
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:more aqueous.
How
hydrogen
yond,
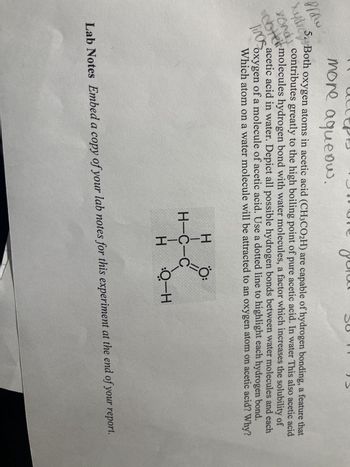
5. Both oxygen atoms in acetic acid (CH3CO₂H) are capable of hydrogen bonding, a feature that
contributes greatly to the high boiling point of pure acetic acid. In water This also acetic acid
Ce molecules hydrogen bond with water molecules, a factor which increases the solubility of
linos
acetic acid in water. Depict all possible hydrogen bonds between water molecules and each
oxygen of a molecule of acetic acid. Use a dotted line to highlight each hydrogen bond.
Which atom on a water molecule will be attracted to an oxygen atom on acetic acid? Why?
HTC-H
H-C-C
Н
Ö:
n=0
Q-H
Lab Notes Embed a copy of your lab notes for this experiment at the end of your report.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hydrogen bond can form among water molecules, proteins and nucleic acids. For a hydrogen bond, there is a "donor" and an "acceptor". Below which is NOT a possible combination of donor/acceptor for a hydrogen bond? O [C-H-0] O [O-H----:0] O N-H-----0] [N-H-----N]arrow_forwardWhen 56.47 grams of fictional compound X is added to water to make 404.5 grams of solution, the temperature increases from 20.05 °C to 72.12 °C. What is the heat of solution for compound X given that the molar mass of compound X is 167.81 g/mol? Assume the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.18 J/g°C. -88.03 kJ/mol -261.6 kJ/mol -10.35 kJ/mol 88.03 kJ/mol 261.6 kJ/molarrow_forward1.65 • Which of the following is expected to have the highest boiling point? H. H. H-C-O C-H а. H H H-C-C-OH b. H H https://bookshelf.vitalsource.com/reader/books/9781119776741/epubcfi/6/16[%3Bvnd.vst.idref%3DC01]u4/2[c01-sec-0000y52[c01-exsec-0400/36/8/1:. 1/2 8/15/2021 VitalSource Bookshelf: Organic Chemistry, Integrated E-Text with E-Solutions Manual H-C-C-H С. H :O. H H-C-C-H d.arrow_forward
- Please explain and solve very correctlyarrow_forward2 pt Please provide an explanation for the relatively high boiling points of H20, HF, and NH3 in comparison to the hydrogen compounds of other elements in the respective groups. 100 H2O Group 16 (6A) HF Group 17 (7A) H,Te SbH3 H,Se HI NH3 Group 15 (5A) H.S ASH5 SnH4 HCI HBr PH, GeH, -100 SiH CH Group 14 (4A) -200 1 3. 4 Period HTML Editor B IUA 工E三州 星xx 三= A 12pt Paragraph Boiling point ('C)arrow_forward3. Maximum solubility of an ionic compounds in water depend on different sets of conditions. Out of five sets of conditions (given below), which one is the best for getting maximum solubility? A. The magnitude of the lattice energy should be large, and the enthalpy of hydration of the ions should be large. B. The enthalpy of hydration (Delta H) of the cation should be equal to the enthalpy of hydration of the anion, regardless of the magnitude of the lattice energy C. The magnitude of the lattice energy should be small, and the enthalpy of hydration of the ions should be small. D. The magnitude of the lattice energy should be small, and the enthalpy of hydration of the ions should be large. E. The magnitude of the lattice energy should be large, and the enthalpy of hydration of the ions should be small.arrow_forward
- Acetic acid (CH3CO₂H) dissolved in water is shown to the right. Which of the labeled interactions represent hydrogen bonding interactions? H I 0: Oll only H OI only O III only I, III, and IV I and III O I and IV III and IV 4. HICH III 0: -C- &mm. :O: II -H H ||||.* H IV Harrow_forwardA water sample is to be treated using alum as Al2(SO4)3●14.2 H2O. The water has the following constituents: mg/L Ca2+ 37 Na+ 6.5 Mg2+ 8.1 K+ 1.2 Fe3+ 1.0 HCO3- 119 SO42- 22 Cl- 20 NO3- 0.1 Is the water analysis complete according to the principle of electroneutrality?arrow_forwardplease just do part barrow_forward
- Calculate the Molar mass of a volatile liquid (g/mol) from the following data:- Mass of dry flask, foil, and rubber band (g) = 142.722 Temperature of boiling water (°C) = 99.9 Mass of dry flask, foil, rubber band, and vapors (g) = 143.801 Volume of Erlenmeyer flask (Litres) = 1.127 Atmospheric Pressure (atm) = 1 7.8 g/mol OA. 19.3 g/mol O B. 24.3 g/mol С. OD 29.3 g/mol 34.3 g/mol OE.arrow_forwardThe amount of UVA radiation hitting a surface at sea level in a lightly clouded day isabout 70W/m2. About half of that can be absorbed by the skin. A typical carbon-carbon bond requires 348 kJ/mol to break. A person lies on the beach for about 1hour without sunscreen (i.e. fully exposed to UVA radiation). Estimate the numberof C-C bonds broken in this person’s back (about 0.18 m2) over that period. Assumethat the average wavelength of UVA is 335 nm.arrow_forwardWhat can you conclude about the relative magnitudes of the lattice energy of ammonium chloride and its heat of hydration? The lattice energy is smaller greater in magnitude than the heat of hydration.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY