
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
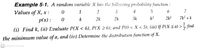
Transcribed Image Text:Example 5-1. A random variable X has the following probability function :
Values of X, x :
1
3
4
5
7
p(x) :
k
2k
2k
3k
k2
2k²
7k? + k
> find
1
(i) Find k, () Evaluate Р(X < 6), Р(Х26), and P(0 <X<5), (i) If P(X Sa) >
2'
the minimum value of a, and (iv) Determine the distribution function of X.
CS Scanned with CamScanner
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A random variable X has a following probability function, X 0 1 3 4 5 6 P(X) 0k 2k 2k | 3k k 2k 7k2 + k Find the value of, (i) k (ii) P(X < 6).arrow_forwardAccording to Bayes' Theorem, the probability of event A, given that event B has occurred, is as follows. P(A) • P(B| A) P(A) • P(B| A) + P (A') •P(B| A') P(A| B) = %3D Use Bayes' Theorem to find P(A B) using the probabilities shown below. P(A) =1. P(A') =, P(B| A) =5, 1 and P(B| A') = %3D %3D 10 %3D 4 The probability of event A, given that event B has occurred, is P(A B) =|. (Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.)arrow_forwardSuppose that X, Y, and Z are jointly distributed random variables, that is, they are defined on the same sample space. Suppose that we also have the following. E(X)=-1 E(Y) = 4 E (Z)=0 Var(X)=20 Var(Y) = 27 Var (Z) = 38 Compute the values of the expressions below. E (5Z-2) = 0 2Z+X -5 Var(2X-3) = 0 E = E (32²) = 0 Explanation Check X O hp Ⓒ2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Termarrow_forward
- 2. Some properties of Expected value and variance of a random variable. a) Assume that X is an arbitrary discrete random variable, and a and b are constant. Using the definitic Show: and E(aX + b) = a · E(X) + b V(aX + b) = a² · V(X ) Stat 3128 Ali Mahzarnia P STAT 3128 Ali Mahzarnia b) Justify the computational formula of Variance of a random variable which is to justify : V(X) = E[(X – µ°] = Ex – µ)P • ptx) = | 2: Here needs justification By Cauchy Schwarz inequality it can be shown that the right hand side is always positive. Analogs expression in Mechanic : Parallel axis theorem Iem = I– md² Moment of Moment of inetria about Inertia of an an axis shifted object about the center of a mass by d from center of mass (a parallel shift) Icm is dispersion around the mean and is like second central moment (variance) I is like second moment if d is mean m is like sum total all the weight of each of the x which all add up to 1 d squared is like squared of mean since we,arrow_forwardA discrete random variable Y has the probability function as given below. Y -2 2 4 P(Y) 0.25 0.50 0.25 If F(Y) denotes the cumulative distribution function for Y, select the correct statement below Group of answer choices F(-3) = 0, F(1)=0.25 and F(3)=0.50 F(-3) = 0, F(1)=0.25 and F(5)=0 F(-3) = 0, F(0) = 0.25 and F(5) = 1 F(-3) = 0, F(1)=0.25 and F(6)=0 F(0)= 0, F(1)= 0 and F(3)=0arrow_forwardLet (X1, X2, X3) be the random outcome of tossing a fair six-faced die three times, and let (Y(1), Y(2), Y(3) be the order statistics from (X1, X2, X3). We have Y(1) = min (X1, X2, X3), Y(3) = max (X1, X2, X3), and Y(1) < Y(2) < Y(3). Find Pr (Y(1) = 3).arrow_forward
- Business Calculus 2Section 11.2: Continuous Random Variablesarrow_forwardPossible values of X, the number of components in a system submitted for repair that must be replaced, are 1, 2, 3, and 4 with corresponding probabilities 0.35, 0.15, 0.35, and 0.15, respectively. (a) Calculate E(X) and then E(5 - X). E(X) E(5-X) = (b) Would the repair facility be better off charging a flat fee of $70 or else the amount $ 150 (5-X) The repair facility ---Select--- be better off charging a flat fee of $70 because E ]= 150 (5-X)] ? Note: It is not generally true that : E ( =) = E(Y)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman