
Understanding Business
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259929434
Author: William Nickels
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
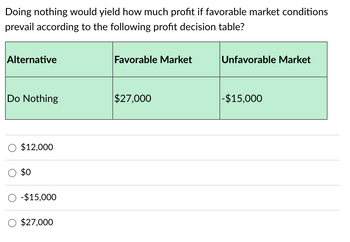
Transcribed Image Text:Doing nothing would yield how much profit if favorable market conditions
prevail according to the following profit decision table?
Alternative
Favorable Market
Do Nothing
$27,000
$12,000
$0
-$15,000
$27,000
Unfavorable Market
-$15,000
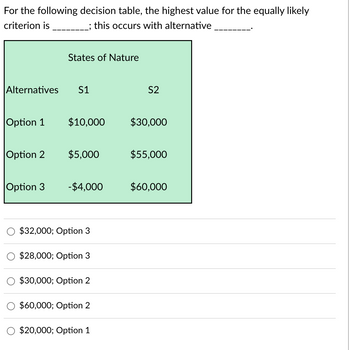
Transcribed Image Text:For the following decision table, the highest value for the equally likely
criterion is __________; this occurs with alternative
States of Nature
Alternatives
S1
S2
Option 1
$10,000
$30,000
Option 2 $5,000
$55,000
Option 3
-$4,000
$60,000
$32,000; Option 3
$28,000; Option 3
$30,000; Option 2
$60,000; Option 2
$20,000; Option 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A2arrow_forwardFind the approximate z-value to a cumulative probability of 0.99 using interpolation. 4 decimal places pleasearrow_forwardConstruct a decision tree for this problem. What is the recommended decision if the agency opinion is not used? What is the expected value? What is the expected value of perfect information? What is Hale’s optimal decision strategy assuming the agency’s information is used? What is the expected value of the agency’s information? Is the agency’s information worth the $5000 fee? What is the maximum that Hale should be willing to pay for the information? What is the recommended decision?arrow_forward
- The XYZ manufacturing company is considering replacing one of its metal cutting machine which can be sold today for $3,000. If they kept this machine for 4 more years, its salvage value will be zero. The challenger costs $18,000, and its life is 4 years. The estimated salvage value of the challenger at the end of four years is $6,000. Should the XYZ company replace the old machine? Use the opportunity cost approach with rate of return of 10%. Assume operating costs per year for defender equals $2,000 and a saving in operating costs per year of 75% for challenger.arrow_forwardA manufacturing company must decide whether to manufacture a component part at its Milan, Michigan, plant or purchase the component part from a supplier. The resulting profit is dependent upon the demand for the product. The following payoff table shows the projected profit (in thousands of dollars). State of Nature Decision Low Alternative Demand $1 Medium Demand $2 High Demand 53 Manufacture, d -5 55 115 Purchase, d₂ 60 85 The state-of-nature probabilities are P(s₁) = 0.35, P(52) = 0.35, and P(53) = 0.30. (a) Use a decision tree to recommend a decision. The best decision is to purchase the component part. (b) Use EVPI to determine whether the company should attempt to obtain a better estimate of demand, assuming the estimate would come at no further cost. EVPI = 9 The EVPI suggests that the company should consider an attempt to obtain a better estimate of demand. (c) A test market study of the potential demand for the product is expected to report either a favorable (F) or…arrow_forwardHow is EMV calculated for these steps. What is the probability and impact in these questions. 1) Should you play at all? (5%) If you play, what is your expected (net) monetary value? (15%)2) If you play and don't win at all on the first try (but don't lose money), should you try again? (5%) Why? (10%)3) Clearly show the decision tree (40%) and expected net monetary value at each node (25%) If you send in your entry before midnight tonight, then here are your chances: 0.1% that you win $1,000,000 75% that you win nothing Otherwise, you must PAY $1,000 But wait, there's more! If you don't win the million AND you don't have to pay on your first attempt, then you can choose to play one more time. If you choose to play again, then here are your chances: 2% that you win $100,000 20% that you win $500 Otherwise, you must PAY $2,000arrow_forward
- DECISION THEORY. A man has to decide wheter to resign or not from his present position and apply for a job offering him 2x his present salary, that is if he passes the qualifying test. At present, he receives $3000 monthly compensation. The offer from another company has a condition that he will not be allowed to take the qualifying test, he will immediately be taken in and have a monthly pay of $6000. If he fails, he will remain jobless, he feels that his chance of passing the test is 35%. Suppose he decides to base his decision on expected value, should he resign from his post or not?arrow_forwardConstruct decision tablearrow_forwardExhibit 20-2Below is a payoff table involving three states of nature and two decision alternatives. Decision States of Nature Alternative s1 s2 s3 A 80 45 –20 B 40 50 15 P(s1) = .1, P(s2) = .6, and P(s3) = .3.Refer to Exhibit 20-2. The expected value of the best alternative equals _____. a. 12 b. 38.5 c. 29 d. 105arrow_forward
