
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Solve question 1
Transcribed Image Text:emirates
aviation
university
Emirates dnata
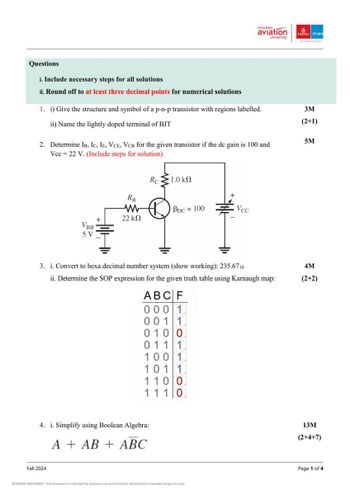
Questions
i. Include necessary steps for all solutions
ii. Round off to at least three decimal points for numerical solutions
1. i) Give the structure and symbol of a p-n-p transistor with regions labelled.
ii) Name the lightly doped terminal of BJT
2. Determine IB, IC, IE, VCE, VCB for the given transistor if the dc gain is 100 and
Vcc 22 V. (Include steps for solution)
3M
(2+1)
5M
Re
1.0 ΚΩ
Ra
ww
22 ΚΩ
PDC = 100
Vec
VBB
5V
3. i. Convert to hexa decimal number system (show working): 235.6710
ii. Determine the SOP expression for the given truth table using Karnaugh map:
ABCF
0001
0011
0100
0111
100 1
101 1
1100
111 0
4. i. Simplify using Boolean Algebra:
AAB + ABC
4M
(2+2)
13M
(2+4+7)
Fall 2024
BUSINESS DOCUMENT This document is intended for business use and should be distributed to intended recipients only.
Page 1 of 4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Just need 1d and 1e answered.arrow_forwardIn a two transistor model of SCR, the leakage current for transistor Q1 is 2 micro-ampere and the leakage current for transistor Q2 is two times of the leakage current of Q1. Given that the current gain for Q1 is 0.7 and the emitter current and gate current is 30 A & 0.25 A respectively. The anode current gain will bearrow_forwardGiven shows the mutual characteristic for a junction gate field effect transistor. When the gate-source voltage is -2.5V, determine the value of drain current, the dynamic value of forward transconductance. -2.5V 2.5V - 12mA 5 mA -5.0-4.5 -4.0 -3.5 -3.0-2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 Gate-source voltage, VGs (V) 0 20 18 16 14 12 10 00 6 4 2 0 Drain current, (mA)arrow_forward
- RL 4. Suppose one NPN transistor is working under activation region, and Ip=0.005A. 12 What's the value of Ic given B=100. What's the value of I-? Vcc VEarrow_forwardHow does the construction of a transistor differ from the construction of a PN junction diode? What are the two types of transistors? What are the three parts of a transistor called? Draw and label the schematic symbols for an NPN and a PNP transistor. What are transistors used for? How are transistors classified? What symbols are used to identify transistors? What purposes does the packaging of a transistor serve? How are transistor packages labeled? What are the basic functions of a transistor? What is the proper method for biasing a transistor? What is the difference between biasing an NPN and a PNP transistor? What is the barrier voltage for a germanium and a silicon transistor? What is the difference between the collector-base junction and the emitter- base junction bias voltages? What may cause a transistor to fail? What are two methods of testing a transistor? When using an ohmmeter, what should the results be for an NPN transistor? What are the two…arrow_forwardPls help ASAP. Pls show all work.arrow_forward
- 1. For the circuit in Figure 1: a) Calculate the input and output power if the input signal results in a base current of 5 mA ms. b) Calculate the input power đissipated by the circuit if Rs is changed to 1.5 kQ. c) What maximum output power can be delivered by the circuit if RE is changed tol.5 kQ? d) If the circuit is biased at its center voltage and center collector operating point, what is the input power for a maximum output power of 1.5 W? +Vcc (18 V) Re = 16 2 1.2 kS2 B-40 100 pF Figure 1arrow_forwardplease quickly thanks !arrow_forwardThe mode of operation for the D-MOSFET is Select one: a. the ohmic region only b. the enhancement mode only c. both the depletion and enhancement modes d. the depletion mode onlyarrow_forward
- Sketch the basic construction of the two types of BJT Transistors and label the various minority and majority carriers in each. Draw the symbol with the three terminals. Is any of this information altered by changing from a silicon to a germanium base?arrow_forwardConsider the BJT transistor circuit in Figure 1. If DC = 150 and VBE = 0.65V, calculate:Base (IB), collector (IC), emitter (IE) currents, voltages VB, VC, VE, VCE and VCB. And what is PD(max) at 75OC? If the power dissipation derating factor for the transistor is 2mW/oC and the PD(max) is0.5 W at 25OCarrow_forwardPlease answer in typing formatarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,