
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
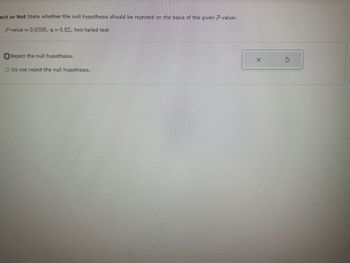
Transcribed Image Text:ect or Not State whether the null hypothesis should be rejected on the basis of the given P-value:
P-value = 0.0500, a=0.02, two-tailed test
Reject the null hypothesis.
O Do not reject the null hypothesis.
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The following hypothesis test is to be conducted. Ho: Median ≤ 190 H₂: Median > 190 A sample of 30 provided 22 observations greater than 190, 3 observations equal to 190, and 5 observations less than 190. Use α = 0.01. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) z = 2.56 X Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = 0.0052 X What is your conclusion? Reject Ho. The population median is less than or equal to 190. Do not reject Ho. The population median is less than or equal to 190. Reject Ho. The population median is greater than 190. Do not reject Ho. The population median is greater than 190.arrow_forwardWe are testing a null hypothesis Ho:P1=P2 against an alternative hypothesis H7:P1 P2 where n = 50, x1 = 11, and n2 = 75, x2 =24. Find the value of the test statistic. 1.22 -1.89 -1.22 -.99arrow_forwardTest the hypothesis using the P-value approach. Be sure to verify the requirements of the test. H0: p=0.72 versus H1: p≠0.72 n=500, x=350, a=0.01arrow_forward
- Compute the P-value. Round the answer to at least four decimal places. P-value = Part: 2/ 4 Part 3 of 4 Determine whether to reject H: Do not reject the null hypothesis Hg. Reject Do not rejectarrow_forwardUse technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for 12 AM body temperatures, the mean is µ< 98.6°F. The sample size is n = 7 and the test statistic is t= P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) hsarrow_forward3042 You'd like to test the null hypothesis that the means of the two samples (column A and column B) are the same. The alternative hypothesis is that they are not the same. You have no reason to believe that the standard deviations of the two samples are equal. Test at the alpha = 0.10 level. After using Excel, what do you conclude? Are the means the same? Group of answer choices You cannot reject the null hypothesis. Therefore, you conclude that the means of the two populations are the same. You cannot reject the null hypothesis. Therefore, you conclude that the means of the two populations are different. You reject the null hypothesis. Therefore, you conclude that the means of the two populations are different. You reject the null hypothesis. Therefore, you conclude that the means of the two populations are the same. X1 X2 97.88 98.66 105.98 102.29 96.01 111.40 99.70 106.15 96.96 100.10 99.80 104.89 92.73 99.24 106.30 104.79 97.90 101.51 95.04…arrow_forward
- A hypothesis test is performed at the 5% significance for a normal population mean u iwth the null and alternative hypotheses given below. Haitl# Ho Orl =r1:0H It is found that the p-value is p = 0.0123. What is the correct decision and interpretation of the hypothesis test? O Inconclusive or not enough information to tell. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. Our data supports the null hypothesis. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. We have proved the null hypothesis is true. O Reject the null hypothesis. We have proved the null hypothesis is false. O Reject the null hypothesis. Our data is statistically insignificant. O Reject the null hypothesis. Our data does not support the null hypothesis.arrow_forwardSelect one for each hypothesis testarrow_forwardAnswer all A, B, C questionsarrow_forward
- A null and alternative hypothesis are given. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Ho: H₂: O O ab What type of test is being conducted in this problem? OA. Two-tailed test OB. Right-tailed test OC. Left-tailed test O O os 6.5 06.5 esc Statcrunch ! 1 Q 2 W #3 E $ ► 4 R % 45 F T MacBook Pro A ^ 6 Y & 7 U * 0arrow_forwardAnswer allarrow_forwardCan you please help me located the null?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman