
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A 82.5-kg man pushes a crate 4.5 m up along a ramp that makes an angle of 19.5° with the horizontal. He exerts a force of 495 N on the crate parallel to the ramp and moves it at a constant speed.
| Calculate the work, in joules, that the man performs to cause the crate and himself to move up the ramp. |
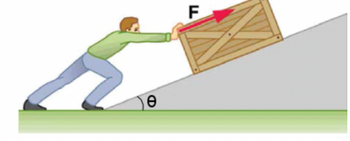
Transcribed Image Text:e
F
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Starting from rest, a 5.50-kg block slides 2.30 m down a rough 30.0° incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is k (a) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. J (b) Determine the work done by the friction force between block and incline. J (c) Determine the work done by the normal force. (d) Qualitatively, how would the answers change if a shorter ramp at a steeper angle were used to span the same vertical height? 0.436.arrow_forwardA force of constant magnitude pushes a box up a vertical surface as shown in the figure. The box moves at a constant speed. If the mass of the box is 3.70 kg, it is pushed 3.60 m vertically upward, the coefficient of friction is 0.350 and the angle ? is 30.0°, determine the following. (a) work done on the box by F J(b) work done on the box by the force of gravity J(c) work done on the box by the normal force J(d) increase in gravitational potential energy of the box as it moves up the wall Jarrow_forwardA man pulls a 4.6-kg sled 50 meters along an angled hill with a force of 36 N, which elevates the man 28 meters above the bottom of the hill. The man then hops on his sled and slides from rest to the bottom of the hill back along his 50 meter path, during which a 299 N frictional force acts upon his sled. How much work in Joules does the man do against friction in pulling the sled up the hill?arrow_forward
- A person pulls a 75-kg box 20 m along a horizontal floor by a constant force Fp = 125 N, which acts at a 42 degree angle. The floor is not smooth and exerts a friction force of Ff = 65 N. Determine the following: The work done by each force acting on the crate (Don’t forget any!) The net work done on the cratearrow_forwardA 4.5-kg block slides down a frictionless incline making an angle of 55.0° with the horizontal. (a) What is the total work done on the block when the block slides 1.4 m (measured along the incline)? (b) What is the speed of the block after it has slid 1.2 m if it starts from rest? m/s (c) What is its speed after 1.2 m if it starts with an initial speed of 1.6 m/s? m/s You can use the definition of work as the scalar product of a constant force and displacement to find the work done by each force acting on the block. Then use the work- kinetic energy theorem the find the speed of the block at any given location and for any initial kinetic energy it may have.arrow_forwardThe graph shows the x component of a force that acts on an object that moves on the x axis. The vertical spacing between adjacent grid lines is 4.98N, while the horizontal spacing between adjacent grid lines is 1.0m. What is the work, in joules, done by the force as the object moves from x = 4m to x = 5m ? F (N) C C 0 x (m)arrow_forward
- An asteroid is moving along a straight line. A force acts along the displacement of the asteroid and slows it down. The asteroid has a mass of 5.3x 104 kg, and the force causes its speed to change from 6900 to 5500m/s. (a) What is the work done by the force? (b) If the asteroid slows down over a distance of 2.3x 10 m determine the magnitude of the force. (a) Work- (b) F- iarrow_forwardA 60 Nt force is exerted on a 5 kg box at an angle of 60° above the horizontal. (a) What is the work done by the 60 Nt force on the box if the box moves a distance of 2 m across the floor? (b) What is the work done by the normal force?: (c) If the box moves at a constant speed, what is the work done by friction on the box?: (d) What is the work done by gravity on the box? (e) What is the total work done by all of the forces on the box?arrow_forwardA sled with total mass m = 46.3 kg is pulled a distance d = 17.1 m across a horizontal surface for which the corficcient of kinetic friction with the sled is = 0.196. The pulling force is constant and makes an angle = 31.2° above the horizontal and the sled moves at a constant velocity. Find an expression for the work done by the pulling force in terms of m, acceleration due to gravity g, 0, Hk, and d, and use it find the work done in Joules by the pulling force. Find an expression for the work done on the sled by friction in terms of m, acceleration due to gravity g, 8, HK, and d, and use it to find the work done in Joules by the friction force. What is the net work in Joules done on the sled?arrow_forward
- Two tugboats pull a disabled supertanker. Each tug exerts a constant force of 2.10×106 N, one at an angle 16.0° west of north, and the other at an angle 16.0° east of north, as they pull the tanker a distance 0.680 km toward the north. What is the total work done by the two tugboats on the supertanker? Express your answer in joules, to three significant figures.arrow_forwardA mother pulls her child on a sled across a rough patch of snow. The sled and child have a combined mass of 25kg. The sled’s tow rope is at 42° angle above the horizontal and the mother exerts a force of 65N. If the sled accelerates from rest at 1.5 m/s2 over 15m, what is the work done by friction on the sled?arrow_forwardA force of magnitude 25.0N directed at an angle of 35.0° above the horizontal moves a 16.0kg crate along a horizontal surface at a constant velocity. How much work is done by this force in moving the crate a distance of 14.0m?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON