
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
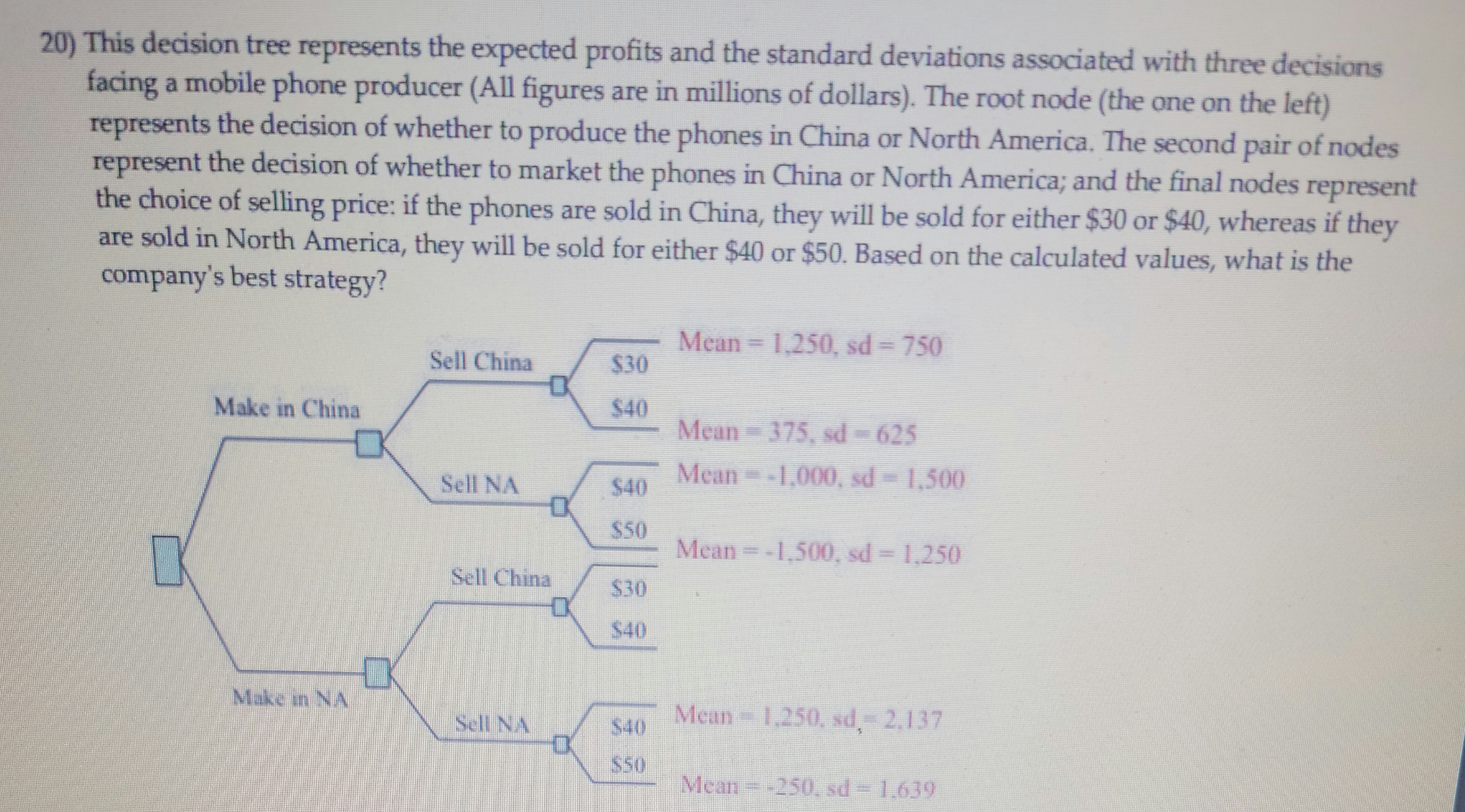
Transcribed Image Text:This decision tree illustrates the expected profits and standard deviations associated with three decisions facing a mobile phone producer. All figures are in millions of dollars. The root node represents the decision of whether to produce the phones in China or North America. The second pair of nodes represents the decision of whether to market the phones in China or North America. The final nodes represent the choice of selling price: if the phones are sold in China, they will be sold for either $30 or $40, whereas if they are sold in North America, they will be sold for either $40 or $50. Based on these calculated values, what is the company's best strategy?
- **Make in China:**
- **Sell in China:**
- $30: Mean = 1,250, SD = 750
- $40: Mean = 375, SD = 625
- **Sell in North America:**
- $40: Mean = -1,000, SD = 1,500
- $50: Mean = -1,500, SD = 1,250
- **Make in North America:**
- **Sell in China:**
- $30: Mean = -1,500, SD = 1,250
- $40: Mean = -250, SD = 1,639
- **Sell in North America:**
- $40: Mean = 1,250, SD = 2,137
- $50: Mean = -250, SD = 1,639
This decision tree helps to visualize the potential outcomes and associated risks for each possible production and sales strategy.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- am. 114.arrow_forwardAs the manager of Smith Construction, you need to make a decision on the number of homes to build in a new residential area where you are the only builder. Unfortunately, you must build the homes before you learn how strong demand is for homes in this large neighborhood. There is a 60 percent chance of low demand and a 40 percent chance of high demand. The corresponding (inverse) demand functions for these two scenarios are P = 400,000 −400Q and P = 900,000 −250Q, respectively. Your cost function is C(Q) = 125,000 + 430,000Q. How many new homes should you build, and what profits can you expect? Number of homes you should build: homes Profits you can expect: $arrow_forwardMega Studios is thinking of producing a megafilm which could be a megahit or a megaflop. Profit is uncertain for two reasons: (1) the cost of producing the film may be low or high, and (2) the market reception for the film may be strong or weak. There is a 0.6 chance of low costs (and a 0.4 chance of high costs). The probability of strong demand is 0.5 (the probability of weak demand is 0.5). The studio’s profits (in millions of dollars) for the four possible outcomes are shown in the table: demand strong weak cost low 80 10 high 0 -70 a) Should the studio produce the film? Justify your answer using expected profits. b) The studio is concerned that the film’s director might let production costs get out of control. Thus, the studio insists on a clause in the production contract giving it the right to terminate the project after the first $30 million is spent. By this time, the studio will know for certain whether total production costs are going to be low (i.e. under control)…arrow_forward
- Question: As the manager of Smith Construction, you need to make a decision on the number of homes to build in a new residential area where you are the only builder. Unfortunately, you must build the homes before you learn how strong demand is for homes in this large neighborhood. There is a 60 percent chance of low demand and a 40 percent chance of high demand. The corresponding (inverse) demand functions for these two scenarios are P = 300,000 − 400Q and P = 500,000 − 275Q, respectively. Your cost function is C(Q) = 140,000 + 240,000Q. How many new homes should you build, and what profits can you expect?arrow_forwardFour companies (Firm 1, 2, 3 and 4) are producing a product for the market. Each company will decide the number of products produced. You are given that • . Each firm can choose its qi. Given the quantites produced by four companies (denoted by 91, 92, 93, 94 respectively), the market price of the product is P = 400 - 91-92-93 - 94. Cost of producing one product is 20 (*Note: So the total cost for producing qi units of product is 20qi. Firm 1 and Firm 2 will first decide the quantities produced simultaneously at the beginning. After knowing 91 and 92, Firm 3 and Firm 4 will decide the quantities produced simultaneously. (a) State the strategic profiles of each firm. (b) Find all possible subgame perfect equilibrium for this games. Provide full justification to your answer.arrow_forwardAs the manager of Smith Construction, you need to make a decision on the number of homes to build in a new residential area where you are the only builder. Unfortunately, you must build the homes before you learn how strong demand is for homes in this large neighborhood. There is a 60 percent chance of low demand and a 40 percent chance of high demand. The corresponding (inverse) demand functions for these two scenarios are P = 400,000-400Q and P=900,000-2500, respectively. Your cost function is C(Q)=125,000+ 430,0000. How many new homes should you build, and what profits can you expect? Number of homes you should build: homesarrow_forward
