
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
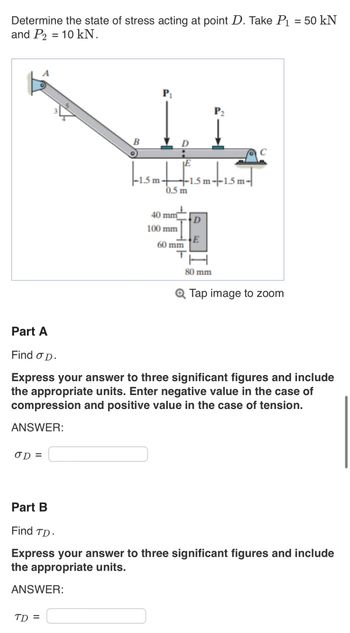
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the state of stress acting at point D. Take P₁ = 50 kN
and P2 = 10 kN.
OD=
B
ANSWER:
P₁
TD=
-1.5 m 1.5 m--1.5 m-
0.5 m
40 mm
100 mm
60 mm
T
D
E
P₂
80 mm
Part A
Find o D.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include
the appropriate units. Enter negative value in the case of
compression and positive value in the case of tension.
ANSWER:
C
Q Tap image to zoom
Part B
Find TD-
Express your answer to three significant figures and include
the appropriate units.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Show complete and detailed solution. Write legibly. Draw illustrations. Follow the decimals places on the directionarrow_forwardConsider the truss shown in (Figure 1). AE is constant. Suppose that F = 3.2 kN. Part A Determine the force in the member 1 of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter negative value in the case of compression and positive value the case of tension. HA ? q1 = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Part B 4 2 m 5 Determine the force in the member 5 of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. 90° Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. The answer is positive if the force is tensive and negative if the force is compressive. 13 μΑ ? 2 m 95 = Value Unitsarrow_forward14.4 Identify the type of masonry block shown belowarrow_forward
- The two bars shown in the figure are used to support a lead P. When unloaded, joint B has coordinates (0, 0). After load Pis applied, joint moves to the coordinate position ( 0.99 in.-0. 45 in.). Assume a = 10ft, b=5 ft, and h=7 ft. Determine the normal strain in each bar. B Answers: EAB = με Egcarrow_forwardmechanics of deformable bodiesarrow_forwardRods AB and BC have diameters of 2.9 mm and 4.6 mm, respectively. A force F = 2.4 kN is applied to the ring at B, as shown. (Figure 1) Determine the angle so that the average normal stress in each rod is equivalent. Express your answer to three significant figures. What is this stress? Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Bar ABC is rigid and rotates freely about B. The loads consist of a point load and a uniform temperature change in both bars CD and EF. Determine the temperature change (AT) at which points A and E first come into contact. Report your answer rounded to the nearest degree. 100 in initial gap = 0.11 in F T E A = 2.0 in² AEF EEF = 12,000 ksi aEF LEF 100 in = 13.5 x 10-6 1/°F = 50 in B 14 k 100 in D с ACD= 1.5 in² ECD CD= 6.5 x 10-6 1/°F = 29,000 ksi = 150 in LCD Y Zarrow_forwardPart A In (Figure 1), r = 30 mm. Locate the centroid a of the metal cross section. Neglect the thickness of the material and slight bends at the corners Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. T = 0 mm Submit Previous Answers Correct Figure < 1 of 1 Part B Locate the centroid ī of the metal cross section. Neglect the thickness of the material and slight bends at the corners Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HẢ ? 150 mm = Value Units Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 50 mm 100 mm 100 mm 50 mmarrow_forwardI Review Consider the truss shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that F = 10 kN . Part A Determine the force in member HI of the truss, and state if the member is in tension or compression. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter negative value in the case of compression and positive value in the case of tension. μΑ ? FHI = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the force in member FI of the truss, and state if the member is in tension or compression. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter negative value in the case of compression and positive value in the case of tension. Figure 1 of 1 > HÀ ? K FFI = Value Units 31 Submit Request Answer B |D E F -2 m--2 m--2 m--2 m--2 m--2 m- Part C 4 kN 5 kN 6 kN F Determine the force in member EF of the truss, and state if the member is in tension or compression. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning