
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
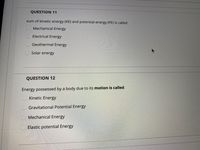
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 11
sum of kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) is called
Mechanical Energy
Electrical Energy
Geothermal Energy
Solar energy
QUESTION 12
Energy possessed by a body due to its motion is called
Kinetic Energy
Gravitational Potential Energy
Mechanical Energy
Elastic potential Energy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- State whether the potential energy of the underlined object increases or decreases as a result of the change described. a hot air balloon lands in a field a diver dives into a pool a car goes up the road to the top of Mount Washingtonarrow_forwardIf a 1 kg stone is thrown vertically upward w/ a kinetic energy of 680 J. it will rise to height of ______ metersarrow_forwardfill out the blank According to the work-energy theorem, the amount of net work done on an object is equal to the change in an object’s ____________________.arrow_forward
- A vehicle weighing 1000 kg goes downhill from 2000 feet to 1000 feet at a velocity of 60 mph. Which one of the statements below is true Potential energy remains the same while kinetic energy decreases to one fourth Potential energy increases to twice of its initial value O potential energy decreases to half Kinetic energy decreases to halfarrow_forwardA person pushes a bookshelf across a level room. There is friction between the floor and thebookshelf. The work done by friction on the bookshelfa) is positiveb) is negativec) is zerod) depends on the speedarrow_forwardState the principle of conservation of energy.arrow_forward
- A spring, whose equilibrium length is 2 m, is compressed to a length of 1 2 m when a force of 10 N is applied. Find the work done by the spring force to compress the spring to a length of 1 marrow_forwardWhich of these energies could be negative? Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Work None of the above All of the above KE and PE PE and Workarrow_forwardA stone is propelled vertically off the ground. After it is released, which of the following are true? It’s total mechanical energy increases It’s total energy is proportional to its distance off the ground It’s kinetic energy decreases It’s gravitational energy increasesarrow_forward
- 3) The figure below illustrates a skier who is skiing on a large frictionless spherical ball of snow. The skier can be treated as a point-like object. The skier starts at the top of the ball with very little speed and picks up speed while traveling along the surface of the snow. During this time, the only forces acting on the skier are the gravitational force applied by the Earth and the normal force applied by the snow. At the moment the radial line extending from the skier to the center of the ball defines an angle a with respect to a vertical line, the skier is about to lose contact with the ball. Determine the value of a.arrow_forwardQuestion 8 Questions #8-9 start with the same description. A 1,100 kg horse is walking at 2.0 m/s. What type of energy is being described? Your answer: O chemical O elastic O gravitational O kineticarrow_forwardPlease answer question 12 and provide all work needed.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON