
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
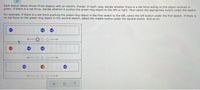
Transcribed Image Text:Each sketch below shows three objects with an electric charge. In each case, decide whether there is a net force acting on the object outlined in
green. If there is a net force, decide whether it pushes the green-ring object to the left or right. Then select the appropriate button under the sketch.
For example, if there is a net force pushing the green-ring object in the first sketch to the left, select the left button under the first sketch. If there is
no net force on the green-ring object in the second sketch, select the middle button under the second sketch. And so on.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the given information to solve part Carrow_forwardEach sketch below shows three objects with an electric charge. In each case, decide whether there is a net force acting on the object outlined in green. If there is a net force, decide whether it pushes the green-ring object to the left or right. Then select the appropriate button under the sketch. For example, if there is a net force pushing the green-ring object in the first sketch to the left, select the left button under the first sketch. If there is no net force on the green-ring object in the second sketch, select the middle button under the second sketch. And so on. X Sarrow_forwardIllustrate the vector diagram with the given situation: (no need to solve just illustration)Two objects with charges Q1 and Q2 experience an electrical force of attraction of 8.0x10-4 N when separated by a distance of d. Determine the force of attraction if the same objects are separated by a distance of 2d and each object having double the charge.arrow_forward
- The diagram below shows a positive point charge placed near a neutral metal cube. The location marked with a × can be ignored. a. Draw the charge distribution within the metal cube and reduce it to an “effective point charge model, as shown in class.b. Is the positive point charge attracted to, repelled by, or unaffected by the metal cube? Please explain using a neat vector diagram to support your arguments.c. In a second identical experiment, the positive point charge +q is replaced by a negative point charge −q. Does a negative point charge interact differently with the metal cube as compared to the positive point charge? Briefly explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardShow your work.arrow_forwardUnderstanding how electrostatic forces cancel Each sketch below shows three objects with an electric charge. In each case, decide whether there is a net force acting on the object outlined in green. If there is a net force, decide whether it pushes the green-ring object to the left or right. Then select the appropriate button under the sketch. For example, if there is a net force pushing the green-ring object in the first sketch to the left, select the left button under the first sketch. If there is no net force on the green-ring object in the second sketch, select the middle button under the second sketch. And so on. Explanation +2 Check +3 +2 tv ♫ A [ 0 © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessib Aarrow_forward
- The sketch below shows three objects with electric charge. (The charge of each object is written on it.) Decide whether there is a net electric force acting on the central object. If there is, select the button under the sketch that shows the direction of this force. If there is no net force on the central object, select the center button. -2 O -2 -3arrow_forwardA small sphere with a mass of 0.450 gram is suspended by a non-conducting silk thread as shown. The sphere is subject to an electric field of 3000 N/C directed to the left and the sphere swings out 8° from the vertical as shown below. Follow the steps below to determine the magnitude of the charge on the sphere. A. e = 8° 1. Label all the forces acting on the small sphere on the diagram on the left. 2. Using the forces on your diagram determine the charge (magnitude and quality (+ or - )) on the ball.arrow_forwardRELATIONSHIP OF ELECTRIC FORCE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE AND DISTANCE OF CHARGES. DIRECTION: Choose the correct term in the parenthesis 1. The magnitude of distance of charges is ( inversely proportional , directly proportional) to the electrical force. 2. If the charge of both particles is doubled, the force ( unchanged, halved, doubled, quadrupled) 3. If the charged of one of the particles id doubled, the force is ( unchanged, halved, doubled, quadrupled) 4. If the distance between the particles is doubled, the force becomes ( one fourth, half, double, 4 times) 5. The product of charges is ( inversely proportional , directly proportional) to the electrical force.arrow_forward
- Practicearrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the electric field at A. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Use Coulomb's law to determine the magnitude of the electric field at points A and B in (Figure 1) due to the two positive charges (Q = 5.1 µC) shown. Suppose that a = 5.1 cm Ti HÁ E, = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the angle between the direction of the electric field at point A and the positive x-direction. Express your answer using two significant figures. nν ΑΣ φ. OA = 0.83 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Figure < 1 of 1 Part C В Determine the magnitude of the electric field at point B. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. +Q• +Q ? 2a EB = Value Units Submit Request Answer P Pearsonarrow_forwardTwo sets of electrostatic force data are shown below (Figure 1) (Figure 2). Perform calculations to determine the plausibility of each data set. Which of the data sets could be a result of the interaction between two point charges?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON