
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
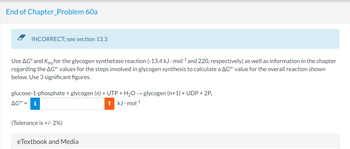
Transcribed Image Text:End of Chapter_Problem 60a
INCORRECT; see section 13.3
Use AGO and Keq for the glycogen synthetase reaction (-13.4 kJ. mol-¹ and 220, respectively) as well as information in the chapter
regarding the AG" values for the steps involved in glycogen synthesis to calculate a AG°' value for the overall reaction shown
below. Use 3 significant figures.
glucose-1-phosphate + glycogen (n) + UTP + H₂O → glycogen (n+1) + UDP + 2P;
AG⁰¹ = i
! kJ.mol-1
(Tolerance is +/- 2%)
eTextbook and Media
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you help me to solve this question?arrow_forwardAt the start of the sucrose hydrolysis reaction, Kevin the Kinetics Experimeter measured a light rotation angle of 8.5 degrees. At the end of the reaction, he measures a -2.0 degree light rotation angle.a. Why does the light rotation angle decrease during the reaction? Group of answer choices Sucrose absorbs and rotates light in a negative direction Fructose absorbs and rotates light in a positive direction Glucose absorbs and rotates light in a negative directionarrow_forwardcan someone explain please? thank you!arrow_forward
- After reviewing the reactions of glutamine formation on page 88 (old edition page 90), explain why each of the following statements concerning the last reaction (or Overall reaction) is true. (Select all that apply) Glutamic acid + NH glutamine; AG" =+3.4 kcal/mole; ATP hydrolyzed in 2 steps 1. This endergonic reaction occurs in the cell because glutamic acid is actually converted to glutamine in 2 sequential reactions, both of which are exergonic: a. 1 reaction: Glutamic acid + ATP ghutamyl phosphate + ADP b. 2nd reaction: Glutamyl phosphate + NHglutamine + Pi 2. Overall reaction: Glutamic acid+ATP+NH: glutamine + ADP+P; AG -3.9 kcal/mole If all reactants and products were at standard conditions at the beginning of an experiment, after a period of time, the [NH3]/[ADP] ratio would decrease assuming enzyme glutamine synthase is present. If the reaction were written in in reverse, its AGO would be 3.9 kcal/mol. none of the remaining In the cell, it is possible for glutamine to be formed…arrow_forwardList all the reducing sugar you learnt List all the non-reducing sugars you learnt. Which of the following would be the correct classification of the carbohydrate shown below? CH₂OH H CH OH H H OH H a. monosaccharide c. polysaccharide d. starch e. cellulose O B. Amylose CH₂ C. Amylopectin -0. H OH H A) disaccharides. B) polysaccharides. C) chlorosaccharides. D) alcohol sweeteners. E) noncarbohydrate sweeteners. H OH 13. Aspartame and Saccharin® are two examples of OH Identify the polysaccharides and types of glycosidic bonds in each of the following: A. Cellulose 130 Identify the polysaccharide_ What is the glycosidic linkage? When this polysaccharide is hydrolysed in aqueous acid solution, what is formed? H 11. TEORE D 11 ANTE 114494 H CHAR -1 ( 11 CR H 11 11 11 B. Maltose ATRORE 43 18 OH 11 C. Sucrose 11 1)-( HO '11 Melibiose is a disaccharide that is 30 times sweeter than sucrose. A. What are the monosaccharide units in melibiose? D 11 03 H DIE I B. What type of glycosidic bond…arrow_forward1. The reaction catalyzed by aldolase splits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F16BP) into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). The AG°" for the reaction is 23.8 kJ/mole. If the concentrations of G3P and DHAP are 2.5 mM and 1 mM, respectively, what concentration of F16BP is needed for the reaction to be at equilibrium in a human cell?arrow_forward
- Which pairs of molecules are interconvertible via mutarotation? O a. D-glucose and D-fructose O b. D-glucose and D-galactose O c. D-glucose and D-glucosamine O d. a-D-glucose and B-D-glucosearrow_forward1. Carbohydrates classification. 2. Write down the reactions: a) α,D-Glucopyranose + C2H5OH → b) D-Glucose + [Ag(NH3)2]+ → c) D-Glucopyranose + (CH3CO)2 O → d) D-Glucopyranose + CH3I → e) D-Glucose + HNO3 → f) D-Glucose + H2 → g) Lactose formation h) Sucrose hydrolysis 3. Write down the formula of β,D-galactopyranosearrow_forward4. Draw the structures for the oxidation of the following carbohydrates. a) C-H 主 H CH CHOH erythrose b) [0] Ho CHOH glicese 5. Draw the structures for the reduction of the following carbohydrates. Ho CHOH Cat. C=0 + Hz It. OH CHOH olwollol enythrulse b) Cat. Ho CHCH gucosearrow_forward
- 1) Phenyl propyl ether can be obtained by reacting? 2) Raffinose is A trisaccharide which is made up of two sugar molecules of aldoses and one sugar molecule of ketoses? True or false!arrow_forward17. Draw the 2-amino sugar and the aldonic acid that can be formed from the following monosaccharide. || C-H H- -OH H -OH HO- -H H -OH CHOH D-gulosearrow_forwardQ2 CH,OH CH,OPO,2- H H OH H OH 0-PO,2- но но OH H. OH OH Glucose-1-phosphate Glucose-6-phosphate Calculate the standard free-energy change (AG°) fo the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. When at standard temperature (25 °C) and pressure, the equilibrium of each molecule is 1 mM glucose 1-phosphate and 19 mM glucose 6-phosphate. HINT: at 25 °C, RT = 2.479 kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY