
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134746241
Author: Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
give me the answer in 30 min
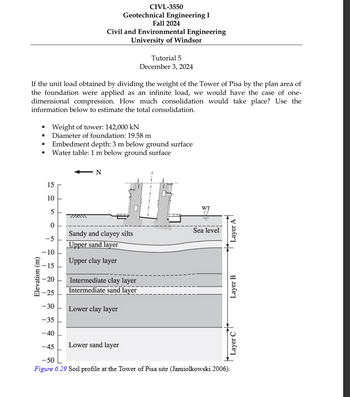
Transcribed Image Text:Elevation (m)
CIVL-3550
Geotechnical Engineering I
Fall 2024
Civil and Environmental Engineering
University of Windsor
Tutorial 5
December 3, 2024
If the unit load obtained by dividing the weight of the Tower of Pisa by the plan area of
the foundation were applied as an infinite load, we would have the case of one-
dimensional compression. How much consolidation would take place? Use the
information below to estimate the total consolidation.
"
15
10
Weight of tower: 142,000 kN
Diameter of foundation: 19.58 m
Embedment depth: 3 m below ground surface
Water table: 1 m below ground surface
← N
0
10
5
Sandy and clayey silts
-5
Upper sand layer
-10
-15
-20
22
Upper clay layer
Intermediate clay layer
Intermediate sand layer
-25
-30
Lower clay layer
-35
-40
-45
Lower sand layer
-50
Figure 6.29 Soil profile at the Tower of Pisa site (Jamiolkowski 2006).
WT
Sea level
Layer C
Layer B
Layer A
Transcribed Image Text:Table 6.5 Gradation of soil layers at the Tower of Pisa site
Formation
Layer
Soil type
A1
Sandy-clayey silts
A
A₂
Silty sands
B₁
Upper clays
Sublayer
Elevation of top
Elevation of base
Sand (%)
Silt (%)
Clay (%)
0.0
-5.4
30.1
56.7
12.5
-5.4
-7.4
56.4
30.3
13.2
1
-7.4
-10.9
14.2
32.2
53.0
2
-10.9
-12.9
2.2
51.9
46.0
3
-12.9
-17.8
2.0
37.7
60.0
4
-17.8
-19.0
6.6
48.1
44.6
B₂
Intermediate clays
5
-19.0
-22.0
16.3
51.4
33.0
B
B₁₂
Intermediate sands
6
-22.0
-24.4
57.7
33.6
8.6
7
-24.4
-29.0
2.8
50.0
47.3
8
-29.0
-30.4
12.7
53.7
33.7
B4
Lower clays
9
-30.4
-34.4
6.4
62.7
31.5
10
с
Lower sands
-34.4
-37.0
-37.0
1.3
52.5
46.3
-68.0
82.5
11.9
5.5
The case history continues at the end of Chapter 9, where we provide more information about the soil profile and explore the likely reason for the initiation of the tower lean.
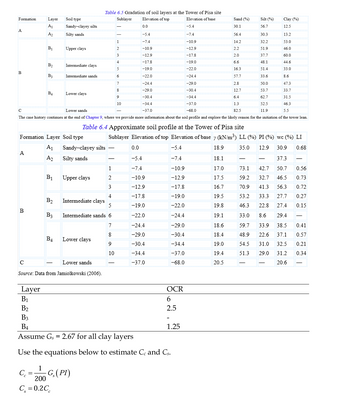
Table 6.4 Approximate soil profile at the Tower of Pisa site
Formation Layer Soil type
Sublayer Elevation of top Elevation of base y (kN/m³) LL (%) PI (%) wc (%) LI
A₁
Sandy-clayey silts
0.0
-5.4
18.9
35.0
A
A2
Silty sands
-5.4
-7.4
18.1
12.9 30.9 0.68
37.3
1
-7.4
-10.9
17.0
73.1
42.7 50.7 0.56
B1
Upper clays
2
-10.9
-12.9
17.5
59.2
32.7 46.5 0.73
3
-12.9
-17.8
16.7
70.9
41.3 56.3 0.72
4
-17.8
-19.0
19.5
53.2 33.3
27.7 0.27
B₂
Intermediate clays
5
-19.0
-22.0
19.8
46.3
22.8 27.4 0.15
B
B3
Intermediate sands 6
-22.0
-24.4
19.1
33.0
8.6 29.4
7
-24.4
-29.0
18.6
59.7
33.9 38.5 0.41
8
-29.0
-30.4
18.4
48.9
22.6 37.1 0.57
B4
Lower clays
9
-30.4
-34.4
19.0
54.5
31.0 32.5 0.21
10
-34.4
-37.0
19.4
51.3
29.0
31.2
0.34
C
Lower sands
-37.0
-68.0
20.5
20.6
Source: Data from Jamiolkowski (2006).
Layer
В1
B2
B3
OCR
6
2.5
-
1.25
B4
Assume Gs = 2.67 for all clay layers
Use the equations below to estimate Cc and Cs.
1
Сс
-G(PI)
200
C₁ = 0.2C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Recommended textbooks for you
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134041360
Author:Greg Carbone
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:9781260153125
Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134543536
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:9781337569613
Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:9781259916823
Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,