
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
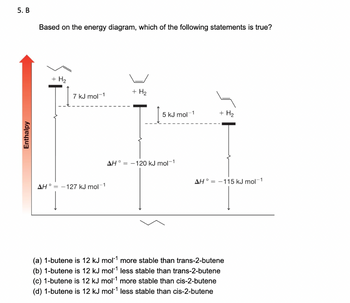
Based on the energy diagram, which of the following statements is true? Please explain why the correct answer is letter B. Include detailed steps explaining the answer.
Transcribed Image Text:Enthalpy
5. B
Based on the energy diagram, which of the following statements is true?
+ H₂
+ H2
7 kJ mol −1
5 kJ mol 1
+ H₂
AH-127 kJ mol-1
AH-120 kJ mol −1
AH-115 kJ mol −1
(a) 1-butene is 12 kJ mol¹ more stable than trans-2-butene
(b) 1-butene is 12 kJ mol¹ less stable than trans-2-butene
(c) 1-butene is 12 kJ mol¹ more stable than cis-2-butene
(d) 1-butene is 12 kJ mol¹ less stable than cis-2-butene
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Using the following bond energies, calculate the molar heat of hydrogenation, AHhydrogenation CH=CH(g) + 2H₂(g) →→→ CH₂CH₂(g) Bond Bond Strength (kJ/mol) C-C 348 839 411 432 || C=C C-H H-H kJ/molarrow_forwardEstimate the heat released when ethene(CH2=CH2) reacts with HBr to giveCH3CH2Br. Bond enthalpies areC-H : 412 kJ/mol; C-C : 348 kJ/mol;C=C : 612 kJ/mol; C-Br : 276 kJ/mol;Br-Br : 193 kJ/mol; H-Br : 366 kJ/mol. Choose the correct answer:1. 1036 kJ/mol2. 58 kJ/mol3. 424 kJ/mol4. 200 kJ/mol5. 470 kJ/molarrow_forwardPleaseeee helpppparrow_forward
- Give answer all questions with explanation pleasearrow_forwardRank the conformations of n-butane with reference to its potential energy from the most stable to the least stable. Rank from the most stable to the least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.arrow_forwardThe two alternative chair conformations of cis-1-cyano-4-methylcyclohexane differ in their Gibbs free energy. Using the data for ΔG° for monosubstituted cyclohexanes at room temperature (25ºC): Axial → Equatorial Group ΔG° (kJ/mol) Group ΔG° (kJ/mol) C-N triple bond −0.8 NH2 −5.9 Br −2.4 CH3 −7.3 OH −3.9 1,2-gauche +3.8 calculate the absolute value of the difference in the Gibbs free energy between the alternative chair conformations.arrow_forward
- The enthalpy for hydrogenation of different isomers of butene is shown in the following figure. Which statement below best interprets this figure? Hy I3D H2 7k mot 5kJ mot + H2 AH-120 kJ mot AH"-127 kJ mot AH-115 kJ mot © GMU 2020 Stability and hydrogenation enthalpies are not correlated. Butene II is less stable than butene I by 7 kJ/mol. O Butene Il is 7 kJ/mol more stable than I and 5 kJ/mol more stable than III. Butene II is 5 kJ/mol less atable than butene IlI. Enthalpyarrow_forwardWhich compound is capable of hydrogen bonding with itself? 1-PROPANOL - (71-23-8) - Physical Properties • Chemical Properties • Solubility • Uses/Function • Reactions • Thermochemistry F F C-F - - F н F ннн Н-с-с-с-H ннн All of the above None of the above L -U -L HICI Iarrow_forwardFollowing are heats of combustion per mole for methane, propane, and 2,2,4-trimeth-ylpentane. Each is a major source of energy. On a gram-for-gram basis, which of these hydrocarbons is the best source of heat energy?arrow_forward
- From the data in Figure 4-12 and Table 4-1, estimate the percentages of molecules that have their substituents in an axial orientation for the following compounds: (a) Isopropylcyclohexane (b) Fluorocyclohexane (c) Cyclohexanecarbonitrile, C6H11CNarrow_forwardCalculate AHrxn for the reaction: CH4 (9) +4 Cl(g) → CCl4 (g) + 4 HCl(g) Use the following reactions and given AH´s: C(s) + 2 H₂(g) → CH4 (9) C(s) + 2 Cl₂(g) → CCl4 (9) H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2 HCl(g) AH = -74.4kJ AH = -95.7kJ AH = -92.3 kJarrow_forwardCH₂ CO₂H N- Br ABCN chlorobenzene CH₂Br CO₂Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
