Question
Transcribed Image Text:er...
Leeds International...
WolfBerry's
Watch Video
Question 11 A
M1 Questions by To...
YouTube
Mail-Al Habsi, As...
G3: (Ahmad, Asma,...
500 N
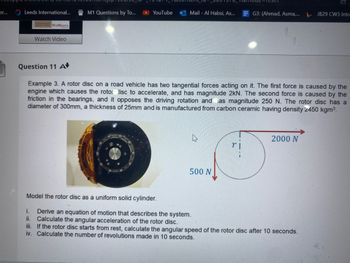
Example 3. A rotor disc on a road vehicle has two tangential forces acting on it. The first force is caused by the
engine which causes the rotor disc to accelerate, and has magnitude 2kN. The second force is caused by the
friction in the bearings, and it opposes the driving rotation and has magnitude 250 N. The rotor disc has a
diameter of 300mm, a thickness of 25mm and is manufactured from carbon ceramic having density 2450 kgm³.
2000 N
JB29 CW3 Intr
Model the rotor disc as a uniform solid cylinder.
i.
Derive an equation of motion that describes the system.
ii. Calculate the angular acceleration of the rotor disc.
iii. If the rotor disc starts from rest, calculate the angular speed of the rotor disc after 10 seconds.
iv. Calculate the number of revolutions made in 10 seconds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Practice Problems: Torque Physics 1. A 200 g mass is placed on the meter stick 20 cm from the fulcrum. An unknown mass is positioned 8 cm from the fulcrum to balance the system. What is the mass of this unknown object? Unknown mass T = rx F Page rccw Fulcrum rcw 2. A 250 g mass is placed on the meter stick 30 cm from the fulcrum. An unknown mass is positioned 40 cm from the fulcrum to place the system in equilibrium. What is the mass of the unknown object? 1 / 2 Load: 200-g mass +arrow_forwardQuestion 4 1 pts A clockwise torque is O negative O positive O torques are always positive Question 5 1 pts Saying that the Sum of torques is zero is the same as saying that the magnitude of clockwise torques is O cqual to the magnitude of counterclockwise torques O opposite to the magnitude of counterclockwise torques O zero Question 6 1 pts For this week's lab, once the pivot is moved away from the center of gravity, the lever arm for the torque of the weight is: O distance between the center of gravity and the position of the pivot O zero O position of the pivotarrow_forward