
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
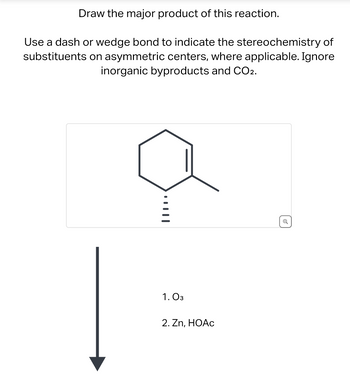
Transcribed Image Text:**Chemical Reaction: Ozonolysis of a Cyclohexene Derivative**
**Reaction Description:**
1. **Objective:** Draw the major product of the reaction.
2. **Instructions:** Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Inorganic byproducts and CO₂ should be ignored.
**Reactant:**
- A cyclohexene ring with a methyl group and a substituent on the same carbon. The substituent is represented with a dashed bond, indicating its position below the plane.
**Reaction Conditions:**
1. First step: Ozone (\(O_3\))
2. Second step: Zinc (\(Zn\)) and Acetic Acid (\(HOAc\))
**Reaction Process:**
- This reaction involves the ozonolysis of the cyclohexene ring. Ozonolysis is a process that cleaves carbon-carbon double bonds using ozone, leading to the formation of carbonyl compounds.
**Expected Outcome:**
- The double bond in the cyclohexene is cleaved.
- The carbon atoms involved in the double bond will likely form carbonyl groups, resulting in ketone or aldehyde functionalities.
- The stereochemistry of the remaining substituents (indicated by dash or wedge bonds) should be considered for the final product structure.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- There is an arrow indicating the sequence from reactant to product following the given steps of ozonolysis and reduction using zinc and acetic acid.
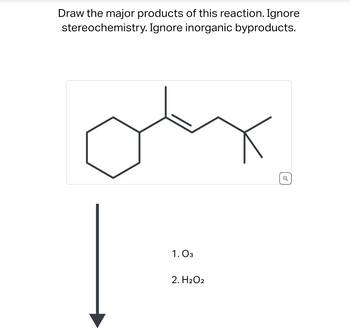
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Ozonolysis Reaction of Cyclohexene Derivative**
**Objective:**
Draw the major products of this reaction. Ignore stereochemistry and inorganic byproducts.
**Reaction Details:**
The starting compound is a cyclohexene derivative featuring an alkene with the following structure:
- Hexagonal cyclohexane ring on the left.
- A branching alkene (double bond) connected to the cyclohexane ring.
- Two alkyl groups branching from the alkene.
**Reagents:**
1. **Ozone (O₃)**
2. **Hydrogen Peroxide (H₂O₂)**
**Reaction Pathway:**
1. **Ozonolysis Step:**
- The alkene undergoes ozonolysis, where ozone cleaves the double bond, forming primary ozonides, which rearrange into more stable ozonides.
2. **Hydrolysis Step:**
- In the presence of hydrogen peroxide, oxidative workup occurs. The ozonides break down to form carboxylic acids instead of aldehydes due to the oxidizing conditions provided by H₂O₂.
**Product Outcome:**
- The alkene double bond is cleaved, leading to the formation of two carboxylic acid groups replacing the carbon atoms originally comprising the double bond.
**Conclusion:**
This process provides a valuable method for transforming alkenes into carboxylic acids, with applications in synthetic organic chemistry for structural elucidation and molecular modifications.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the product(s) of the following reactions. HOCH₂-CEC-(CH₂)7-C . OCH3 H₂ Lindlar catalyst • Consider E/Z stereochemistry of alkenes. • If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardDraw structural formulas for the major organic product of the reagents shown. CH3 • CH3 **YEL + HNO3 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. Apply formal charges to any nitro groups. . If there is more than one major product possible, draw all of them. ● Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menus H₂SO4arrow_forward
- Draw the structural formula for the product formed upon hydroboration/oxidation of the Alkene below.arrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] An alkene having the molecular formula C6H10 is treated sequentially with ozone (03) and zinc/acetic acid to give the product/s shown. CH3CCH,CH,CH2CH Draw a structural formula for the alkene. • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. P. aste Ado ChemDoodle Previous Nextarrow_forwarda-pinene When a-pinene reacts with 1. BH3; 2. H₂O2, NaOH, H₂O 4 possible cis,trans isomers can be formed, but one of these is formed more readily than the others. Draw the structure of this preferred isomer. • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • To aid you in your drawing, the structure of a-pinene is provided for you in the drawing palette.arrow_forward
- 1) RCO H 2) [H₂SOJ. ? Modify the given structure to draw the major product(s). Use the single bond tool to interconvert between double and single bonds. If a racemic mixture of enantiomers is expected, draw both enantiomers. Note: you can select a structure and use Copy and Paste to save drawing time. H₂C. OH th CH, CH₂ OH H₂C OH aff CH₂ CH₂ Edit Drawingarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the substitution product of the reaction shown below. H3C CI CH3OH • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • If more than one stereoisomer of product is formed, draw both. • Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu.arrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. Draw the structure of the organic product of the following dehydration reaction. If more than one product is possible, draw the structure of the major product. tosH heat CH • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. P. opy aste [片 CH4 Previous Ne ChemDoodle" Saarrow_forward
- Draw the predominant product(s) of the following reactions including stereochemistry when it is appropriate. 2 HBr CH3-CEC-CH3 + • Consider E/Z stereochemistry of alkenes. • Do not show stereochemistry in other cases. If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu. WP ***** ? ChemDoodleⓇ n [F < 56arrow_forwardf) 5. Write the organic product(s) of the following substitution reactions. Indicate cis or trans, axial or equatorial, or R or S or racemic, where appropriate. If there is no reaction write NR. a) d) Br b) Ph (R) Br Hill (S) (S) (R) F Br (S) Br CI esbun to nois Br Br excess NaN, DMSO solvent NaN 3 DMSO solvent KCN DMSO solvent (S) NaO Ac DMSO solvent excess KCN DMSO solvent as ant olght way new soigh oblid yashhodsa s to nol SM2 du 5071 631 2031 203uborg sbiler yabancone lears a to nobosen Z KCN DMSO solvent ancifoser: the galwollet sit to (e)bubong sing bannot as stogbong to autxime adw erabatesharrow_forwardCH3 CH₂CH₂C CHCH3 *%8 [.. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • If there is more than one major product possible, draw all of them. • Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu. H₂O ·OO ? Ⓡ ChemDoodle H₂SO4 ? [F <arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY