
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
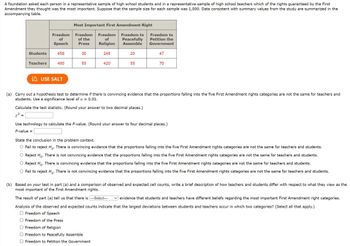
Transcribed Image Text:A foundation asked each person in a representative sample of high school students and in a representative sample of high school teachers which of the rights guaranteed by the First
Amendment they thought was the most important. Suppose that the sample size for each sample was 1,000. Data consistent with summary values from the study are summarized in the
accompanying table.
Students
=
Teachers
Freedom
of
Speech
658
400
USE SALT
Most Important First Amendment Right
Freedom
of
Religion
Freedom to
Peacefully
Assemble
Freedom
of the
Press
30
55
245
420
20
55
Freedom to
Petition the
Government
47
70
(a) Carry out a hypothesis test to determine if there is convincing evidence that the proportions falling into the five First Amendment rights categories are not the same for teachers and
students. Use a significance level of a = 0.01.
Calculate the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
x²=
Use technology to calculate the P-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
P-value =
State the conclusion in the problem context.
O Fail to reject Ho. There is convincing evidence that the proportions falling into the five First Amendment rights categories are not the same for teachers and students.
Reject Ho. There is not convincing evidence that the proportions falling into the five First Amendment rights categories are not the same for teachers and students.
Reject Ho. There is convincing evidence that the proportions falling into the five First Amendment rights categories are not the same for teachers and students.
Fail to reject Ho. There is not convincing evidence that the proportions falling into the five First Amendment rights categories are not the same for teachers and students.
(b) Based on your test in part (a) and a comparison of observed and expected cell counts, write a brief description of how teachers and students differ with respect to what they view as the
most important of the First Amendment rights.
The result of part (a) tell us that there is [---Select---
evidence that students and teachers have different beliefs regarding the most important First Amendment right categories.
Analysis of the observed and expected counts indicate that the largest deviations between students and teachers occur in which two categories? (Select all that apply.)
O Freedom of Speech
Freedom of the Press
Freedom of Religion
O Freedom to Peacefully Assemble
O Freedom to Petition the Government
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. Hypothesis Test of Proportions On April 15th, 1912, the R.M.S. Titanic sank into the North Atlantic Ocean, resulting in the loss of more than 1,500 passengers and crew. Below is a table which summarizes the total number of passengers and the number of survivors for the crew, first-, second-, and third-class. Find the proportion of survivors by type of service (crew, first, second, third). Test the hypothesis at the 99% confidence level that the proportion of first-class survivors is the same as third class (.25). What do you calculate for the test-statistic? What is the critical statistic? What is the conclusion of your hypothesis test?arrow_forwardIf the consequences of making a Type I error are severe, would you choose the level of significance, a, to equal 0.01, 0.05, or 0.10? Choose the correct answer below. A. 0.05 B. 0.10 C. 0.01arrow_forwardBased on your explanation, I selected the options, however they seem to be wrongarrow_forward
- E Question Help According to a newspaper, 78% of high school seniors have a driver's license. Suppose we take a random sample of 200 high school seniors and find the proportion who have a driver's license. a. What value should we expect for our sample proportion? b. What is the standard error? c. Use your answers to parts (a) and (b) to complete this sentence: We expect d. Suppose we increased the sample size from 200 to 800. What effect would this have on the standard error? Recalculate the standard error to see if your prediction was correct. % to have their driver's license, give or take %. a. We should expect a sample proportion of %. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) b. The standard error is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) c. Use your answers to fill in the blanks below. We expect % of students to have a driver's license, give or take %. (Type integers or decimals rounded to one decimal place as needed.) d. Select the correct…arrow_forwardDo a hypothesis for the following, make sure to include and label all five steps: Test the claim that tutoring influences a student’s test scores. Use a 0.01 level of significance. Use the following before and after scores for 5 students. Before 78 79 65 78 68 After 85 83 62 85 79arrow_forwardSocial networking is becoming more and more popular around the world. Pew Research Center used a survey of adults in several countries to determine the percentage of adults who use social networking sites (USA Today, February 8, 2012). Assume that the results for surveys in Great Britain, Israel, Russia and United States are as follows. Country Use Social Great United Networking Sites Britain Israel Russia States Yes 344 265 301 500 No 456 235 399 500 a. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine whether the proportion of adults using social networking sites equal for all four countries. Using a .05 level of significance. Use Table 12.4. 1. H, P + P, = P; = P. 2. H, P = P: = P, = P. 3. H, P, * P: = P, P, Choose correct answer from above choice Select your answer - V H a:- Select your answer The p-value is - Select your answer - What is your conclusion? |- Select your answer - b. What are the sample proportions for each of the four countries? Round your answers to two decimal places. Great…arrow_forward
- Use the sample data below to test the hypotheses Ho: P₁ = P₂ = P3 Ha: not all population proportions are equal where p; is the population proportion of Yes responses for population i. Response Yes No Populations 145 2 3 155 96 95 155 104 Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value Using a 0.05 level of significance, state your conclusion. O Do not reject Ho. We cannot conclude that not all population proportions are equal. O Do not reject Ho. We conclude that not all population proportions are equal. O Reject Ho. We conclude that not all population proportions are equal. Reject Ho. We cannot conclude that not all population proportions are equal.arrow_forwardPlease Answer d,e,f Please provide typed answer. ONLY TYPED ANSWERSarrow_forwardUse the sample data below to test the hypotheses Ho: P₁ = P₂ = P3 H₂: not all population proportions are equal where P₁ is the population proportion of Yes responses for population i. Response Yes No Populations 1 23 145 140 111 95 140 119 Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = Using a 0.05 level of significance, state your conclusion. O Do not reject Ho. We cannot conclude that not all population proportions are equal. O Do not reject Ho. We conclude that not all population proportions are equal. O Reject Ho. We cannot conclude that not all population proportions are equal. O Reject Ho. We conclude that not all population proportions are equal.arrow_forward
- Urgent need help immediatelyarrow_forward3) Examine your t-test score in the paired samples t-test table. Is the p value significant? State in one to two sentences whether the test was significant and interpret this result.arrow_forwardSome experts believe that 16% of all freshwater fish in a country have such high levels of mercury that they are dangerous to eat. Suppose a fish market has 200 fish tested, and 29 of them have dangerous levels of mercury. Test the hypothesis that this sample is not from a population with 16% dangerous fish, assuming that this is a random sample. Use a significance level of 0.05. Comment on your conclusion. State the null and alternative hypotheses. О А. Но: р30.16 Hạ: p+0.16 В. Но: р#0.16 Ha: p= 0.16 Ос. Но: р> 0.16 Hại p0.16 ОЕ. Но: р0.16 Determine the z-test statistic. Z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the p-value. p-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman