
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
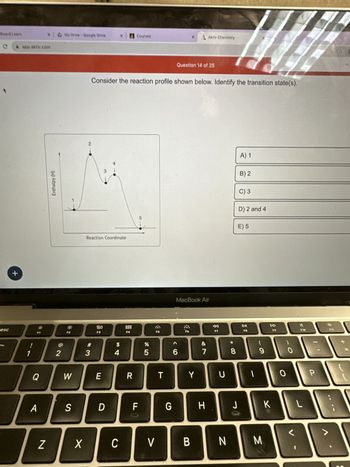
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 14 of 25**
Consider the reaction profile shown below. Identify the transition state(s).
(Graph Description)
The graph is a reaction profile showing the change in enthalpy (H) with respect to the reaction coordinate. It features several labeled points along the curve:
- Point 1: Represents the starting reactants on a stable energy level.
- Point 2: A peak indicating a transition state with the highest energy point on the graph.
- Point 3: A slight dip showing an intermediate state with lower energy than points 2 and 4.
- Point 4: Another peak similar to point 2, indicating a second transition state.
- Point 5: The ending products on a stable, lower energy level than the starting reactants.
**Options:**
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 4
E) 5
(The transition states are typically the highest points in the energy diagram, representing points 2 and 4.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Reaction Time (s) 0.000 26.01 37.57 54.23 [A](M) 0.192 0.114 0.0780 0.0300 Which best describes the order of this reaction? Ozeroth O first Osecondarrow_forwardPracdne o8 Consider the following reaction co-ordinate diagram H20 H20 Br A D Energy Reaction Co-ordinate a) Identify the various species on the diagram by adding the letter identifying each of the structures. b) Which species does the first transition state of the overall reaction most resemble? What kind of transition state is this? c) Which species does the second transition state of the overall reaction most resemble? What kind of transition state is this?arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forward
- 0 State what rate law you would expect from this mechanism (Rate = k[Acetone]"[H*]"[[₂]') • Compare the expected rate law from the mechanism to the rate law you got from the Method of Initial rates and the Method of Isolation. If they are different, suggest 1-2 valid, specific, experimental reasons why they might be different. (fast, equilibrium) CH3 ソース H3C ག་ CH3 + H* = H3C H3C H. + H (slow) CH3 H3C CH2 + ↳2 Т + HIarrow_forward3. The following reaction: A' (a) + B (ag + C (an)→ G* (ae) +2 H ) AH = -250 kJ There are two proposed mechanism: Mechanism 1 A' () + B aa) AB' a) + D (a) Step 1 AB" (a) (fast) + E (a) + Hm → G' sae) + H ) + D² (n) Step 2 (slow) Step 3 E (agi+ C (a) (fast) Mechanism 2: Step 1 AB' (a) A' (an) + B (ag) AB' (a) + C ja) (fast) Step 2 + G' (a) + 2 H() (slow) The reactions was determined to have the following rate law: r= k[A'][B] a) Which of the two proposed mechanisms is valid? Explain. b) List any reaction intermediates: catalysts: c) What is a rate determining step? d) If the activation energy for the overall forward reaction is 150 kJ, sketch the potential energy diagram for the above reaction; showing the overall reaction, the reaction mechanism, labelling the AHu, AHy, Eapu, Eag, reaction intermediates, and activated complex. rvs fwd drvs/arrow_forwardIn comparing these two reactions, which one would occur faster via the SÃ2 mechanism and why? Reaction I CI OH- Reaction II CI 1 NH₂arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY