
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please complete Table A1.
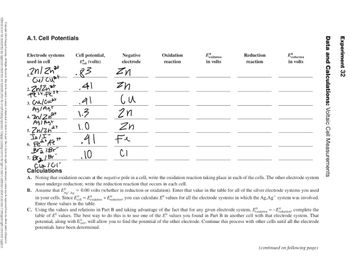
Transcribed Image Text:A.1. Cell Potentials
Electrode systems
used in cell
2nl Zn²+
Cul Cuat
2. Zn/Znat
Fest Fest
3. Cu/cuat
AS/Agr
4.Zn/Zn²+
Ag/Agr
5. Zn/2h27
I₂/I-
6. Fe2+ ke
3+
Bra Br
7. Bra / Br
Cia 101
Calculations
Cell potential,
Ecell (volts)
.83
.41
.41
1.3
1.0
.41
.10
Negative
electrode
zn
zn
си
2n
Zn
Fe
CI
Oxidation
reaction
E
Foxidation
in volts
Reduction
reaction
Ereduction
in volts
A. Noting that oxidation occurs at the negative pole in a cell, write the oxidation reaction taking place in each of the cells. The other electrode system
must undergo reduction; write the reduction reaction that occurs in each cell.
B. Assume that E
Ag-Ag
= 0.00 volts (whether in reduction or oxidation). Enter that value in the table for all of the silver electrode systems you used
in your cells. Since Ecell = Eoxidation +Ereductions you can calculate Eº values for all the electrode systems in which the Ag.Ag system was involved.
Enter those values in the table.
C. Using the values and relations in Part B and taking advantage of the fact that for any given electrode system, Exidation =-Eroductions complete the
table of E values. The best way to do this is to use one of the Eº values you found in Part B in another cell with that electrode system. That
potential, along with Ell, will allow you to find the potential of the other electrode. Continue this process with other cells until all the electrode
potentials have been determined.
(continued on following page)
Data and Calculations: Voltaic Cell Measurements.
Experiment 32
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I am struggling to get this question right and would really appreciate any help. Pls make sure you’re anser is corrrecf 100% pls and thank you !arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist measures the amount of Elements E₁ and E₂ in four samples of an unknown Substance. sample of E1 1 2 3 mass mass of E2 4 16.0 g 9.1 g 17.1 g 9.8 g 18.5 g 10.6 g 12.0 g 6.9 g It's known that X contains no elements other than E₁ and E₂. Using this information, answer the questions in the table below. Is X a pure substance or a mixture? If you don't have enough information to decide, choose can't decide. If you said X is a pure substance, calculate the mass of Element E₁ the analytical chemist would find in a new 10.0 g sample of X. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. O pure substance O mixture O (can't decide) garrow_forward1a. Determine the volume of 1.000 g of water (Densitywater = 0.9999 g/mL). 1b. Determine the volume of 1.000 g of ice (Density ce = 0.9168 g/cm³). (1 mL = 1 cm³) %3D %3D 1c. From the volumes above, what can we conclude about 1.000 g of water when it freezes?arrow_forward
- An oxygen atom has a mass of 2.6610−23g and a glass of water has a mass of 0.050kg. Use this information to answer the questions below. Be sure your answers have the correct number of significant digits. What is the mass of 1 mole of oxygen atoms? How many moles of oxygen atoms have a mass equal to the mass of a glass of water?arrow_forwardPercentage Abundance. The element rubidium consists of two isotopes, one having an isotopic mass of 84.912 and the other having an isotopic mass of 86.920. Determine the percentage abundance of the lighter isotope. Record the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Show the numerical set-ups. Include units and the correct number of significant figures in the set-up.arrow_forwardCalculate the formula mass for each of the following compounds. ZnCO3ZnCO3 Express your answer using two decimal places. H2SO4H2SO4 Express your answer using two decimal places. CBr4CBr4 Express your answer using two decimal places. AlPO4AlPO4 Express your answer using two decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY