
Concept explainers
Drow and explainthe use of vr data for calculating the final temperature during an isentropic process
The use of Vr data for calculating the final temperature during an isentropic process can be easily explained by taking an example.
Now let us take an example of Isentropic compression of Air in a car engine.
In this example consider air is compressed in a car engine from T1 K and P1 KPa in a reversible and adiabatic manner. If the compression ratio of this engine is V1/V2, determine the final temperature (T2)
Here in the above example, the process is easily recognized as being isentropic since it is both reversible and adiabatic.
Now with the help of relative specific volume data (Vr) from the relative specific volume table, we can calculate the final temperature as:
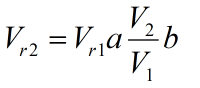
Where a and b are the constants determined from boundary conditions, Vr1 is the relative specific volume at point 1 and Vr2 is the relative specific volume at point 2.
Now corresponding to temperature T1 we can find the value of Vr1 from a relative specific volume table and then putting the values in the above equation for finding Vr2.
Now corresponding to Vr2 from a relative specific volume table we can determine the final temperature T2.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

- Derive a control volume form of the second law of thermodynamics.Suggest some practical uses for your relation inanalyzing real fl uid fl ows.arrow_forwardSolve it using the chat and show how you get the answers from the chatarrow_forward3-56. One particular zone served by a multizone air handler has a design cooling load of 1750 Btu/hr (0.5 kW) with a SHF of 0.8. The coil has air entering at 84 F (29 C) db and 70 F (21 C) wb with air leaving at 50 F (10 C) db and 90% relative humidity (RH). Zone conditions are 75 F (24 C) db and 50% RH. (a) What amount of air must be supplied to the space? (b) At what condition is the air supplied to the space? (c) How much air flows over the coil and how much er the coll air bypasses the coil for this one zone? Assume sea-level pressure.arrow_forward
- Please show steps how you come up with rate of heat transferarrow_forwardI need help with this. Thermodynamicsarrow_forward36 -S 42 2. Metal castings can sometimes develop a gap between the casting and mold as the molten metal hardens. The result can be a substantially altered cooling process. Set up a simple heat-transfer model that would let you look at the effect of the gap on the cooling process. Assume the casting and mold are square in shape, with an air gap of thickness das shown in the figure. The mold sits in some ambient room temperature. State clearly all assumptions and develop a corresponding model of the heat transfer problem. Assuming that the casting is aluminum, the mold is diatomaceous earth and the gap is filled with air, see if you can arrive at and summarize some insight into the effect of the gap and its size on the heat transfer process.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





