
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Describe in words and illustrate by means of complete chemical equations, how a mixture of 1.25 g of benzoic acid tert-butylbenzene can be separated. Apply what you learned in organic 1, reviewing in your manual the experiment of separation of 2 components by liquid-liquid extraction.
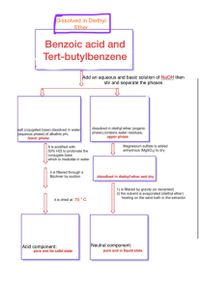
Transcribed Image Text:Dissolved in Diethyl
Ether
Benzoic acid and
Tert-butylbenzene
Add an aqueous and basic solution of NaOH then
stir and separate the phases
salt (cojugated base) dissolved in water
Kaqueous phase) of alkaline pH.
lower phase
dissolved in diethyl ether (organic
phase).contains water residues.
upper phase
It is acidified with
50% HCI to protonate the
conjugate base
which is insoluble in water
Magnesium sulfate is added
anhydrous (M9SO,) to dry
it is filtered through a
Büchner by suction
dissolved in diethyl ether and dry
1) is filtered by gravity (or decanted)
2) the solvent is evaporated (diethyl ether)
heating on the sand bath in the extractor
it is dried at 70 * C
Acid component:
Neutral component:
pure and in liquid state
pure and its solid state
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give detailed Solutionarrow_forwardIs 1-octadecene and/or heptane soluble in benzene? Why?arrow_forwardGiven the following statements, which would be the ideal solvent to use for recrystallization of this compound? Why? Compound X is soluble in both cold ethyl acetate and hot ethyl acetate. Compound X is insoluble in cold benzene but soluble in hot benzene. Compound X is insoluble in both cold hexanes and hot hexanes. Compound X is insoluble in cold ethanol but soluble in hot ethanol.arrow_forward
- After purification via extraction, any organic substance should be rigorously dried; otherwise, its further purification via recrystallization will often fail to achieve the desired result. In a typical purification of an organic unknown, a solution of crude product in an organic solvent (i.e. diethyl ether) is what will remain following extraction. Suggest a simple means to remove small quantities of water from this solution.arrow_forwardassuming that charcoal and sugar are the main impurities in a sample of crude acetanilide explain how recrystallization from water would remove each.arrow_forwardBalance the following sodium borohydride reduction equations showing the structures for the following organic compounds: a.) benzil to benzoin; and b.) benzil to hydrobenzoin. Calculate the theoretical amount of NaBH, needed to convert 100 mg of a.) benzil to benzoin; and b.) benzil to hydrobenzoin.arrow_forward
- .What volume of 1.37 M nitric acid is needed to convert 9.0 g of m-bromophenol to 3-bromo-4,6-dinitrophenol? (No excess of nitric acid is used.) Specify the units on the volume.arrow_forwarda) To a solution of 10 g (60 mmol) of 3-nitrophenylacetic acid in 120 ml of ethanol were added 20 ml of a saturated 5 solution of hydrogen chloride in ethyl acetate and the mixture was heated at reflux for 4 hours, cooled and left to stand at room temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was evaporated and the residue was partitioned between 120 ml of diethyl ether and 100 ml of saturated aqueous sodium 10 bicarbonate solution. The organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and evaporated to give 10.3 g. (82%) of ethyl 3-nitrophenylacetate as a pale yellow oil. [NMR spectrum (250 MHz) 81.25(t) (3H), 83.68(s) (2H), 84.6(q) (2H), 86.5-86.7(m) (3H), 87.09(dd) (1H)].arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY