
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
PLEASE SOLVE PARTS (E) AND (F)
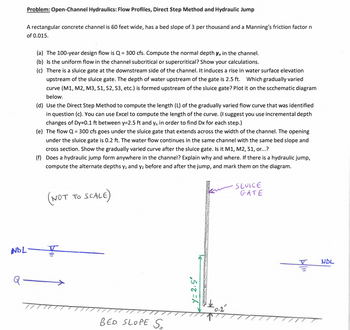
Transcribed Image Text:Problem: Open-Channel Hydraulics: Flow Profiles, Direct Step Method and Hydraulic Jump
A rectangular concrete channel is 60 feet wide, has a bed slope of 3 per thousand and a Manning's friction factor n
of 0.015.
NDL-
(a) The 100-year design flow is Q = 300 cfs. Compute the normal depth y, in the channel.
(b) Is the uniform flow in the channel subcritical or supercritical? Show your calculations.
(c) There is a sluice gate at the downstream side of the channel. It induces a rise in water surface elevation
upstream of the sluice gate. The depth of water upstream of the gate is 2.5 ft. Which gradually varied
curve (M1, M2, M3, S1, S2, S3, etc.) is formed upstream of the sluice gate? Plot it on the scchematic diagram
below.
(d) Use the Direct Step Method to compute the length (L) of the gradually varied flow curve that was identified
in question (c). You can use Excel to compute the length of the curve. (I suggest you use incremental depth
changes of Dy=0.1 ft between y=2.5 ft and y, in order to find Dx for each step.)
(e) The flow Q = 300 cfs goes under the sluice gate that extends across the width of the channel. The opening
under the sluice gate is 0.2 ft. The water flow continues in the same channel with the same bed slope and
cross section. Show the gradually varied curve after the sluice gate. Is it M1, M2, S1, or...?
(f) Does a hydraulic jump form anywhere in the channel? Explain why and where. If there is a hydraulic jump,
compute the alternate depths y₁ and y₂ before and after the jump, and mark them on the diagram.
(NOT TO SCALE)
BED SLOPE S
y=2.5°
$0.2
•SLUICE
GATE
NDL
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please explain this problems step by step and its concept clear so I can understandarrow_forwardConsider a rectangular cross-section beam having width b and height h that is taking bending load. The beam can be oriented in two different ways (shown in case a and b), and the corresponding neutral axes are shown as well. In which case, the beam will provide more resistance to bending (i.e., larger value of 1)? b Case (a) Neutral axis O I. Case (b) O II. Depends on other parameters III. Case (a) IV. Both cases will give the same value of I Case (b) Neutral axisarrow_forward3-9. The 1 x 8 plate shown in Fig. P3-9. The holes are for -in Ø bolts. (Ans. 6.44 in?) 3 in 3 in 8 in - 2 in 1 in PL 1 x 8arrow_forward
- Please help me solve this, Thank you so much.arrow_forwardThe beam cross section shown below has been proposed for a short pedestrian bridge. The cross section will consist of two pipes that are welded to a rectangular web plate. Dimensions of the cross section are: h= 430 mm tw= 12 mm d= 110 mm t= 9.6 mm Additionallv: • The area of each pipe is A = 3028 mm2. • The moment of inertia of the entire beam cross section about the z centroidal axis is I>= 320410000 mm4. If the beam will be subiected to a shear force of V = 110 kN, determine the shear stress at point K, located at yK = 70 mm below the z centroidal axis.arrow_forwardIn your words, discuss the strengths and limitations of the Bishop’s (1959) equation.arrow_forward
- Show all units and step by step solution.Formula attached.arrow_forwardTwo concurrent forces are allied to the box. Add the two vectors together to get the resultant with triangle methodarrow_forwardA cantilever beam consists of two sections, the first is a straight section, AB, of length, L, and thesecond is a curved section, BC, with a radius of a. The elastic modulus, E, is constant. The beam has arectangular cross-section of length b (width and height of the cross-section are both equal to b).Disregard the width of the beam and use centreline dimensions when making calculations.a) Use energy methods to calculate the vertical deflection of point Cb) Use energy methods to calculate the horizontal deflection of point Carrow_forward
- Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are joined at C and restrained by rigid supports at A and E. For the loading shown and knowing that E, = 200 GPa and Eb = 105 GPa, determine the deflection of point C. Sc A um →>> Dimensions in mm 120 180130- Steel B 65 KN 40-mm diam. D Brass 120 E 50 KN 30-mm diam.arrow_forwardDetermine the coordinates of the mass center of the welded assembly of uniform slender rods made from the same bar stock. a 0.93 a Answers: (X, Y, Z) = ( i ) a i iarrow_forwardА L B 425 mm C 1,000 mm V P A steel bar (1) and an Aluminum bar (2) are connected to a rigid angle ACD. Assuming: • Steel [E = 200 GPa] bar (1) is 6mm x 40mm x 600mm long. • Aluminum [E = 70 GPa] bar (2) is 10mm x 40mm x 600mm long. Poisson's ratio, v = 0.35 • A distance L of 500mm. a)Determine the force P (in kN) required to stretch the Aluminum bar by 1mm. Enter the force, P, into the d21 answer box (in kN, 3 sig digs). b) Determine the final width and thickness of the Aluminum bar. (1) Your Answer:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning