
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
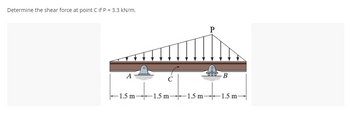
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website**
---
**Problem Statement:**
Determine the shear force at point C if P = 3.3 kN/m.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a simply supported beam with triangular distributed loading. The structure includes:
- **Supports:**
- Support A (left support) and support B (right support) are represented as rollers, indicating that the beam is simply supported.
- **Load Distribution:**
- The triangular distributed load acts over the entire length of the beam, starting from zero at the left end (near support A) and increasing linearly to a maximum value at the right end (near support B).
- The maximum intensity of the distributed load is labeled as P = 3.3 kN/m at the right end.
- **Dimensions:**
- The beam is divided into equal sections of 1.5 meters each:
- From A to C: 1.5 meters
- From C to an unspecified point to the right: 1.5 meters
- Total length from A to B: 4.5 meters
- **Important Points:**
- Point C is the specific point of interest where the shear force needs to be determined. It is located at 1.5 meters from the left support (A).
This setup requires the calculation of shear force resulting from the triangular distributed load, taking into account the equilibrium of the beam and applying principles of static equilibrium.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the weight of the counterweight W that should be used. Calculate the shear forces and bending moments and draw the diagrams.arrow_forwardIf the tension in cable DE is 455 N, determine the moments of this tensile force (as it acts at point D) about point O and about line OF. EQ 2.3 m Answers: BC=CD = 2.2 m MOF= 3.0 m Moi -1203.39 i 2.3 m 3.1 m 1.3 m i+ i N.m 1.7 m 39° j+ i k) N-marrow_forwardDetermine the reaction forces R1 and R2 and show the shear and bending moment diagram. Data: Point load (left-most) = 90.126 N Uniformly distributed load (80mm to 260mm) = 0.14444 N/mm Uniformly distributed load (160mm to 180mm) = 6.5 N/mmarrow_forward
- Determine the magnitude of the pin force at A. Assume W = 830 lb, a = 5.5 ft, b = 4.0 ft, r = 8 in. r W с Answer: A = i a B a A D lb barrow_forwardThe bar of negligible weight is supported by two springs,each having a stiffness k = 80 N>m. If the springs are originally unstretched, and the force is vertical as shown,determine the angle theta the bar makes with the horizontal,when the 45-N force is applied to the bar. 1.5 m- 3 m C В 45 Narrow_forwardP = 93.3 N Determine the force at F. Take it apart to help you solvearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY