
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
USING THE CONJUGATE BEAM METHOD
ps. The 2nd pic is the answer key.
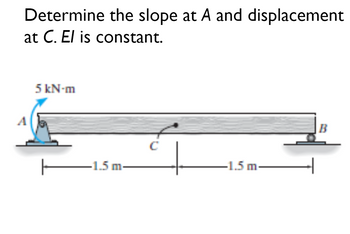
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the slope at A and displacement
at C. El is constant.
5 kN-m
1.5 m-
-1.5m
B

Transcribed Image Text:Ө = -5/El kN/m² counterclockwise;
A = -2.8125/El kN/m³ upward
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Olny need you to draw and label the element and nodes. Also identify the unconstrained and contrained degree of freedomarrow_forwardExplain it correctly. Not copy pastearrow_forwardThe beam is made from a soft linear elastic material having a constant EI. If it is originally a distance from the surface of its end support, determine the length a that rests on this support when it is subjected to the uniform load w0, which is great enough to cause this to happen.arrow_forward
- SOLVEarrow_forwardFigure below shows a uniformly tapering bar of rectangular cross-section of length L and thickness t. The width of the bar at one end is b₁ and the width at the other end is b2, where (b₂> b₁). The bar is subjected to an axial force P. The axial deformation due to load P is given by _mm. b₂ PL atE b₁ = 20 mm b₂-40 mm -In () then the value of (a + c) isarrow_forwardFor the structure in the figure below , determine the correct answer. Roller- The structure is stable and determinate. The structure is statically unstable. The structure is geometrically unstable. The structure is stable and indeterminate.arrow_forward
- The beam cross section shown below has been proposed for a short pedestrian bridge. The cross section will consist of two pipes that are welded to a rectangular web plate. Dimensions of the cross section are: h = 470 mm tw = 14 mm d = 120 mm t = 9.6 mm Additionally: • The area of each pipe is A = 3330 mm2. • The moment of inertia of the entire beam cross section about the z centroidal axis is IZ = 428040000 mm4. If the beam will be subjected to a shear force of V = 225 kN, determine the shear stress at point H, located at yH = 110 mm above the z centroidal axis.arrow_forward3= no matter if you solve if by hand writingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning