
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
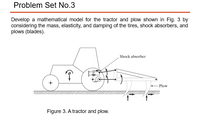
Transcribed Image Text:Problem Set No.3
Develop a mathematical model for the tractor and plow shown in Fig. 3 by
considering the mass, elasticity, and damping of the tires, shock absorbers, and
plows (blades).
Shock absorber
Plow
Figure 3. A tractor and plow.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the double slider mechanism shown in the following figure, the crank OA rotates at a uniform speed of 200 rad/s CCW. we need to find the required torque for the crank, if two forces act at sliders B and C as shown in the figure. (P = 2 kN, Q = 4 kN). OA = 20 cm, AB = AC = 80 cm. mg =10 kg, mc = 5 Kg. Neglect other links weights. (3) (2)45° (5) B (4) X The velocity of slip of slider B in m/s? = Choose... + The velocity of slip of slider C in m/s? = Choose... + The acceleration of slip of slider B in m/s2 = Choose... + The acceleration of slip of slider C in m/s? = Choose... + The magnitude of required torque for the crank in N.m = Choose... +arrow_forward!sub= solve question 3.6 onlyarrow_forwardFigure P3.40 illustrates a pendulum with a base that moves horizontally. Thisis a simple model of an overhead crane carrying a suspended load with cables.The load mass is m, the cable length is L, and the base acceleration is a(t).Assuming that the cable acts like a rigid rod, derive the equation of motion interms of ? with a(t) as the input.arrow_forward
- Please Take Care. Provide Handwritten Solution.arrow_forwardm2 Two masses connected by a massless string of length I slide without friction on two inclined planes as shown in the figure above. The motion is restricted to the x-y plane indicated in the figure. Gravity is acting in the negative y-direction. (a). Explain the term "virtual displacement". (b). State d'Alembert's principle of virtual work. (c). Write down d'Alemberts equation for this system in cartesian coordinates. Need detailed and step by step answer of all subparts with good handwriting Please I want to learnarrow_forward1) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object-m-368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 9 = 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel=h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object →R=0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u=0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: →V=Ro= 0.075 x 14.28 = 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsin0 = 0.368 × 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the questions below…arrow_forward
- Drop-load (I)This exercise is part of a series of problems aimed at modelling a situation by progressively refining our model to consider more and more parameters. This progressive approach is very close to what professional scientists do! Context We want to lower a suspended load in a controlled way so that it hits the ground with a speed whose modulus is not too great. To do this, the suspended load (B) is connected by a rope passing through a pulley to another mass (A), which can move on a horizontal surface. Information The masses of the charges A and B are known.The pulley is a ring of mass mp and radius R that can rotate without friction.The surface on which mass A is placed is horizontal.There is no friction between mass A and the surface on which it is placed.The string attached to mass A is perfectly parallel to the surface on which the mass rests. SchematizationDraw a diagram of each object that interests us. Draw x- and y-axes for each object. Draw and name each force…arrow_forward(2) A 30° MK = 0.45 Мк G B MA= 1 = 2 ку .8 kg - In the above arrangement of two blocks and card, the blocks start Use PWE to at rest, and the pulleys are frictionless. Find VA (mag and direc) after may assume that the card tension You B has descended by 0.65 m. is constant. You will need to use NSL to relate N₁ to WA E=mAg), NA and you Should show all the steps of this preliminary step also.arrow_forwardTheory of machinesarrow_forward
- You are moving to a new place and to go faster, you are pushing with a force P, two boxes at the same time. Your homogenous box 1, on the top has dimensions I₁=1.5m, h₁= 1.6m and a mass of m₁=12kg Your homogenous box 2, on the top has dimensions 1₂=2.4m, h₂= 2.8m and a mass of m2=19kg The coefficient of static friction between the 2 boxes is $12 = 0.34. The coefficient of static friction between box 2 and the ground is SG2 =0.25. Analyze the 4 scenarios: • Box 1 tips on box 2. • Box 1 slides on box 2. . P • Boxes 1 & 2 tip together. • Boxes 1 & 2 slide together on the ground. ls + Gi + G₂ W₂ |h₂ T Find the minimum for P for all 4 scenarios (include FBD and equations of equilibrium for each scenario), and conclude which scenario will occur first and why. In the box below, enter the required force P to strat motion (either tipping or slipping) in N with one decimal.arrow_forward4) Calculations for the red dog food can rolling down the slope in the Rube Goldberg design are as follows (we will name it Step 1): Step 1 (calculations are given): Coefficient of friction → μ = 0.14 Mass of the object → m = 368 gm = 0.368kg Initial height of the object (red can on top of books) → h=8.89, cm = 0.0889 m Slope of the file folder → 0 = 14° Travelling Distance by the object = 11.5 inch = 0.292 m And length that the object will travel = h/sin 0 = 0.0889/ sin14° = 0.367 m So, the radius of the object → R=0.367 -0.292 = 0.075 m Initial Velocity of red can → u = 0 Velocity and Force Calculations for Step 1: -From total mechanical energy conservation: → Initial mechanical energy = final mechanical energy → mg - In case of pure rolling, the velocity of the center of mass: → V = Ro = 0.075 × 14.28 1.07 m/s. -Hence the change in force acting on the object for the travel: →F=mgsine = 0.368 × 9.81 × sin14° =0.89 N Step 2: The Selective Step (Step 2) in this design and for the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY