
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Can you help me solve this please?

Transcribed Image Text:nomic Theory: Micro
Page
Consider a market with two firms (Firm 1 and Firm 2), which produce an identical good.
Both firms have the same constant marginal cost: MC = m = 40.
The demand in this market is given by:
Q = 100 – .25p p = 400 – 4Q
Let p1, 91, and T, denote the price charged by firm 1, the quantity firm 1 produces and sells, and
firm 1's profits, respectively. Analogously, let p2,92, and t, denote the price, the quantity, and
profits for firm 2. When appropriate, assume the firms split total quantity and profits evenly.
a. Assume that consumers in this market demand Q = 50 and the two firms compete by choosing
prices simultaneously (Bertrand oligopoly with identical products). What will be the price,
quantity, and profit for each firm in equilibrium? How does this equilibrium compare to a
perfectly competitive equilibrium?
b. Assume now that the two firms compete by choosing quantities simultaneously (Cournot
oligopoly with identical products). What will be the price, quantity, and profit for each firm in
equilibrium?
c. Assume now that the two firms now collude to act as monopolist. That is, they form a cartel.
What will be the price, quantity, and profit for each firm in equilibrium?
d. Compare the equilibrium price, quantities, and profits in the Bertrand, Cournot, and Cartel
cases. Which market structure is the most efficient in terms of total welfare, which benefits
consumers the most, and which benefits producers the most? Hint: You do not need to calculate
the surpluses, an economic argumentation supported by your previous answers is enough.
99+
Transcribed Image Text:onomic Theory: Micro
Page
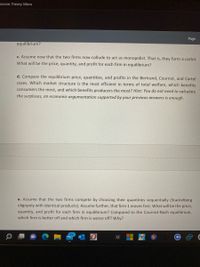
equilibrium?
c. Assume now that the two firms now collude to act as monopolist. That is, they form a cartel.
What will be the price, quantity, and profit for each firm in equilibrium?
d. Compare the equilibrium price, quantities, and profits in the Bertrand, Cournot, and Cartel
cases. Which market structure is the most efficient in terms of total welfare, which benefits
consumers the most, and which benefits producers the most? Hint: You do not need to calculate
the surpluses, an economic argumentation supported by your previous answers is enough.
e. Assume that the two firms compete by choosing their quantities sequentially (Stackelberg
oligopoly with identical products). Assume further, that firm 1 moves first. What will be the price,
quantity, and profit for each firm in equilibrium? Compared to the Cournot-Nash equilibrium,
which firm is better off and which firm is worse off? Why?
99+
U
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Imagine you are the mayor of a town and you are trying to decide if you should pay for a fireworks show. Your staff survey your 400 citizens who say that they each value a fireworks show at $10. The fireworks show only costs $3,000 so you put on the show but when you ask for donations to pay for the fireworks you only receive $25 total. What does this result show? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. You staff's survey must have overestimated the value of a fireworks show. b The fireworks cost must have been greater than their economic benefit. The firework show suffered from the Tragedy of the Commons problems d The town's citizens were free-riders.arrow_forwardA sentence that contains a metaphorarrow_forwardTrying to figure out?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education