
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134463216
Author: Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
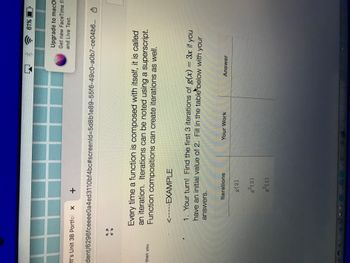
Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding Function Iterations
Every time a function is composed with itself, it is called an iteration. Iterations can be noted using a superscript. Function compositions can create iterations as well.
#### Example
---
#### Exercise: Your Turn!
Find the first 3 iterations of \( g(x) = 3x \) if you have an initial value of 2. Fill in the table below with your answers.
| Iterations | Your Work | Answer |
|-----------------|-------------|--------|
| \( g(2) \) | | |
| \( g^2(2) \) | | |
| \( g^3(2) \) | | |
In this exercise, you need to apply the function \( g(x) = 3x \) iteratively starting with an initial value.
#### Note:
- For \( g(2) \), substitute \( x \) with 2 in the function.
- For \( g^2(2) \), apply the function \( g \) to the result of \( g(2) \).
- For \( g^3(2) \), apply the function \( g \) to the result of \( g^2(2) \).
Write down each step of your work in the corresponding row under "Your Work", and the final result in the "Answer" column.
Use this method to understand the process of function iterations and their applications.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305657960
Author:Joseph Gallian
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780135163078
Author:Michael Sullivan
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:9780980232776
Author:Gilbert Strang
Publisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:9780077836344
Author:Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education