
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
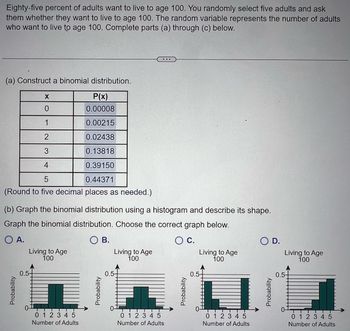
Transcribed Image Text:Eighty-five percent of adults want to live to age 100. You randomly select five adults and ask
them whether they want to live to age 100. The random variable represents the number of adults
who want to live to age 100. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
(a) Construct a binomial distribution.
X
P(x)
0
0.00008
1
0.00215
2
0.02438
3
0.13818
4
0.39150
5
0.44371
(Round to five decimal places as needed.)
(b) Graph the binomial distribution using a histogram and describe its shape.
Graph the binomial distribution. Choose the correct graph below.
O A.
O B.
O C.
Probability
Living to Age
100
0.5-
0-
0 1 2 3 4 5
Number of Adults
Probability
Living to Age
100
0.5-
0-
H
0 1 2 3 4 5
Number of Adults
Probability
Living to Age
100
0.5-
U
TTT
0 1 2 3 4 5
Number of Adults
O D.
Probability
Living to Age
100
0.5+
0 1 2 3 4 5
Number of Adults
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose that the random variable xx, shown below, represents the number of speeding tickets a person received in a three-year period. P(x)P(x) represents the probability of a randomly selected person having received that number of speeding tickets during that period. Use the probability distribution table shown below to answer the following questions. xx P(x)P(x) 0 0.3891 1 0.281 2 0.1497 3 0.098 4 0.0471 5 0.0351 6+ 0.0000 What is the probability that a randomly selected person has received four or more tickets in a three-year period?P(x≥4)=What is the probability that a randomly selected person has received more than four tickets in a three-year period?P(x>4)=Help me, please?arrow_forward4 decimal answersarrow_forwardSuppose that the random variable xx, shown below, represents the number of speeding tickets a person received in a three-year period. P(x)P(x) represents the probability of a randomly selected person having received that number of speeding tickets during that period. Use the probability distribution table shown below to answer the following questions. xx P(x)P(x) 0 0.3891 1 0.281 2 0.1497 3 0.098 4 0.0471 5 0.0351 6+ 0.0000 Would it be unusual to randomly select a person who has received four or more tickets in a three-year period? A. Yes B. NoIs it correct answer B?arrow_forward
- Use the distribution to find the probability of getting less than 3 correct when making random guesses on a 4 question multiple choice exam. P(x) 0.198 1 0.395 0.296 3 0.099 4 0.012 0.593 0.889 None of these 0.111 0.296arrow_forwardEighty-three percent of adults in a certain country believe that life on other planets is plausible. You randomly select five adults and ask them whether they believe that life on other planets is plausible. The random variable represents the number of adults who believe that life on other planets is plausible. Find the mean, variance, and standard deviation of the binomial distribution for the random variable. Interpret the results find the mean, variance, and standard deviationarrow_forwardThe probability distribution of the random variable X represents the number of hits a baseball player obtained in a game for the 2012 baseball season. 1 2 3 4 P(x) 0.1666 0.3437 0.2774 0.1486 0.0384 0.0253arrow_forward
- A company has seven applicants for two positions: three women and four men. Suppose that the seven applicants are equally qualified and that no preference is given for choosing either gender. Let x equal the number of women chosen to fill the two positions. (a) Write the formula for p(x), the probability distribution of x. (b) What are the mean ? and variance ?2 of this distribution? (Round your mean to one decimal place and your variance to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardK The data on the right represent the number of live multiple-delivery births (three or more babies) in a particular year for women 15 to 54 years old. Use the data to complete parts (a) through (d) below. Age 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-54 Number of Multiple Births (a) Determine the probability that a randomly selected multiple birth for women 15-54 years old involved a mother 30 to 39 years old. P(30 to 39)= (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) (b) Determine the probability that a randomly selected multiple birth for women 15-54 years old involved a mother who was not 30 to 39 years old. P(not 30 to 39) = 90 510 1622 2838 1845 373 119arrow_forwardDecide whether you can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution. If you can, use the normal distribution to approximate the indicated probabilities and sketch their graphs. If you cannot, explain why and use the binomial distribution to find the indicated probabilities. A survey of adults found that 8% say their favorite sport is auto racing. You randomly select 400 adults and ask them to name their favorite sport. Complete parts (a) through (d). .... . Determine whether a normal distribution can be used to approximate the binomial distribution. Choose the correct answer below. A. No, because np < 5. B. No, because nq < 5. C. Yes, because both np 25 and nq 2 5. (a) Find the probability that the number of people who say auto racing is their favorite sport is at most 39. (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- In a recent survey, approximately 90% of U.S. adults own a cell phone. Let's assume this can be modeled as a binomial distribution. In a group of 20 randomly selected adults, what is the standard deviation of the number of adults you would expect to own a cell phone? TTT Arial v T RBC 3 (12pt) Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers.arrow_forwardSolve for Darrow_forwardEighty-four percent of adults in a certain country believe that life on other planets is plausible. You randomly select five adults and ask them whether they believe that life on other planets is plausible. The random variable represents the number of adults who believe that life on other planets is plausible. Find the mean, variance, and standard deviation of the binomial distribution for the random variable. Interpret the results. Find the mean of the binomial distribution. μ=_________ (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman