Question
Direction of the force on the wire going through point p
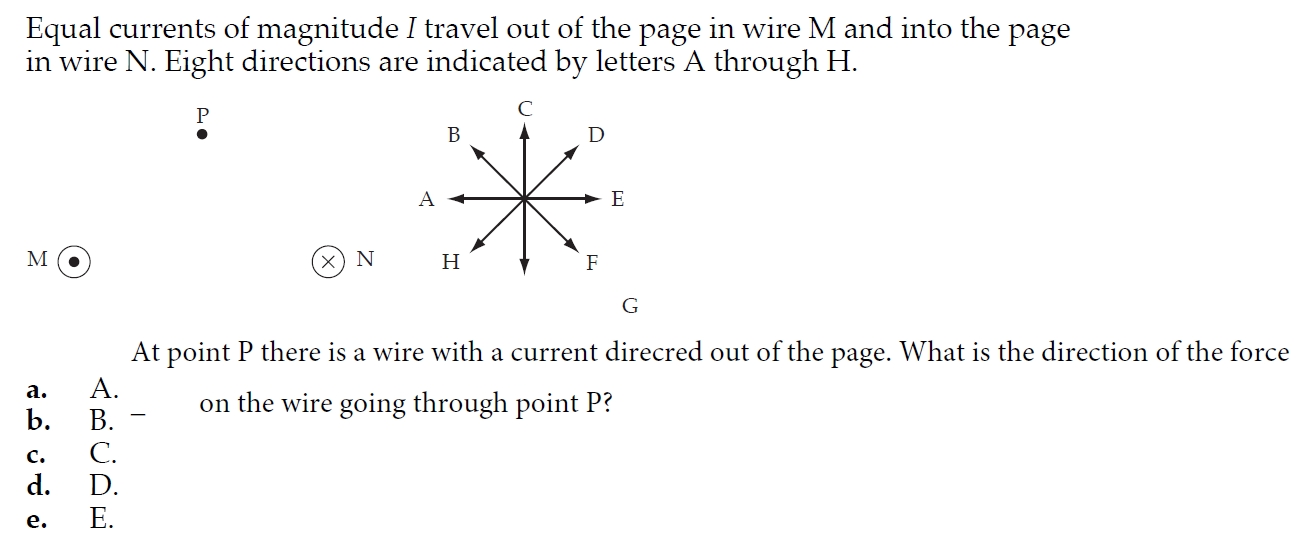
Transcribed Image Text:Equal currents of magnitude I travel out of the page in wire M and into the page
in wire N. Eight directions are indicated by letters A through H.
(x) N
Н
At point P there is a wire with a current direcred out of the page. What is the direction of the force
a.
A.
on the wire going through point P?
b.
B.
c.
C.
d.
D.
E.
e.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The figure below is a cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, an outer conductor, and another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is I, = 1.06 A out of the page and the current in the outer conductor is I, = 3.04 A into the page. Assuming the distance d = 1.00 mm, answer the following. d d (a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point a. magnitude pT direction |---Select--- (b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point b. magnitude direction -Select---arrow_forwardSuppose in the figure that the four identical currents i = 20 A, into or out of the page as shown, form a square of side 76 cm. a) What is the force per unit length (magnitude and direction) on the wire in the bottom left hand corner? (N/m) Take the positive y direction as up and the positive x direction as to the right. b)What is the magnitude of the force per unit length? c)What is the x component of the force per unit length? d)What is the y component of the force per unit length?arrow_forwardWhat is the current on the path 1-2 in the circuit below? 3 A 6.92e-4 A 1.4e-2 A 0 Aarrow_forward
- Two power lines run parallel for a distance of 283 m and are separated by a distance of 40.0 cm. If the current in each of the two lines is 115 A and if they run in opposite directions, determine the magnitude and direction of the force each wire exerts on the other.arrow_forwardLet's take a current-carrying cable with a gradually narrowing cross-sectional area along the length of the wire so the wire turns into the shape of a very long, truncated cone. How does the drift speed (vd) vary along the length of the wire? It speeds up with the length or vd first increases and then goes down after it reaches to a critical value.or It slows down with the length of the cable or vd remains the same regardless the cross section of the cable.arrow_forward9. Two differential current elements, I₁AL₁= 3×10° ay Am at P₁(1,0, 0) and 1₂AL2= 3×10 (-3a +4ay+5a) A⋅m at P₂(2, 2, 2), are located in free space. Find the vector force exerted on 12AL2 by I₁AL₁.arrow_forward
- In the figure below, the blue wire has a current I = 25 A. The red loop is a square with sides that are 42 cm long and it has a current of 94 A. The distance between the blue wire and wire BC is 4.5 cm. Determine the force the blue wire exerts on wire BC and the force the blue wire exerts on wire AD. www B Force of blue wire on BC = direction of force on BC = Choose direction ✓ Force of blue wire on AD = direction of force on AD = Choose directionarrow_forwardIn a classroom demonstration, two long parallel wires are separated by a distance of 2.20 cm. One wire carries a current of 1.70 A while the other carries a current of 3.45 A. The currents are in opposite directions (a) What is the magnitude of the force per unit length (in N/m) that one wire exerts on the other? N/m (b) Is the force attractive or repulsive? O attractive O repulsive O The magnitude is zero.arrow_forwardThe figure below is a cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, an outer conductor, and another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is I1 = 1.14 A out of the page and the current in the outer conductor is I2 = 2.90 A into the page. Assuming the distance d = 1.00 mm, answer the following.(a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point a.find magnitude ut and direction(b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point b.find magnitude ut and directionarrow_forward
- The figure below is a cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, an outer conductor, and another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is I1 = 1.20 A out of the page and the current in the outer conductor is I2 = 2.86 A into the page. Assuming the distance d = 1.00 mm, answer the following. (a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point a. magnitude µT direction (b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point b. magnitude µT directionarrow_forwardA cylindrical wire carries a steady current density modeled as J(r) = Cr², where ris radial distance from 1.5 mm. If 15.0 C of charge flows through the wire in 5.0 s, center of the wire. The radius of the wire is R determine C.arrow_forwardThe figure below is a cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, an outer conductor, and another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is I, = 1.20 A out of the page and the current in the outer conductor is I, = 3.06 A into the page. Assuming the distance d = 1.00 mm, answer the following. (a) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point a. magnitude pT direction --Select-- (b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point b. magnitude pT direction --Select---arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios