
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please don't provide handwrittewn solution .....
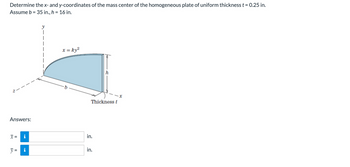
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the x- and y-coordinates of the mass center of the homogeneous plate of uniform thickness t = 0.25 in.
Assume b = 35 in., h = 16 in.
Answers:
X =
II
M
y
|
x = ky²
Thickness t
in.
h
in.
x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In Orthogonal Cutting Model, why chip thickness after cut is greater than chip thickness before cut?arrow_forwardSubject: manufacturing processarrow_forward3- Consider the precedence relationship between the activities of an assembly line. Knowing that the cycle time (T) of the assembly line is 10, then: a) Show the activities are assigned to the work station? (Note that you must show which activities are assigned to which stations. Do not give a number of workstations) b) Calculate efficiency and smoothness indices.arrow_forward
- b) An orthogonal cutting operation is performed using a rake angle of 15°, and having a chip thickness before the cut = 0.3 mm and width of cut = 2.5 mm. The chip thickness ratio is measured after the cut to be 0.55. Determine the following: i) the chip thickness after the cut, ii) shear angle, iii) friction angle, iv) coefficient of friction, and v) shear strain.arrow_forwardRead the description of the operations required to make a part, and considering the production rate, select a machine or machines to do the job Note: "Transverse" means perpendicular to the axis of rotation v Part requires turning, drilling, boring, and parting off, at a production rate of a. A swiss automatic or a CNC lathe with a live center in the tailstock, and possibly 10,000 parts per month. a steady rest Part requires turning, drilling, boring, and parting off, at a production rate of b.A manual lathe with no special fixturine 10 parts per month. v Part requires turning, drilling, boring, and parting off plus a transverse hole, d.A manual lathe, followed by setup on a manual milling machine at a production rate of 10,000 parts per month, • Part requires turning, drilling, boring, and parting off, plus a transverse hole, at a production rate of 10 parts per month. v Parts are very slender and require high precision for turning and parting off, at a rate of 10,000 parts per month…arrow_forwardQ.1) An arrangement of three boxes is shown in figure below. Box A weighs 20 N and rests on an inclined plane, while box B weighs 40 N and rests on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between box A and the inclined plane is 0.25, and between box B and the horizontal plane is 0.35. The pulleys are all frictionless. Determine the range of weight of box C for which no motion will occur. -0.7 m 40 N 1 m 0.5 m 0.6 m B 20 N 0.7 m A 4 5arrow_forward
- Investigate the non-traditional machining methods. Describe each in your own words and sketch out the process and appropriate scale (inches/microns etc). Then tabulate the material removal mechanism, workpiece materials, applications, costs/speed, advantages and limitations/disadvantages of each. The slides are for your starting point. List references, articles, videos, etc... Mechanical Methods 1. Water Jet Machining (WJM) 2. Abrasive Water Jet Machining (AWJM) 3. Ultrasonic Machining (USM) Non-Mechanical Methods 1. Electrochemical Machining (ECM) 2. Electro-Discharge Machining (EDM) 3. Wire EDM 4. Laser Drilling 5. Electron beam machining (EBM)arrow_forwardA circular shape blank will be cut of 100 mm diameter from a strip of 2.8 mm with a clearance value of 0.25 mm. Take the shear strength as 400 MPa. Determine a) The appropriate punch diameter. b) Blanking force. c) Blanking force when the blade angle is (5)°.arrow_forwardA HSS tool is used to turn a steel workpart that is 300 mm long and 80 mm in diameter. The parameters in the Taylor equation are: n = 0.13 and C = 75 (m/min) for a feed of 0.4 mm/rev. The operator and machine tool rate = $30.00/hr, and the tooling cost per cutting edge = $4.00. It takes 2.0 min to load and unload the workpart and 3.50 min to change tools. Determine: Tutting speed for maximum production rate, Tool life in min of cutting, and Cycle time and cost per unit of product. determine cutting speed for minimum cost.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY