
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
When traits show complete dominance, the genotype can be revealed by a test cross. In the example of tall and dwarf plants (Figure) why is it necessary to use the dwarf parent? In general, why is it necessary to use a parent that is homozygous recessive?
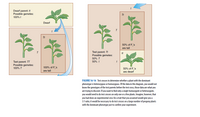
Transcribed Image Text:Dwarf parent: t
Possible gametes:
Tt
100% t
Dwarf
Tt
50% of F,'s
are tall
Test parent: Tt
Possible gametes:
tt
50% T
50% t
Test parent: TT
Possible gametes:
100% T
t
100% of F,'s
50% of F,'s
are tall
are dwarf
FIGURE 16-14 Test crosses to determine whether a plant with the dominant
phenotype is heterozygous or homozygous. Of the data in this diagram, you would not
know the genotypes of the test parents before the test cross; those data are what you
are trying to discover. If you want to find only a single homozygote or heterozygote,
you would need to do test crosses on only one or a few plants. Imagine, however, that
you had done an experimental cross for a trait that you assumed would give you a
3:1 ratio; it would be necessary to do test crosses on a large number of progeny plants
with the dominant phenotype just to confirm your experiment.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Y = yellow, y = green; R = round seed, r = wrinkled seed %3D An individual has the genotype YYRR and has offspring with an individual with the genotype yyrr. If the genes are both expressed with complete dominance, then what phenotype will all the offspring have? Yellow and Wrinkled Yellow and Round Green and Round Green and Wrinkledarrow_forwardIn a plant, stems can appear fuzzy or smooth. The allele for fuzzy (F) is dominant. These plants can also have blue (B-) or white flowers. White is the recessive trait. A cross was made between plants heterozygous for both traits. You observed 290 blue fuzzy, 80 blue smooth, 70 white fuzzy, and 40 white smooth plants. Are your observations consistent with your expectations?arrow_forwardRed flowering plant are crossed with white flowering plant. The offspring shows: 1 red: 2 pink: 1 white. What are the genotypes of the parents?arrow_forward
- In snapdragons, red flower color is incompletely dominant to white flower color. Tall is completely dominant to short. You cross a true breeding red-flowered tall plant to a true breeding white-flowered short plant. You cross the F1 offspring to each other. In the F2, what is the probability of offspring that are white-flowered and tall?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT required for adaptations to evolve? Heritable variation in fitness Genetic diversity within populations Sexual reproduction Natural selection Question 2arrow_forwardGregor Mendel discovered the basis of heredity with his sweet pea plant experiments. In his studies, he determined that certain traits, such as pod color and pea shape, express complete dominance. Trait Dominant Recessive Pod color Yellow Green Pea shape Round Wrinkled A cross occurs between a plant with heterozygous yellow pods and wrinkled peas and a plant with green pods and heterozygous round peas. What is the probability that the offspring will exhibit recessive genes for both traits? a) 1/2 b) 1/4 c) 1/8 d) 1/16arrow_forward
- In swallowtail butterflies, let's pretend that the R gene codes for coloring on the forewing. The R1 allele, which codes for red color, is dominant to the R2 allele, which codes for white color. If R1 is a recessive lethal allele, what phenotypic ratio would you expect when crossing two swallowtails with red forewings? 1 red : 2 white 1 red : 3 white 3 red : 1 white there is not enough information given to answer this question 1 red : 1 white 2 red : 1 whitearrow_forwardIn a particular plant, leaf color and leaf shape are controlled by two linked genes. Leaves of the wild-type plant are red. A recessive mutation in this gene causes white leaves. Wild-type leaves are pointed and a recessive mutation in this gene causes them to be smooth. The following cross was performed: Heterozygous red, pointed 43 white, smooth 42 red, pointed 8 white, pointed 7 red, smooth Homozygous white, smooth RESULTS: What is the recombination frequency between the gene for leaf color and the gene for leaf shape?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education