
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
What is the enthalpy change when 175 g of C3H8 are burned in excess O2?
C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) H = -2220 kJ
a. -1.71 107 kJ
b. -1.79 10-3 kJ
c. -3.47 100 kJ
d. -3.89 105 kJ
e. -8.83 103 kJ
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
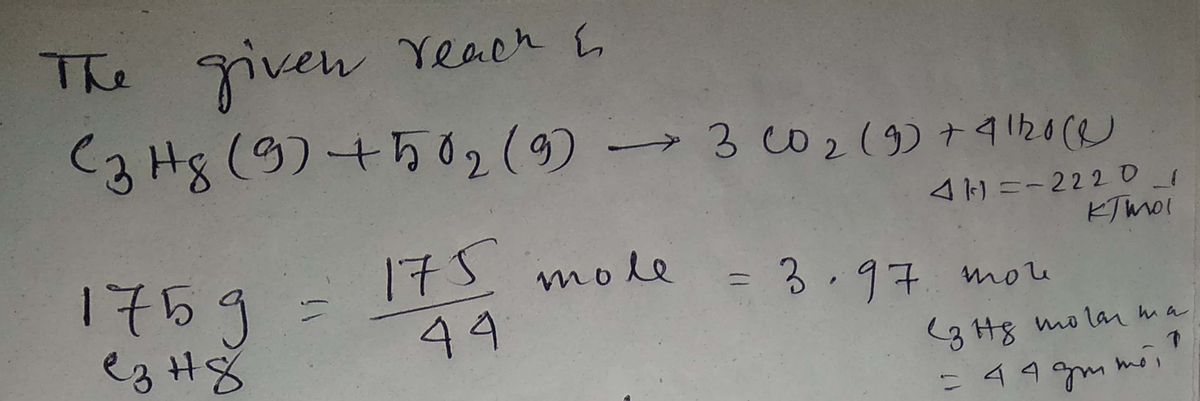
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4. Which of the following aqueous soluti ons is the best conductor of electricity? A 0.10M CH,OH R LOM CH,OH C. 0.10 M NaOH D. 1.0M NaDHarrow_forwardМо Peer Leader: Date: Name: calculation and follow significant figure rules. _CH18(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + _H;O(1) H2O(1) > AH°pxn = -10940 kJ/mol CO:(g) AH°F = -393.5 kJ/mol %3D H¿O(1) AH°f = -285.8 kJ/molarrow_forwardCalcium oxide (CaO) is used to remove sulfur dioxide generated by coal-burning power stations: 2CaOs + 2502i) + O21) → 2CaSO4s) What is the heat (in kJ) involved for this removal process if 6.6 g of SO2 (64.07 g/mol) is converted? AH (Cao) = -635.6 kJ/mol AH; (SO2) = -296.1 kJ/mol AH?(CasOa) = -1432.7 kJ/molarrow_forward
- Which equation would correctly calculate the enthalpy for the reaction: 2H2 + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)? - ΔΗq(H2o) – (ΔΗq(02) + ΔΗq(H2)) a. ΔΗ = b. ΔΗ = ΔΗ;(H2O) C. ΔΗ = 2ΔΗ,(H2O) d. ΔΗ = 2Hg(H2o) + 2ΔΗ,ap(H2O) e. ΔΗ = 2Hg(H20) – 2ΔΗvap(120)arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solutionarrow_forwardUsing the information in the table below, calculate the heat of released from the following reaction in kJ per g of NO. ( Mw. Of NO = 30.01 g/mol). 4NH3(g) + 5O2 (g) 6H2O(g) + 4 NO(g) NH3 H2O NO Hfº (kJ/mol) - 46.1 -241.8 + 90.3arrow_forward
- 04) (g Calculate the volume of air at 30°C and 1.00 atm that is needed to burn completely 10.0 grams of propane. Assume that air is 21.0 percent O₂ by volume. The heat of combustion of propane is -2,220.1 kJ/molrxn. Calculate the heat of formati of propane given that AHO of H₂0(1) = -285.3 kJ/mol and AHO of CO2(g) = -393.5 kJ/ f AH-[(3•Co₂) + (4•H₂0)]-[C3H8 + 5(0₂)] [ F)+(4(-285.3)]-[AH C3H5] [200arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction: CH4 (9) + 20, (g) → CO2(g) + 2H,0(1) AH=-891 kJ a. Calculate the enthalpy change if 2.59 g methane is burned in excess oxygen. Enthalpy change = kJ b. Calculate the enthalpy change if 3.04 × 10° L methane gas at 737 torr and 25°C is burned in excess oxygen. Enthalpy change = kJarrow_forwardFor a particular isomer of Cg H₁g, the combustion reaction produces 5108.7 kJ of heat per mole of C, H₁g (g) consumed, under standard conditions. 25 Cg H18 (8) + O₂(g) →→→ 8 CO₂(g) + 9 H₂O(g) What is the standard enthalpy of formation of this isomer of Cg H₁g (g)? AH; = $ V T B MacBook Air Y H & 7 8 AH-5108.7 kJ/mol 18 N M K 1 38 kJ/molarrow_forward
- Consider the following equation: CH4 + 02 -> H2O + CO2 +890 kJ 1. Balance the Equation 2. How much heat is released when 5.50L of oxygen is reacted with methane at STP? 1 mole of oxygen will occupy 22.4L at STP (standard temperature and pressure (0 degrees celsius) and standard pressure (1atm)).arrow_forwardQ4: Calculate the enthalpy of the reactions below: 1. H;Om + CO2 (aq) - H,CO3 (aa) 2. H;POalag) + 3OH, → 3H;0m + POaloa) 3. C;Ha (a) + 302 () → 2H,06) + 2CO2 (9) AHP of H,CO3 (oa) is -699.65 kJ/molearrow_forwardSucrose, C12 Hzm011, is common table sugar. The enthalpy change at 25°C and 1 atm for the complete burning of 3 mol of sucrose in oxygen to give CO:(9) and H3O(1) is - 1.692 x 10' kJ. From this and from data given below: AH; (H2O(1)) =-285.8 kJ/mol AH(CO2(9) = -393.5 kJ/mol AH (02(9)) = 0 kJ/mol Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of sucrose. AH; - k]/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY