
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
6
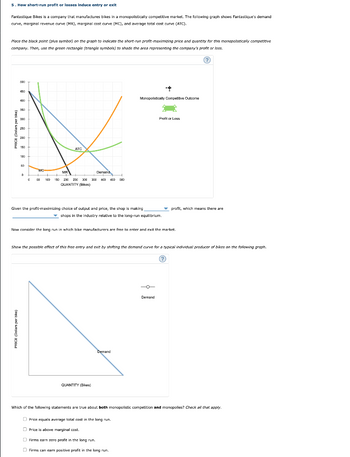
Transcribed Image Text:5. How short-run profit or losses induce entry or exit
Fantastique Bikes is a company that manufactures bikes in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows Fantastique's demand
curve, marginal revenue curve (MR), marginal cost curve (MC), and average total cost curve (ATC).
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run profit-maximizing price and quantity for this monopolistically competitive
company. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the company's profit or loss.
500
450
Monopolistically Competitive Outcome
400
350
20
Profit or Loss
300
250
200
150
ATC
100
50
Demand
MR
0
H
0
GU
100
150 200 250 300 350 400 450 000
QUANTITY (Bikes)
Given the profit-maximizing choice of output and price, the shop is making
profit, which means there are
shops in the industry relative to the long-run equilibrium.
Now consider the long run in which bike manufacturers are free to enter and exit the market.
Show the possible effect of this free entry and exit by shifting the demand curve for a typical individual producer of bikes on the following graph.
(?)
PRICE (Dollars per bike)
(છત્રાવ થd 1)
PRICE (Dollars per bike)
MG
Demand
Demand
QUANTITY (Bikes)
Which of the following statements are true about both monopolistic competition and monopolies? Check all that apply.
Price equals average total cost in the long run.
Price is above marginal cost.
Firms earn zero profit in the long run.
Firms can earn positive profit in the long run.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A79. Which of the following is the most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments. (b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades. (c) FDI inflows will drastically increase. (d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.arrow_forwardGive me accurate answer with proper calculation ; otherwise, I will give multiple downvote and complain to bartelby Note:- Please avoid using ChatGPT and refrain from providing handwritten solutions; otherwise, I will definitely give a downvote. Also, be mindful of plagiarism. Answer completely and accurate answer. Rest assured, you will receive an upvote if the answer is accurate.arrow_forwardOnly typed answerarrow_forward
- Learning 9g.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentld%35982812479578414089770649020&elSBN=978035; A Tax Document E ECSI - TaxSelect Do. SeAccount Quick Car. B Calendar | Navigate Main Street Comm. CENGAGE MINDTAP Homework (Ch 10) Back to Assignment Attempts Keep the Highest/1 4. Understanding different policy options to correct for negativeexternalities Carbon dioxide emissions have been linked to increased air pollution. The following table lists some possible public policies aimed at reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the air. For each policy isted, identify whether it is a command-and-control policy (regulation), tradable permit system, corrective subsidy, or corrective tax Tradable Permit System Corrective Subsidy Command-and- Corrective Public Policy Control Policy Tax The government orders every factory to adopt a new technology, which reduces carbon-dioxide emissions into the atmosphere. Trees take cartbon dioxide out of the air and convert it to okygen, so the…arrow_forwardQuestion:- Cyber risk insurance that covers both customers and legal settlements would be known asarrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- What are your thoughts about the future of properties in Los Angeles that are subject to this new tax? Will it help, will it hurt, what are the potential impacts?arrow_forwardFind value of output if:- Net value added at FC = $200 million Intermediate consumption = $150 million Depreciation = $20 million Tax = $40 Subsidy = $20 millionarrow_forwardQuestion 4Calculate the gross value added : Sale - 400 Changein stock -(-20) Depreciation - 30Net indirect taxes - 40 Purchasea of mchinery - 200 Purchaseof an intermediate production - 250arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education