
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
do 8.15!
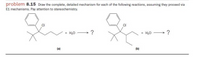
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 8.15:**
Draw the complete, detailed mechanism for each of the following reactions, assuming they proceed via E1 mechanisms. Pay attention to stereochemistry.
**Reaction (a):**
- Reactants: A chlorinated alkane with a phenyl group and water (H₂O).
- Process: An arrow indicates a reaction, producing an unspecified product.
**Reaction (b):**
- Reactants: Another chlorinated alkane with a phenyl group and water (H₂O).
- Process: An arrow indicates a reaction, producing an unspecified product.
Both reactions request the detailed mechanistic steps following the E1 (unimolecular elimination) mechanism, which involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate, followed by deprotonation to form a double bond. Stereochemistry should also be considered in the mechanism.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. What is the formal charge on N in this ion? (Show your work) :0: || 2. Consider the molecule below. Determine the atomic geometry at each of the 2 labeled| carbons. H „CH3 H 3. Draw the best Lewis structure for ICI.. 4. Thionyl chloride is used as an oxidizing and chlorinating agent in organic chemistry. Draw the best Lewis structure for SOCI. 5. Draw a Lewis structure for XeOs in which all formal charges are zero. 6. If a 500mL solution of 5.34M Potassium nitrate, KNO:, is to be prepared, how many grams must be weighed out? (show your work) (MW 101.1 g/mole) 7. Progesterone is a sex hormone that is comprised of 80.21% C, 9.62% H, and 10.18% O. Determine the empirical formula of progesterone 8. Why is H-C=N: a better representation than H-N=C: for hydrogen cyanide?arrow_forwardH H TI H (1) H C H H H (3) H C H H The ideal value for bond angle (1) is (Choose one) ▼ and the ideal value for bond angle (3) is (Choose one) degrees, the value for bond angle (2) is (Choose one) degrees. degrees,arrow_forwardConsider the following Lewis structure. Note, all valence electrons are shown. a. Assign formal charges to any atoms that that have a formal charge.b. Draw another Lewis structure that is a more important contributor to the actual structure than the one shown. c. Listed to the right are some typical C-N bond lengths. From the choices below, circle the best estimate for the carbon-nitrogen bond in the actual structure above. (a)1.46 A (b) 1.43 A (c) 1.26 A (d) 1.36 A (e) 1.12 Aarrow_forward
- What is the formal charge on the carbon atom in methane, CH4? Report your answer as a whole number without any decimal places. Provide your answer below:arrow_forwardIs there anything wrong with this Lewis Structure of ICI4" ? If no, explain why not. If yes, explain why it is wrong and how to fix it. Edit View Insert Format Tools Table 12pt v Paragraph BIU esc * 23 % @ 2 3 4arrow_forwardElectron-Dot Formulas and Shapearrow_forward
- Can someone please help me with number 28? It’s driving me nuts?arrow_forwardQuestion 2 (1 point) (Q94) During the process of bond formation, what happens when the nuclei of two atoms come closer than the optimal bond distance? A) The two nuclei fuse B) The energy of the system increases dramatically and the system become unstable C) The energy of the system decreases dramatically and the system becomes unstable O D) A photon is released from the system E) The system becomes hyper-stable, resulting in an energy value approaching zeroarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY