
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
E=8.3V and R=5 ohms
a) Find the current in the 2 ohm resistor (in mA)
b) Find the potential difference between points a and b (in V)
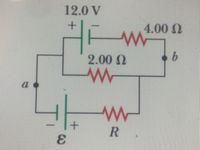
Transcribed Image Text:This image depicts an electrical circuit diagram with the following components:
1. **Voltage Source**:
- A 12.0 V battery on the top left, with its positive terminal connected to the circuit.
2. **Resistors**:
- Three resistors are connected in the circuit:
- A 4.00 Ω resistor on the top horizontal path between points `a` and `b`.
- A 2.00 Ω resistor in the middle horizontal path parallel to the first resistor.
- Another resistor labeled `R` in the bottom horizontal path parallel to the other resistors.
3. **Connections**:
- The circuit forms a parallel configuration with the three resistors as each path connects between nodes `a` and `b`.
4. **Additional Voltage Source**:
- There is another voltage source labeled `ε` at the bottom, oriented with the positive terminal towards the right.
This diagram can be used to analyze current distribution, voltage drops across each resistor, and equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit setup. Understanding such diagrams is essential for solving circuit analysis problems in physics and electrical engineering.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A resistance of 10 ohms and C=0.1F is connected in series with a 12V battery. Find the charge at any time and the charge current 0.4 seconds after switch is closed.arrow_forwardC -Q (A) 0.25 uF 10V 2uF 4uF (B) Figure 3: 3. In Figure 3 the capacitors were discharged before being connected to the battery. (a) In Figure 3A the net positive charge delivered by the battery is +Q1 to C1 and a net negative charge -[Q2 + Q3] is delivered to C2 and C3 [-Q2 is delivered to C2 and -Q3 to C3]. From conservation of charge[net charge is zero since both the battery and the capacitors have a zero net excess charge] and path independence of the electric field[sum of voltages must add up to zero for a closed path or conservation of energy]: Q1 + (-Q2) + (-Q3) = 0 conservation of charge +%-왕-용 (True, False) = 0 conservation of energy +V - = 0 conservation of energy (b) If (a) is true then the charge Q1, Q2 and Q3 follow from above three equations as C1(C2 + C3) V Q2 = Ci + C2 + C3 C1 C3 Ci + C2 + C3 Q1 = Q3 = V, (True, False) C1 + C2 + C3 (c) In Figure 3A the net positive charge delivered by the battery is Qtot = Q1 = C1(C2+C3) v which implies an equivalent capacitance of Qtot…arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,