
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Other information:
(a) On April 30, the only jobs still in process were 203 and 206.
(b) All workers are paid P20 per hour. Wage rates have been stable through-
out the year.
(c) Tuason maintains only one raw materials account (Materials Control) from
which it issues both direct and indirect materials. The balance in this ac-
count was P2,750 on April 1.
(d) All sales are billed on account at 150% of total cost.
(e) Other items in April:
Depreciation factory equipment
Raw materials purchased
Indirect labor
Factory rent and utilities
Indirect materials used
P 1,375
11,500
2,500
2,700
2,790
Required:
(1) Determine the April 30 balances for Materials Control and for Work
in Process.
(2) Prepare all journal entries required for Job 202 in April.
Calculate the cost of goods manufactured in April. (A complete state-
(3)
ment of cost of goods manufactured is not required.)
(4) Calculate the over- or underapplied overhead for April.
(5) Calculate the gross profit for April.
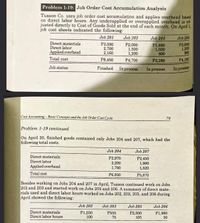
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1-19: Job Order Cost Accumulation Analysis
Tuason Co. uses job order cost accumulation and applies overhead based
on direct labor hours. Any underapplied or overapplied overhead is ad-
justed directly to Cost of Goods Sold at the end of each month. On April 1,
job cost sheets indicated the following:
Job 201
Job 202
Job 203
Job 204
Direct materials
Direct labor
Applied overhead
Total cost
P3,590
2,700
2,160
P2,000
1,500
1,200
P1,480
1,000
800
P2,000
1,200
960
P8,450
P4,700
P3,280
P4,160
Job status
Finished
In process
In process
In process
Cost Accounting- Basic Concepts and the Job Order Cost Cycle
79
Problem 1-19 continued
On April 30, finished goods contained only Jobs 204 and 207, which had the
following total costs.
Job 204
Job 207
Direct materials
P2,970
P2,450
1,900
1,520
Direct labor
Applied overhead
2,200
1,760
Total cost
P6,930
P5,870
Besides working on Jobs 204 and 207 in April, Tuason continued work on Jobs
202 and 203 and started work on Jobs 205 and 206. A summary of direct mate-
rials used and direct labor hours worked on Jobs 202, 203, 205, and 206 during
April showed the following:
Job 202
Job 203
Job 205
Job 206
Direct materials
Direct labor hours
P1,250
P555
75
P2,500
105
P1,980
50
100
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Entries for Materials GenX Furnishings manufactures designer furniture. GenX Furnishings uses a job order cost system. Balances on June 1 from the materials ledger are as follows: Fabric Polyester filling Lumber Glue The materials purchased during June are summarized from the receiving reports as follows: Fabric Polyester filling Lumber Glue Job 601 $40,500 28,600 62,400 6,550 Materials were requisitioned to individual jobs as follows: Job 602 Job 603 $440,000 180,000 360,000 40,000 Fabric $205,000 110,000 130,000 Polyester Filling Lumber $75,000 $120,000 36,000 88,000 55,000 125,000 Glue Total $400,000 234,000 310,000arrow_forward5.Balmond Manufacturing Company uses the FIFO method of accounting for Raw Materials. Determine the amount charged to work in process for the quarter using the following information * 6.What is the balance of the Raw Materials accounts at the end of the quarter? *arrow_forwardNo need generalized okarrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardDo not give image formatarrow_forwardCH Marco Company shows the following costs for three jobs worked on in April Balances on March 31 birect materials used (in March) Direct labor used (in March) Overhead applied (March) Costs during April Direct materials used Direct Labor used Overhead applied Status on April 30 Additional Information Job 305 Problem 2-2A (Algo) Part 4 $ 37,880 28.000 18.880 155 800 93,000 A (sold) 306 387 $ 48,000 4 Fontshed Job 388 1 128.000 125,000 a. Raw Materials Inventory has a March 31 balance of $88,000. b. Raw materials purchases in April are $520.000, and total factory payroll cost in April is $333,000. c. Actual overhead costs incurred in April are indirect materials, $55.000; indirect labor, $28,000; factory factory utilities, $24.000, and factory equipment depreciation, $56.000. d. Predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct lacor cost. e. Job 306 is sold for $655,000 cash in April. In process 4. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month ended April 30.arrow_forward
- Exercise 3-5 (Algo) Journal Entries and T-accounts [LO3-1, LO3-2] The Polaris Company uses a job-order costing system. The following transactions occurred in October: a. Raw materials purchased on account, $210,000. b. Raw materials used in production, $189.000 ($151,200 direct materials and $37,800 Indirect materials). C. Accrued direct labor cost of $50,000 and Indirect labor cost of $21,000. d. Depreciation recorded on factory equipment, $106,000. e. Other manufacturing overhead costs accrued during October, $129,000. f. The company applies manufacturing overhead cost to production using a predetermined rate of $8 per machine-hour. A total of 76,000 machine-hours were used in October. g. Jobs costing $512,000 were completed and transferred to Finished Goods. h. Jobs costing $448,000 were shipped to customers. These jobs were sold on account at 28% above cost. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions given above. 2. Prepare T-accounts for Manufacturing Overhead…arrow_forwardFully complete both requirement sarrow_forwardCan you please check my workarrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Watercraft's predetermined overhead rate is 200% of direct labor. Information on the company's production activities during May follows. a. Purchased raw materials on credit, $220,000. b. Materials requisitions record use of the following materials for the month. Job 136 Job 137 Job 138 Job 139 Job 140 Total direct materials Indirect materials $ 49,500 34,000 20,000 22,800 6,400 132,700 20,500 Total materials requisitions $ 153,200 c. Time tickets record use of the following labor for the month. These wages were paid in cash. Job 136 Job 137 $ 12,100 Job 138 Job 139 Job 140 Total direct labor Indirect labor Total labor cost 10,700 37,900 39,000 4,000 103,700 26,500 $ 130,200 d. Applied overhead to Jobs 136, 138, and 139. e. Transferred Jobs 136, 138, and 139 to Finished Goods Inventory. f. Sold Jobs 136 and 138 on credit at a total price of $540,000. g. Recorded the cost of goods sold for Jobs…arrow_forwardTorio.cam/secured#lockdown Manufacturing overhead was estimated to be $489,600 for the year along with 20,400 direct lebor hours. Actual manufacturing overhead was $470,220, and actual labor hours were 21,800. The predetermined manufacturing overhead rate per direct labor hour would be nabled: Exam 1(Ch 1-4)0 Multiple Choice $0.07. $23.05 $24.00. $22.75arrow_forwardTB MC Qu. 15-121 (Algo) Oxford Company uses a job order... Oxford Company uses a job order costing system. In the last month, the system accumulated labor time tickets totaling $25,500 for direct labor and $5,200 for indirect labor. The journal entry to record indirect labor consists of a: Multiple Choice Debit Factory Overhead $5,200; credit Factory Wages Payable $5,200. Debit Factory Overhead $5,200; credit Work in Process Inventory $5,200. Debit Work in Process Inventory $5,200; credit Factory Wages Payable $5,200. Debit Work in Process Inventory $25,500; credit Factory Wages Payable $25,500. Debit Factory Wages Payable $5,200; credit Cash $5,200.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education