
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
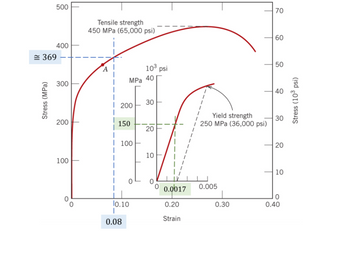
[Elastic deformation after plastic deformation] A cylindrical specimen of a brass alloy has a diameter of d0 and a
length of l. The tensile stress–strain behavior for this alloy is shown below.
(1) The specimen is subjected to a tensile force of F1; then, the force is released. Compute the final length of the
specimen at this time.
(2) The specimen is subjected to a tensile force of F2; then, the force is released. Compute the final length of the
specimen at this time.
Use d0 = 7.0 mm; l = 90 mm; F1 = 5000N; F2 = 14200N
Transcribed Image Text:500
Stress (MPa)
400
369
300
200
100
Tensile strength
450 MPa (65,000 psi)
200
MPa 40
150
100
10.10
I
0.08
10³ psi
30
20
10
0
0 0.0017
0.20
Strain
Yield strength
250 MPa (36,000 psi)
0.005
0.30
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0.40
Stress (10³ psi)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need help with review Engineering of Materialsarrow_forward3 please include sketcharrow_forwardA 3-mm-long gold alloy wire intended to electricallybond a computer chip to its package has an initial diameter of30 μm. During testing, it is pulled axially with a load of 15grams-force. If the wire diameter decreases uniformly to29 μm, compute the following:a. The final length of the wire.b. The true stress and true strain at this load.c. The engineering stress and strain at this load.arrow_forward
- If the engineering strain in a tensile bar is 0.0025 and Poisson’s ratio is 0.33, find the original length and the original diameter if the length and diameter under load are 2.333 ft. and 1.005 in. respectively.arrow_forwardTrue stress-strain Engineering stress-strain strain Calculate the engineering ultimate tensile strength of a material whose strength coefficient is 535 MPa and of a tensile-test specimen that necks at a true strain of 0.55. 200 MPa O 267 MPa O 244 MPa O 222 MPa stressarrow_forwardTutorial 1: Stress and Strain Deformation Analysis Question 1 A compressive force (F) of 10kN is applied to a 25mm diameter round bar. Calculate the stress that the bar experiencing.arrow_forward
- Consider a cylindrical specimen of a steel alloy with 8.5 mm diameter and 80 mm long that is pulled in tension. Estimate the following mechanical properties using Fig. 1: a. Modulus of Elasticity and Resilience in MPa and psi b. Ultimate Tensile Strength in MPa and psi c. Fracture Strength in MPa and psi d. Ductility or % elongation at fracture in MPa and psi 2000 10³ psi MPa 300 2000 200 1000 100 0 0.000 0.005 0.010 0.015 Strain 0.020 0.040 0.060 Strain Fig. 1 Engineering Stress-Strain Curve Stress (MPa) 1000 0 0.000 Stress 0.080 300 200 100 0 Stress (10³ psi)arrow_forward1. Sketch stress-strain curves for the following three materials (mechanically worked tungsten metal, annealed tungsten metal, and tungsten carbide) on the same plot. On each curve, label the following: ultimate compressive strength (UCS), yield stress (YS), modulus of elasticity (E), and rupture stress (RS).arrow_forwardAn unknown specimen having a rectangular cross section of dimensions 5 mm × 20 mm isdeformed in tension. Using the load-elongation data shown in the below table, answer thefollowing questions.(d) Determine the tensile strength.(e) Compute the modulus of resilience.(f) What is the ductility, in percent elongation? only d,e,and farrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY