
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
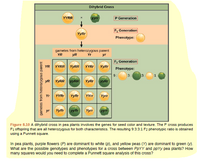
Figure 8.10 In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white (p), and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green (y). What are the possible genotypes and
Transcribed Image Text:Dihybrid Cross
YYRR
yyrr
P Generation
F, Generation
YyRr
Phenotype:
gametes from heterozygous parent
yR
YR
Yr
yr
F2 Generation
YR
YYRR
YYRR
YYRI
YyRr
Phenotype:
9:
3:
3:
yR
YYRR yyRR
YyRr
yyRr
Yr
YYRI
YyRr
YYrr
Yyrr
yr
YyRr
yyRr
Yyrr
yyrr
Figure 8.10 A dihybrid cross in pea plants involves the genes for seed color and texture. The P cross produces
F1 offspring that are all heterozygous for both characteristics. The resulting 9:3:3:1 F2 phenotypic ratio is obtained
using a Punnett square.
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white (p), and yellow peas () are dominant to green (V).
What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PPYY and ppYy pea plants? How
many squares would you need to complete a Punnett square analysis of this cross?
gametes from heterozygous parent
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In roan cattle, red (R) and white (W) are codominant. Heterozygous individuals produce both red and white hairs, known as roan. When two roan cattle are crossed, what are the phenotypic ratios of the offspring?arrow_forwardTwo true-breeding varieties of maize, one 11 cm high and the other 47 cm high were crossed and the resultant F1 hybrids were then crossed to generate the F2 . In the F2 there were a total of 13,923 plants with a continuous variation in heights between the two extremes and with only 3 plants as large as 47 cm high and 5 plants of 11 cm high.SO In a cross between a 29cm plant and a 20cm plant what would be the genotypes giving the smallest number of different phenotypes? specify the phenotypes observed.arrow_forwardIn tomatoes, regular leaves (L) are multilobed and serrated and potato leaves (l) are broad, smooth, and single (Image 1). Red fruit (F) is dominant to yellow fruit (f). A cross is carried out between two pure lines of tomato plants, one having regular leaves and red fruit and the other having potato leaves and yellow fruit. The F1 generation all have regular leaves and red fruit. The F1individuals are then crossed with one another. Complete a Punnett square to determine the expected F2 progeny on the basis of Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment, which states that the alleles for one gene segregate independently of the alleles for other genes during gamete formation. The information below represents two sets of data collected from the above cross. Phenotypes Data Set 1 Data Set 2 Regular Red 26 846 Regular Yellow 15 273 Potato Red 6 287 Potato Yellow 12 94 Total 59 1 500 Convert the expected phenotype ratio into the expected probability for each of the four…arrow_forward
- The trait for medium-sized leaves in iris is determined by the genetic condition PP'. Plants with large leaves are PP, whereas plants with small leaves are P'P'. The trait for red flowers is controlled by the genes RR, pink by RR', and white by R'R'. A cross is made between two plants each with medium-sized leaves and pink flowers. If they produce 640 seedlings, what would be the expected phenotypes, and in what numbers would they be expected? View keyboard shortcuts EditViewInsertFormatToolsTable 12pt Paragrapharrow_forwardA) In these plants, green leaf color is dominant to yellow leaf color. You are given a plant with green leaves and are asked to determine its genotype. What type of cross will you perform? B) The results of this cross are: 50% green leaf plants and 50% yellow leaf plants. What is the genotype of the green leaf plant you were given?arrow_forwardIn pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white flowers (p) and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green peas (y). a) What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea plants? b) What is the minimum number of squares needed to do a Punnett square analysis of this cross?arrow_forward
- Mendel crossed two Pea plants for plant height and flower color Tall plant (T) is dominant to Short Plant (t). Purple Flower (P) is dominant to white flower (p). Using the following information perform the dihybrid cross using punnett squares that will predict all possible genotypes of the offspring and list the number and description of the phenotypes of the offspring. A. One plant homozygous dominant for plant height and flower color crossed with another plant homozygous recessive for plant height and heterozygous for flower color.arrow_forwardYou are handed a mystery pea plant with tall stems and axial flowers and asked to determine its genotype as quickly as possible. You know that the allele for tall stems (T) is dominant to that for dwarf stems (t) and that the allele for axial flowers (A) is dominant to that for terminal flowers (a). Identify all the possible genotypes for your mystery plant. Describe the one cross you would do in your garden to determine the exact genotype of your mystery plant. While waiting for the results of your cross, you predict the results for each possible genotype listed in part a. Explain how you do this and why this is not called “performing a cross.” Explain how the results of your cross and your predictions will help you learn the genotype of your mystery plant. Question is also in the picture.arrow_forwardAssume that plant height is determined by a pair of alleles at each of two loci (A and a, B and b) that are additive in their effects. Further assume that each allele represented by an uppercase letter contributes 6 feet to height and that each allele represented by a lowercase letter contributes 2 foot to height. If a plant with genotype Aabb is crossed to a plant with genotype aaBb, what heights are expected in the progeny? 1/216ft : 1/2 12ft 1/4 16ft : 1/2 12ft : 1/4 8ft 1/4 20ft : 1/2 16ft : 1/4 12ft 1/4 24ft : 1/2 20ft : 1/4 16ft 1/2 20ft : 1/2 16ftarrow_forward
- An individual with the genotype F/f • G/g • H/h is testcrossed. Among the progeny, the proportions of genotypes from this cross are shown in the following table: a) What gene is in the middle? Type you answer in this box: b) Calculate the genetic distances (in centimorgans, cM) between: genes g and f: genes f and h: genes g and h: c) What are the genotypes of the two parents? d) Calculate the interference and type your answer here:arrow_forwardIn a dihybrid cross of two bi-allelic Mendelian genes, A (two alleles – completely dominant A and recessive a), and B (two alleles – completely dominant B and recessive b), such that the parental generation comprises of pure-bred homozygotes (i.e. AABB with aabb), what are the expected genotype and phenotype ratios in the F1 and F2, if the F1 cross is (a) an intercross and if the F1 cross is (b) a testcrossarrow_forwardAssume that the length of a type of cucumber at maturity is controlled by two genes (A and B), each of which has two alleles. The A and B alleles each add 3 inches of cucumber growth, while the a and b alleles add only 1 inches. If a plant with genotype Aabb is crossed to a plant with genotype AaBb, what ratios of lengths are expected in the progeny? 1/8-12”, 3/8-10”, 3/8-8”, 1/8-6” 1/2-8”, 3/8-6”, 1/8 4” 1/8-10”, 3/8-8”, 3/8-6”, 1/8-4” 1/2-12”, 3/8-10”, 1/8 8” 1/2-10”, 3/8-8”, 1/8 6”arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education