? (Assume exactly 24 hours in a day). Express your answer with the appropraite number of significant figures and a unit.arrow_forward
- the mass of water is 9.953g and the density of water is 0.997992g/mL. How do we calculate to find the volume of water?arrow_forwardConsider the following two volume measurements: 57.7 mL and 57.68 mL. Which of these is the more precise measurement, and why?arrow_forwardA bar of gold measures 0.127 m x 0.0483 m x 0.0155 m. How many gallons of water have the same mass as this bar? Number Unitsarrow_forward
- Convert 643 milimeters to meters.arrow_forward3. The density of titanium is 4.54 g/mL. What is the volume, in milliliters (mL), of 163 g of titanium? Please follow correct significant figures and show your solution.arrow_forwardA sample containing 29.05g of metal pellets is poured into a graduated cylinder initially containing 15.0ml of water, causing the water level to rise to 18.1 ml. Calculate the density of the metal.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY