
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Determine v using Superposition
Please answer in typing format please ASAP for the
Please
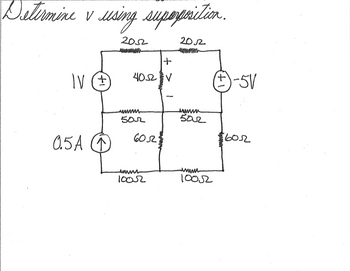
Transcribed Image Text:### Circuit Analysis Using Superposition
#### Objective:
Determine the voltage \( v \) using the Superposition Theorem.
#### Circuit Description:
The circuit consists of:
- Three sources:
- A 1V voltage source on the left side.
- A 0.5A current source below the 1V voltage source.
- A -5V voltage source on the right side.
- Resistors connected as follows:
- Two 20Ω resistors at the top forming a series path between the 1V and -5V sources.
- A 40Ω resistor in between the two 20Ω resistors, connected vertically with the polarity marked for \( v \).
- Two 50Ω resistors in parallel with the 40Ω resistor, vertically aligned between the middle nodes.
- Two 60Ω resistors in parallel, vertically aligned on the right side between the top and bottom nodes.
- Two 100Ω resistors at the bottom form a parallel path below the 50Ω and 60Ω resistors.
#### Explanation of Diagram:
- This circuit is analyzed using the Superposition Theorem by considering each source independently while turning off other sources (i.e., replacing voltage sources with short circuits and current sources with open circuits).
#### Steps for Analysis Using Superposition:
1. **Consider the 1V voltage source alone:**
- Deactivate the -5V voltage source (replace with a short circuit).
- Deactivate the 0.5A current source (replace with an open circuit).
- Analyze the resulting circuit to determine the contribution to \( v \) from the 1V source.
2. **Consider the -5V voltage source alone:**
- Deactivate the 1V voltage source (replace with a short circuit).
- Deactivate the 0.5A current source (replace with an open circuit).
- Analyze the resulting circuit to determine the contribution to \( v \) from the -5V source.
3. **Consider the 0.5A current source alone:**
- Deactivate the 1V voltage source (replace with a short circuit).
- Deactivate the -5V voltage source (replace with a short circuit).
- Analyze the resulting circuit to determine the contribution to \( v \) from the current source.
4. **Calculate the total voltage \( v \):**
- Sum up all contributions from each independent
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: what is given and what is required:
Given:
a network,
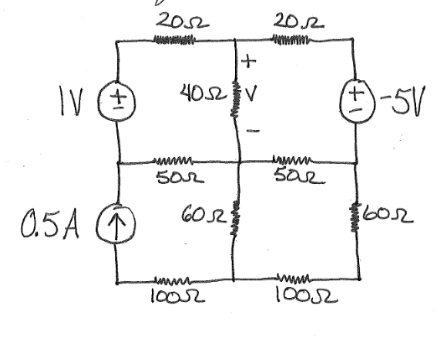
To find:
the voltage across 40 resistance using superposition theorem.
Note:
In superposition theorem, one source is applied at a time and remaining independent voltage source and current source are replaced by short circuit and open circuit respectively. Individual responses are added to get final response.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 15 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What I/0 device number will activate this decode circuit? Remember that I/0 device numbers are given in hex. A7 Аб A5 A4 2G diG A3 A2 A1 A0arrow_forwardI am unsure of how to fill in this table, an explanation would be appreciated!arrow_forwardHi, I need help in completing the truth table and completing the waveforms (timing diagram) for Q1, Q2, and Q3 with respect to the clock. Please answer in typing format solution please only typingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,