- Scenario: In the town of Isoville there are two grocery stores: Alfonso’s Ammenities and Bernice’s Bargains. The grocery stores are located at either end of the town, 1km apart. Recently, the manager of Alfonso’s Ammenities has proposed installing new self-service checkout technology, which promises to reduce the cost of each transaction at the grocery store by reducing staffing costs. The new technology is expected to reduce the marginal cost of selling a typical basket of groceries by $3. However, experience in other locations has shown that in about 25% of installations the self-service technology results in a significant increase in shop-lifting. In these cases, the need to hire extra security staff means that the marginal cost of a typical basket only falls by $1.50. Unfortunately, there is no way to know whether extra security will be required until after the new checkouts are installed.The Market: Isoville has 12,000 households, each of which purchases 1 basket of groceries per…arrow_forwardk : ces As the manager of Smith Construction, you need to make a decision on the number of homes to build in a new residential area where you are the only builder. Unfortunately, you must build the homes before you learn how strong demand is for homes in this large neighborhood. There is a 50 percent chance of low demand and a 50 percent chance of high demand. The corresponding (inverse) demand functions for these two scenarios are P= 300,000-400Q and P= 500,000 -225Q, respectively. Your cost function is CQ) = 165,000+ 243,750Q. How many new homes should you build, and what profits can you expect? Number of homes you should build: homes Profits you can expect: $1arrow_forwardPhilippines You're the manager of global opportunities for a U.S. manufacturer that is considering expanding sales into Asia. Your market research has identified the market potential in Malaysia, the Philippines, and Singapore as described in the following table: Malaysia Probability Units Philippines Probability Units Singapore Probability Units Big Success Level 0.3 1,100,000 0.3 1,300,000 Mediocre Failure 0.2 352,000 0.3 650,000 0.1 0.7 600,000 360,000 0.5 0 0.4 0 0.2 0 The product sells for $20, and each unit has a constant marginal cost of $16. Assume that the (fixed) cost of entering the market (regardless of which market you select) is $500,000.arrow_forward
- You manage a company that competes in an industry that is comprised of 3 equal-sized firms that produce similar products. A recent industry report indicates that the market is fairly saturated, in that a 10 percent industry-wide price increase would lead to a 22 percent decline in units sold by all firms in the industry. Currently, Congress is considering legislation that would impose a tariff on a key input used by the industry. Your best estimate is that, if the legislation passes, your marginal cost will increase by 1 dollar. Based on this information, what price increase would you recommend if the tariff legislation is passed by Congress? Instructions: Enter your response rounded to the nearest penny (two decimal places).arrow_forwardYou are the manager of a firm that sells a “commodity” in a market that resembles perfect competition, and your analytics team estimates that your cost function is C(Q) = 2Q + 2Q2. Unfortunately, due to production lags, you must make your output decision prior to knowing for certain the price that will prevail in the market. You believe that there is a 65 percent chance the market price will be $200 and a 35 percent chance it will be $400. Calculate the expected market price. $ What output should you produce in order to maximize expected profits? units What are your expected profits? $arrow_forwardI would advise taking the following measures to ensure a successful entry into international markets: Conduct thorough market research to identify potential target countries with a demand for premium-quality stylish clothing. Consider factors like consumer preferences, cultural differences, existing competitors, and potential barriers to entry. There needs to research in regards to the export regulations and requirements of the target countries. Different countries may have specific rules and restrictions on textile imports, labeling, and quality standards. Before entering international markets, ensure that the brand identity is well-established and consistent. Make sure that the premium positioning, quality, and unique selling propositions are communicated clearly through branding and marketing materials. Maintain stringent quality control measures to ensure that the clothing consistently meets or exceeds the premium standards expected by target customers. Reputation is critical in…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education