- A well-known plastic mould and die manufacturer in Toronto intends to expand internationally in anticipation of strong demand and expansion in the plastic die manufacturing sector. use the table beneath. Using the Maximax, Maximin, and equally likely conditions, assist the business in making the best option in an unclear situation. 0.5 for a highly favourable condition, 0.2 for an average demand, and 0.3 for an unfavourable state are the probabilities linked with the states of nature.a) Choose the course of action that will give Andrew the highest predicted monetary value (EMV).b) Determine the anticipated value of perfect information (EVPI).arrow_forwardAn oil company must decide whether or not to drill an oil well in a particular area that they already own. The decision maker (DM) believes that the area could be dry, reasonably good or a bonanza. See data in the table which shows the gross revenues for the oil well that is found. Decision Drill $0 Abandon $0 Probability 0.3 Dry (D) Seismic Results No structure(N) Open(0) Closed (C) Drilling costs 40M. The company can take a series of seismic soundings (at a cost of 12M) to determine the underlying geological structure. The results will be either "no structure", "open structure or "closed structure". The reliability of the testing company is as follows that is, this reflects their historical performance. Reasonably good(G) $85 $0 0.3 Note that if the test result is "no structure" the company can sell the land to a developer for 50 m. otherwise (for the other results) it can abandon the drilling idea at no benefit to itself. Dry(d) 0.7 0.2 Bonanza(B) 0.1 $200 m SO 0.4 Conditional…arrow_forwardQWE Inn has recorded the following number of rooms sold for the first quarter of the year: January 2100 February 2500 March 2550 What is the 3-month moving average forecast of rooms sold equal to for the month April?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Understanding BusinessManagementISBN:9781259929434Author:William NickelsPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Understanding BusinessManagementISBN:9781259929434Author:William NickelsPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Management (14th Edition)ManagementISBN:9780134527604Author:Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. CoulterPublisher:PEARSON
Management (14th Edition)ManagementISBN:9780134527604Author:Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. CoulterPublisher:PEARSON Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Pract...ManagementISBN:9781305947412Author:Cliff RagsdalePublisher:Cengage Learning
Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Pract...ManagementISBN:9781305947412Author:Cliff RagsdalePublisher:Cengage Learning Management Information Systems: Managing The Digi...ManagementISBN:9780135191798Author:Kenneth C. Laudon, Jane P. LaudonPublisher:PEARSON
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digi...ManagementISBN:9780135191798Author:Kenneth C. Laudon, Jane P. LaudonPublisher:PEARSON Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in...ManagementISBN:9780134728391Author:Ronald J. Ebert, Ricky W. GriffinPublisher:PEARSON
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in...ManagementISBN:9780134728391Author:Ronald J. Ebert, Ricky W. GriffinPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)ManagementISBN:9780134237473Author:Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter, David A. De CenzoPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)ManagementISBN:9780134237473Author:Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter, David A. De CenzoPublisher:PEARSON

Understanding Business
Management
ISBN:9781259929434
Author:William Nickels
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Management (14th Edition)
Management
ISBN:9780134527604
Author:Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter
Publisher:PEARSON

Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Pract...
Management
ISBN:9781305947412
Author:Cliff Ragsdale
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Management Information Systems: Managing The Digi...
Management
ISBN:9780135191798
Author:Kenneth C. Laudon, Jane P. Laudon
Publisher:PEARSON

Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in...
Management
ISBN:9780134728391
Author:Ronald J. Ebert, Ricky W. Griffin
Publisher:PEARSON

Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Management
ISBN:9780134237473
Author:Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter, David A. De Cenzo
Publisher:PEARSON