Question
Determine the speed of the block with a mass of 0.60 kg after it has fallen 145 cm. The sphere is a shell with M = 4.5 kg and R = 8.5 cm. The pully has a rotational inertia of 0.0030 kg m2 and r = 5.0 cm. Use g = 9.8 m/s/s. Use conservation of energy.
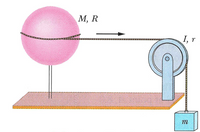
Transcribed Image Text:М, R
I, r
m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A Ferris wheel has moment of inertia 2.2 x 105 kg·m2. From rest, the operator starts the wheel and it accelerates for 13.4 seconds. If the engine does a total of 5.3 x 105 joules of work, calculate the number of revolutions the wheel makes as it accelerates.arrow_forwardThe propeller of a light plane has a length of 1.772 m and a mass of 21.96 kg. The propeller is rotating with a frequency of 2300. rpm. What is the rotational kinetic energy of the propeller? You can treat the propeller as a thin rod rotating through its center.arrow_forwardTo drive a typical car at 40 mph on a level road for one hour requires about 3.2 × 10^7 J of energy. Suppose we tried to store this much energy in a spinning, solid, uniform, cylindrical flywheel. A large flywheel cannot be spun too fast or it will fracture. If we used a flywheel of diameter 1.26 m and mass 450 kg, what angular speed would be required to store 3.2 x 10^7 J? Give your answer in rad/s.arrow_forward
- To drive a typical car at 40 mph on a level road for one hour requires about 3.2 × 10^7 J of energy. Suppose we tried to store this much energy in a spinning, solid, uniform, cylindrical flywheel. A large flywheel cannot be spun too fast or it will fracture. If we used a flywheel of diameter 1.26 m and mass 450 kg, what angular speed would be required to store 3.2 x 10^7 J? Give your answer in rad/s.arrow_forwardA piece of wood is pressed against a spindle sanding disk which is a uniform disk with a radius of 0.090 m, rotating at an initial angular velocity of 37.0 rad/s (ωi = 37.0 rad/s). This motion results in a constant tangential frictional force of magnitude f = 9.00 N and causes the sanding disk to come to a complete stop in = 25.0 s. 1. What is the torque on the sanding disk due to the force exerted by the wood; no additional torques act other than the one caused by the wood.2. What is the mass of the sanding disk, assuming it is a uniform disk.3. During the first 7.0 s of sanding, what is the change in rotational kinetic energy of the disk.arrow_forwardA uniform rod is set up so that it can rotate about an axis at perpendicular to one of its ends. The length and mass of the rod are 0.759 m and 1.31 kg, respectively. A force of constant magnitude F acts on the rod at the end opposite the rotation axis. The direction of the force is perpendicular to both the rod's length and the rotation axis. Calculate the value of F that will accelerate the rod from rest to an angular speed of 6.69 rad/s in 8.49 s. F =arrow_forward
- A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk rotates on a frictionless bearing about a vertical axle through the center of the disk. The platform has a radius of 1.83 m and a rotational inertia of 261 kg⋅m² about the axis of rotation. A 73.1 kg student walks slowly from the rim of the platform toward the center. If the angular speed of the system is 1.97 rad/s when the student starts at the rim, what is the angular speed when she is 0.673 m from the center? Number Unitsarrow_forwardA large door is a uniform rectangle, with height h and width w and mass m, which is free to rotate about one long side. What is the smallest force required to open the door with constant angular acceleration a? Parameters: h = 2.70 m; w = 1.30 m; m = 50 kg; a = 0.30 rad/s^2. (in N) OA: 0.883 OB: 1.174 OC: 1.562 OD: 2.077 OE: 2.763 OF: 3.675 OG: 4.887 OH: 6.500arrow_forwardA turntable (disk) of radius r= 25.0 cm and rotational inertia 0.395 kg · m rotates with an angular speed of 3.04 rad/s around a frictionless, vertical axle. A wad of clay of mass m = 0.254 kg drops onto and sticks to the edge of the turntable. What is the new angular speed of the turntable? rad/sarrow_forward
- A 24 g block sits at the center of a turntable that rotates at 80 rpm. A compressed spring shoots the block radially outward from the center along a frictionless groove in the surface of the turntable. Calculate the turntable's angular speed when the block reaches the outer edge. Treat the turntable as a solid disk with mass with mass 200 g and diameter 54.0 cm. Express your answer in revolutions per minute.arrow_forwardA uniform rod is set up so that it can rotate about an axis at perpendicular to one of its ends. The length and mass of the rod are 0.701 m and 1.29 kg , respectively. A force of constant magnitude ?F acts on the rod at the end opposite the rotation axis. The direction of the force is perpendicular to both the rod's length and the rotation axis. Calculate the value of ?F that will accelerate the rod from rest to an angular speed of 6.59 rad/s in 8.95 s.arrow_forwarda small 0.383 kg block slides down a frictionless surface through height h = 0.752 m and then sticks to a uniform vertical rod of mass M = 0.766 kg and length d = 2.34 m. The rod pivots about point O through angle θ before momentarily stopping. Find θ.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios