
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Need help on #4 and onward
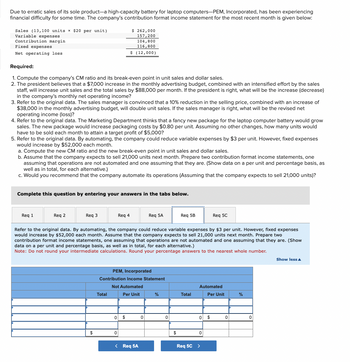
Transcribed Image Text:Due to erratic sales of its sole product-a high-capacity battery for laptop computers-PEM, Incorporated, has been experiencing
financial difficulty for some time. The company's contribution format income statement for the most recent month is given below:
Sales (13,100 units x $20 per unit)
Variable expenses
Contribution margin.
Fixed expenses
Net operating loss
Required:
1. Compute the company's CM ratio and its break-even point in unit sales and dollar sales.
2. The president believes that a $7,000 increase in the monthly advertising budget, combined with an intensified effort by the sales
staff, will increase unit sales and the total sales by $88,000 per month. If the president is right, what will be the increase (decrease)
in the company's monthly net operating income?
3. Refer to the original data. The sales manager is convinced that a 10% reduction in the selling price, combined with an increase of
$38,000 in the monthly advertising budget, will double unit sales. If the sales manager is right, what will be the revised net
operating income (loss)?
4. Refer to the original data. The Marketing Department thinks that a fancy new package for the laptop computer battery would grow
sales. The new package would increase packaging costs by $0.80 per unit. Assuming no other changes, how many units would
have to be sold each month to attain a target profit of $5,000?
5. Refer to the original data. By automating, the company could reduce variable expenses by $3 per unit. However, fixed expenses
would increase by $52,000 each month.
a. Compute the new CM ratio and the new break-even point in unit sales and dollar sales.
b. Assume that the company expects to sell 21,000 units next month. Prepare two contribution format income statements, one
assuming that operations are not automated and one assuming that they are. (Show data on a per unit and percentage basis, as
well as in total, for each alternative.)
c. Would you recommend that the company automate its operations (Assuming that the company expects to sell 21,000 units)?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req 1
Req 2
Req 3
$
$ 262,000
157,200
104,800
116,800
$ (12,000)
Total
Req 4
0
Refer to the original data. By automating, the company could reduce variable expenses by $3 per unit. However, fixed expenses
would increase by $52,000 each month. Assume that the company expects to sell 21,000 units next month. Prepare two
contribution format income statements, one assuming that operations are not automated and one assuming that they are. (Show
data on a per unit and percentage basis, as well as in total, for each alternative.)
Note: Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your percentage answers to the nearest whole number.
PEM, Incorporated
Contribution Income Statement
Not Automated
Per Unit
0
$
Req 5A
< Req 5A
0
%
Req 5B
0
Total
Automated
Per Unit
0
0
Req 5C
Req 5C >
$
0
%
0
Show less A
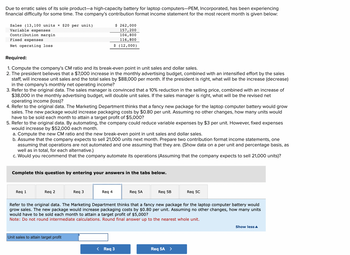
Transcribed Image Text:Due to erratic sales of its sole product-a high-capacity battery for laptop computers-PEM, Incorporated, has been experiencing
financial difficulty for some time. The company's contribution format income statement for the most recent month is given below:
Sales (13,100 units x $20 per unit)
Variable expenses
Contribution margin
Fixed expenses
Net operating loss
Required:
1. Compute the company's CM ratio and its break-even point in unit sales and dollar sales.
2. The president believes that a $7,000 increase in the monthly advertising budget, combined with an intensified effort by the sales
staff, will increase unit sales and the total sales by $88,000 per month. If the president is right, what will be the increase (decrease)
in the company's monthly net operating income?
3. Refer to the original data. The sales manager is convinced that a 10% reduction in the selling price, combined with an increase of
$38,000 in the monthly advertising budget, will double unit sales. If the sales manager is right, what will be the revised net
operating income (loss)?
4. Refer to the original data. The Marketing Department thinks that a fancy new package for the laptop computer battery would grow
sales. The new package would increase packaging costs by $0.80 per unit. Assuming no other changes, how many units would
have to be sold each month to attain a target profit of $5,000?
5. Refer to the original data. By automating, the company could reduce variable expenses by $3 per unit. However, fixed expenses
would increase by $52,000 each month.
a. Compute the new CM ratio and the new break-even point in unit sales and dollar sales.
b. Assume that the company expects to sell 21,000 units next month. Prepare two contribution format income statements, one
assuming that operations are not automated and one assuming that they are. (Show data on a per unit and percentage basis, as
well as in total, for each alternative.)
c. Would you recommend that the company automate its operations (Assuming that the company expects to sell 21,000 units)?
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req 1
$ 262,000
157,200
104,800
116,800
$ (12,000)
Req 2
Req 3
Unit sales to attain target profit
Req 4
Req 5A
< Req 3
Req 5B
Refer to the original data. The Marketing Department thinks that a fancy new package for the laptop computer battery would
grow sales. The new package would increase packaging costs by $0.80 per unit. Assuming no other changes, how many units
would have to be sold each month to attain a target profit of $5,000?
Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer up to the nearest whole unit.
Req 5C
Req 5A >
Show less A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- NWP Assessment Player UI Ap X + -> A education.wiley.com/was/ui/v2/assessment-player/index.html?launchld=c59069c8-77ac-43ad-888c-80c06e514aa6#/question/0 Update : Apps M Gmail YouTube P MyLab & Masterin... E Brytewave eReader E Home | North Car... VitalSource Books... GRLContent WP WileyPLUS E Reading List E Chapter 6.A Homework Question 1 of 6 > -/3 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress Wildhorse Co. just took its physical inventory on December 31. The count of inventory items on hand at the company's business locations resulted in a total inventory cost of $ 289,300. In reviewing the details of the count and related inventory transactions, you have discovered the following items that had not been considered. 1. Wildhorse has sent inventory costing $ 30,510 on consignment to Richfield Company. All of this inventory was at Richfield's showrooms on December 31. The company did not include in the count inventory (cost, $ 18,270) that was sold on December 28, terms FOB shipping point.…arrow_forwardAssistarrow_forwardNot a previously submitted question. Thank youarrow_forward
- MindTap - Cengage Learning CengageNOWv2 | Online teachin x 9 Cengage Learning b Answered: CengageNOWv2| Onli x i v2.cengagenow.com/ilrn/takeAssignment/takeAssignmentMain.do?invoker=&takeAssignmentSessionLocator=&inprogress=false Ch 13-2 Practice Exercises E Calculator eBook Show Me How Print Item Reporting Stockholders' Equity Using the following accounts and balances, prepare the Stockholders' Equity section of the balance sheet using Method 1 of Exhibit 8. 50,000 shares of common stock authorized, and 2,000 shares have been reacquired. Common Stock, $80 par $3,200,000 Paid-In Capital from Sale of Treasury Stock 64,000 Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Common Stock 440,000 Retained Earnings 1,728,000 Treasury Stock 42,000 Stockholders' Equity Paid-In Capital: Common Stock, $80 Par 3,200,000 Excess over par 440,000 Treasury Stock From Sale of Treasury Stock 64,000 Total Paid-in Capital $ 3,704,000 Retained Earnings Total Treasury Stock Total Stockholders' Equity Check My Work 2 more…arrow_forwardHow would I calculate this problem? I just guessed on which answer made sense to me. Please help. thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPlease help on parts 4 and 5. Please also show work on how to do.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education