
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
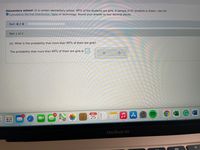
Transcribed Image Text:Elementary school: In a certain elementary school, 49% of the students are girls. A sample of 65 students is drawn. Use the
O Cumulative Normal Distribution Table or technology. Round your answer to four decimal places.
Part: 0/ 2
Part 1 of 2
(a) What is the probability that more than 60% of them are girls?
The probability that more than 60% of them are girls is
W
OCT
25
MacBook Air
DD
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- K One question from a survey was "How many credit cards do you currently have?" Answer the parts (a) through (c) based on the results of the 3 4 2 0.173 0.074 0.121 X P(x) 0 1 0.384 0.248 ... Q Search The question: 3 point(s) possible (a) Compute the mean and standard deviation number of credit cards from the probability distribution. The mean is credit cards. (Type an integer or a decimal.) (b) Determine the probability that a randomly selected individual has less than the mean number of credit cards. The probability is. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (c) Determine the probability of randomly selecting two individuals who are issued exactly two credit cards. [Hint: Are the events independent?] The probability is. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) 13 10. Time Remaining: 01:13:2 1arrow_forwardHypothesis test for a population proportion using the p value... Based on their records, a hospital claims that the proportion, p, of full-term babies born in the community that weigh more than 7 pounds is 44%. A pediatrician who works with several hospitals in the community would like to verify the hospital's claim. In a random sample of 175 babies born in the community, 89 weighed over 7 pounds. Is there enough evidence to reject the hospital's claim at the 0.01 level of significance? Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis Ho and the alternative hypothesis H₁. HO H₁ :0 (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. (Choose one) ▼ (c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) 0 (d) Find the p-value. (Round to three or more decimal places.) 0 (e) Can we reject the claim that the…arrow_forwardDetermine whether you can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution. If you can, use the normal distribution to approximate the indicated probabilities and sketch their graphs. If you cannot, explain why and use the binomial distribution to find the indicated probabilities. A survey of adults in a region found that 33% name professional football as their favorite sport. You randomly select 11 adults in the region and ask them to name their favorite sport. Complete parts (a) through (d) below (a) Find the probability that the number who name professional football as their favorite sport is exactly 8.arrow_forward
- do fast with explanationarrow_forwardMath 23 Practice Test 3 (1) The diameters of oranges from a Florida orchard are normally distributed = 3.2 inches and standard deviation o= 1.1 inches. with mean (a) What is the probability that a randomly selected orange is more than 3.5 inches? (b) What is the probability that a randomly selected orange is between 3 and 3.5 inches? (c) A gift box contains 9 oranges. What is the probability that the mean diameter for this sample is smaller than 3.5 inches? (2) Let a denote the amount spent at a grocery store. Assume x is normally distributed with standard deviation a $11.46. Ten customers' bills were recorded, there average bill was $89.38. Find a) The margin of error. b) A 95% confidence interval for the population mean.arrow_forwardNew Survey A survey was conducted two years ago asking college students their top motivations for using a credit card. To determine whether this distribution has changed, you randomly select 425 college students and ask each one what the top motivation is for using a credit card. Can you conclude that there has been a change in the claimed or expected distribution? Use a= 0.05. Complete parts (a) through (d). Old Survey % Frequency, f 112 Response Rewards 27% 23% 97 Low rates Cash back Discounts Other 21% 108 9% 48 20% 60 a. State H, and H, and identify the claim. What is the null hypothesis, Ho? O A. The distribution of motivations is 27% rewards, 23% low rate, 21% cash back, 9% discounts, and 20% other. O B. The distribution of motivations is 112 rewards, 97 low rate, 108 cash back, 48discounts, and 60 other. O C. The distribution of motivations differs from the expected distribution. What is the alternate hypothesis, H2? O A. The distribution of motivations differs from the claimed…arrow_forward
- Pay your taxes: According to the Internal Revenue Service, the proportion of federal tax returns for which no tax was paid was p=0.326. As part of a tax audit, tax officials draw a simple sample of n=140 tax returns. Use Cumulative Normal Distribution Table as needed. Round your answers to at least four decimal places if necessary. Part 1 of 4 (a) What is the probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is less than 0.32? The probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is less than 0.32 is Part 2 of 4 (b) What is the probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is between 0.37 and 0.40? The probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is between 0.37 and 0.40 isarrow_forwardCould you help in the process pleasearrow_forwardPlzz explainarrow_forward
- Determine whether you can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution. If you can, use the normal distribution to approximate the indicated probabilities and sketch their graphs. If you cannot, explain why and use the binomial distribution to find the indicated probabilities. A survey of adults in a region found that 52% have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards. You randomly select 100 adults in the region. Complete parts (a) through (d) below ) Find the probability that the number who have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards is (a) exactly 54, (b) at least 54, and (c) fewer than 54. enter your response here (Round to four decimal places as needed.) .arrow_forwardDetermine whether you can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution. If you can, use the normal distribution to approximate the indicated probabilities and sketch their graphs. If you cannot, explain why and use the binomial distribution to find the indicated probabilities. A survey of adults in a region found that 77% have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards. You randomly select 100 adults in the region. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Determine whether a normal distribution can be used to approximate the binomial distribution. Choose the correct answer below. O A. No, because nq H= 77 H= 77 H=77 The normal distribution cannot be used to approximate the binomial distribution. 63 79 91 63 79 91 63 79 91 (b) Find the probability that the number who have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards is at least 79.arrow_forwardPay your taxes: According to the Internal Revenue Service, the proportion of federal tax returns for which no tax was paid was p=0.326.As part of a tax audit, tax officials draw a simple sample of n=130 tax returns. Use Cumulative Normal Distribution Table as needed. Round your answers to at least four decimal places if necessary. 1.(a)What is the probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is less than 0.29?The probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is less than 0.29 is (b) What is the probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is between 0.35 and 0.41? The probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is between 0.35 and 0.41 is (c)What is the probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid is greater than 0.32? The probability that the sample proportion of tax returns for which no tax was paid…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman