
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
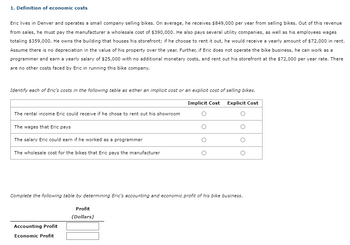
Transcribed Image Text:1. Definition of economic costs
Eric lives in Denver and operates a small company selling bikes. On average, he receives $849,000 per year from selling bikes. Out of this revenue
from sales, he must pay the manufacturer a wholesale cost of $390,000. He also pays several utility companies, as well as his employees wages
totaling $359,000. He owns the building that houses his storefront; if he choose to rent it out, he would receive a yearly amount of $72,000 in rent.
Assume there is no depreciation in the value of his property over the year. Further, if Eric does not operate the bike business, he can work as a
programmer and earn a yearly salary of $25,000 with no additional monetary costs, and rent out his storefront at the $72,000 per year rate. There
are no other costs faced by Eric in running this bike company.
Identify each of Eric's costs in the following table as either an implicit cost or an explicit cost of selling bikes.
Implicit Cost Explicit Cost
The rental income Eric could receive if he chose to rent out his showroom
The wages that Eric pays
The salary Eric could earn if he worked as a programmer
The wholesale cost for the bikes that Eric pays the manufacturer
Complete the following table by determining Eric's accounting and economic profit of his bike business.
Profit
(Dollars)
Accounting Profit
Economic Profit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Your boss is impressed with your performance over the past year and has decided to give you a 5% increase in your salary. Are you clearly better off with your increased salary? What factors must be considered?arrow_forwardAs distance to the city center increases, an office firm’s willingness to pay for space [increases / decreases / remains] at a(n) [increasing / decreasing / constant] rate.arrow_forwardYou and your friends love to go fishing. There is a sporting goods store in your neighborhood that sells a fishing pole for $82 but costs the store $60, and a fully stocked tackle box that sells for $58 but costs $40. Assuming the mark-up policy is linear, determine the equation that relates price (P) to cost (C). Following this same mark-up policy for other items, what would be the price of a pair of waders which cost the company $80?arrow_forward
- You are the County Commissioner of Hazard County. Recently a severe wave of storms swept across Hazard County, spawning several tornadoes and creating a wide path of mayhem. The citizens of Hazard County are demanding that you do something to protect them. You decide to install some early warning tornado sirens. However, there is no money left in the county budget, so you ask each citizen to donate some money to build the system. Many citizens donate money to help build the warning system; however, Ms. Nancy, who is wealthy, decides she is not going to donate. The early warning sirens are an example of a and Ms. Nancy represents a Public goods are in rivalry and in excludability. What approach would be the least effective way to deal with free riders? OA. Appeal to their civic sense of responsibility. OB. Exclude citizens from benefiting from the good or service. OC. Threaten to expose the free riders to their neighbors. OD. Offer citizens a favor or a small gift if they agree not to…arrow_forwardRecall a sharecropping agreement is where a farmer provides a percentage of their yield to a landowner in exchange for renting the land. Consider the graph below and answer the following questions (include calculations in work): 11 VMPL 10 8 a*VMPL 5 4 3 2 1 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 Labor (Hour) "andınoarrow_forwardThe regular air fare between Boston and San Francisco is 419. An airline using planes on this route observes that they fly with an average of 236 passengers. Market research tells the airlines’ managers that each $7 fare reduction would attract, on average, 3 more passengers for each flight. How should they set the fare to maximize their revenue?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education