
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Does height have an effect on the average velocity of a dropped object?
Given the chart can you make a conclusion- I filled out the last column it was originally blank
(when I did this I found average velocity to be inversely proportional because the average velocity slightly decreased as height increased) is this correct? I'm having trouble
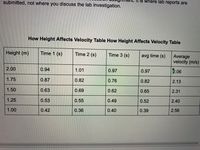
Transcribed Image Text:**How Height Affects Velocity Table**
This table demonstrates the effect of drop height on velocity. It consists of the following columns:
1. **Height (m)**: The height from which the object is dropped, measured in meters.
2. **Time 1 (s)**, **Time 2 (s)**, **Time 3 (s)**: Three recorded times in seconds, representing how long it takes for the object to reach the ground from the specified heights.
3. **Avg Time (s)**: The average of the three recorded times for each height.
4. **Average Velocity (m/s)**: The calculated average velocity in meters per second.
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Height (m)</th>
<th>Time 1 (s)</th>
<th>Time 2 (s)</th>
<th>Time 3 (s)</th>
<th>Avg Time (s)</th>
<th>Average Velocity (m/s)</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>2.00</td>
<td>0.94</td>
<td>1.01</td>
<td>0.97</td>
<td>0.97</td>
<td>2.06</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1.75</td>
<td>0.87</td>
<td>0.82</td>
<td>0.76</td>
<td>0.82</td>
<td>2.13</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1.50</td>
<td>0.63</td>
<td>0.69</td>
<td>0.62</td>
<td>0.65</td>
<td>2.31</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1.25</td>
<td>0.53</td>
<td>0.55</td>
<td>0.49</td>
<td>0.52</td>
<td>2.40</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1.00</td>
<td>0.42</td>
<td>0.36</td>
<td>0.40</td>
<td>0.39</td>
<td>2.56</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
**Analysis**: As the height decreases, the average time taken for the object to fall decreases, leading to an
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A disoriented physics professor drives 3.25 km north, then 2.20 km west, and then 1.50 km south. Find the magnitude and direc tion of the resultant displacement, using the method of components. In a vector-addition diagram (roughly to scale), show that the resultant dis placement found from your diagram is in qualitative agreement with the result you obtained by using the method of components.arrow_forward) An object follows as shown below. What is the displacement from the last point to the starting point? Express your answer (a) in unit vector notation, and (b) as a magnitude and direction.arrow_forwardAn object is initially located at 7, = (1, 9) m. After a single displacement the object is located at 7, = (-3, 5) m. a) Draw a picture b) Find the displacement of the object. c) How far did the object travel? (A: V32 m)arrow_forward
- The a- s graph for a boat moving along a straight path is given. (Figure 1) 1 of 1 Figure a (ft/s²) 5 a = 5 + 6(√5-10)5/3 100 s (ft) If the boat starts at s = 0 when v = 0, determine its speed when it is at s = 64 ft. Express your answer using three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA ? V = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Use a numerical method to determine its speed at s = 136 ft. Express your answer using three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? V = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardPlease help me answer number 5 with complete solutionarrow_forwardA driver takes a wrong turn at an intersection and travels 2.6 km north, then 8.7 km east and finally 7.5 km south. What is his displacement from the intersection? Enter your answers without units, correct to three significant digits. (a) The magnitude of the displacement is: This question accepts numbers or formulas. Help | Switch to Equation Editor | Preview (b) The direction of the displacement is: Enter your answer in standard position as an angle in degrees such that 0º < 0< 360°arrow_forward
- Calculating Displacement- 1. A woman walking her dog travels 200 m north, then 400 m west, then 500 m south. (a). What was the total distance she travelled? (b) What was the magnitude of her displacement for the entire trip?arrow_forwardanswer c and d pleasearrow_forwardI really need help in figuring out which equation I need to be using for the slope. Please help!arrow_forward
- A student stands at the edge of a cliff and throws a stone horizontally over the edge with a speed of vo = 20.5 m/s. The cliff is h = 26.0 m above a flat, horizontal beach as shown in the figure.arrow_forwardProblem 1: An object is launched off the top of a 45-m tall building with velocity of 70.9 m/s in the horizontal direction (no angle with respect to the horizontal). Pai. (a) In the space below, explain how you would find the time that the object is in the air. (Type the equation(s) you would use and the variable(s) you would solve for. Describe any other important steps. Do not show calculations or the numeric answer.)arrow_forwardA vector has a horizontal component of -21 and vertical component of 46, what is the magnitude of this vector? Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON