
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
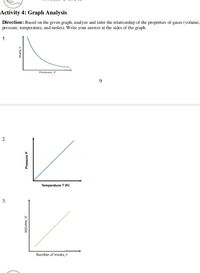
Transcribed Image Text:Activity 4: Graph Analysis
Direction: Based on the given graph, analyze and infer the relationship of the properties of gases (volume,
pressure, temperature, and moles). Write your answer at the sides of the graph.
1.
Pressure, P
9.
Temperature T (K)
3.
Number of moles, n
2.
Pressure P
Volume,'
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A flexible container at an initial volume of 8.15 L contains 8.51 mol of gas. More gas is then added to the container until it reaches a final volume of 18.7 L. Assuming the pressure and temperature of the gas remain constant, calculate the number of moles of gas added to the container. number of moles of gas: molarrow_forwardA sample of an ideal gas with an initial volume of 18.0 L at a pressure of 679 mm Hg is compressed until the volume is 3.4 L with no change of temperature. What is the final pressure (mm Hg) of the gas?arrow_forward16. A gas with a pressure of 25.0 psi and a temperature of 18°C is heated to 24°C. What is the new pressure of this gas?arrow_forward
- A sample of an ideal gas initially has a pressure of 0.775 atm at a temperature of 21.5°C. If the temperature of the gas increases to 97.5°C while volume is kept constant, what is the new pressure of the gas?arrow_forwardA mixture of neon and krypton gases is maintained in a 9.84 L flask at a temperature of 90°C. If the partial pressure of neon is 0.462 atm and the partial pressure of krypton is 0.401 atm, what is the total pressure in the flask? atmarrow_forwardA flexible container at an initial volume of 7.14 L contains 9.51 mol of gas. More gas is then added to the container until it reaches a final volume of 12.1 L. Assuming the pressure and temperature of the gas remain constant, calculate the number of moles of gas added to the container. number of moles of gas: molarrow_forward
- A 5.00-mol sample of oxygen gas is confined to a pressure of 5 atm at a temperature of 27 degrees Celsius. What must be the volume of the vessel containing these oxygen gas molecules? (*Solution required) a. 2494.2 m³ b. 0.02 m³ c. 12.47 x 10³ m³ d. 0.12 m³arrow_forwardgas mixture consists of H2, SO2, and N2. The partial pressures of each gas are: H2 = 0.15 atm, SO2 = 1.50 atm, N2= 3.30 atm. The pressure of the mixture is: a) 4.95 atm b) 11.4 atm c) 1 atm d) 10 atmarrow_forward4. A glass container was initially charged with 2.00 moles of a gas sample at 3.75 atm and 21.7 °C. Some of the gas was released as the temperature was increased to 28.1 °C, so the final pressure in the container was reduced to 0.998 atm. Assume the volume stayed the same. How many moles of the gas sample are present at the end?arrow_forward
- 2) Which one of the following statements about gases is FALSE? a) The volume and temperature of a gas are directly proportional. b) The partial pressure of gas A is equal to the total pressure multiplied by the mole fraction of gas A. c) The total pressure in a vessel is the sum of the partial pressures of all gases in the vessel. d) The volume and pressure of a gas are directly proportional.arrow_forwardName 4 factors that affect the properties of gasesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY