
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Determine the resultant force magnitude, direction, and its angle from the x-axis for force components F1 & F2, components F2 & F3, and components F3 & F4.
NOTE: must be solved using the parallelogram method, not the rectangular
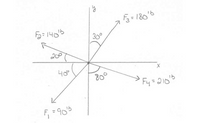
Transcribed Image Text:ら=180
'%
%3D
ら:140
30°
200
40°
80°
Fy = 2100
F,
90'5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two muscles in the back of the leg pull upward on the Achilles tendon, as shown in the figure below. (These muscles are called the medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle.) F₂ = 205 N F₁ = 205 N 26° 26° Find the magnitude (in N) and direction (in degrees counterclockwise from the dotted line) of the total force on the Achilles tendon. XN magnitude direction X counterclockwise from the dotted line 410 25.45 What type of movement could be caused by this force? O This force can raise the heel of the foot. This force can twist the ankle to the left or right. This force can turn the foot to the left or right. This force can lower the heel of the foot. Needs Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardUse the rectangular component method to solve the fol- lowing problems. Determine the magnitude R of the re- sultant of the forces and the angles 8, By, and 8, between the line of action of the resultant and the positive *-, y-, and z-coordinate axes for F2 = 200 Ib F, = 100 Ib 70arrow_forwardF = (-30i + 60j + 60k )kN %3D Forces are concurrent at point O. Determine the magnitude of the resultant of the three vectors. a 71.5 kN b 187 kN F, = (60i – 20j+ 15k )kN c 116 kN d 83.7 kN Determine the angle between F, andF,. F, = (20j – 25k)kN X а 111° b 132° c 69.0° d 21.0° Select the expression that denotes a unit vector in the direction and sense of F,. a 0.625j -0.781k b 0.625i -0.781j c -0.625 j –0.781k d 0.625i +0.781jarrow_forward
- The force F has a magnitude of 480 Ib and acts along the diagonal of the parallelepiped as shown. Express Fin terms of its magnitude times the appropriate unit vector and determine its x-, y-, and z-components. A 6' F = 480 b 8' 3' B Answers: i+ i j+ i F= ( i Ib)( i Fx Ib i Fy Ib F2 Ib iarrow_forwardDon't use chat gpt It Chatgpt means downvotearrow_forwardThe force F is applied 45 degrees counter clockwise from the surface of the slope. The slope is 20 degrees counter clockwise from the horizontal. The magnitude of F is 60lbs. Determine the magnitude of the Force F applies along the slopearrow_forward
- Two forces F1 and F2 act at point O. R is the resultant of force F1 and F2, and it is expressed as R = F1 + F2. Given the magnitude of |F1| = 60 N and |R| = 100 N, calculate. must use parallelogram law/triangle rule and sine & cosine laws.arrow_forwardA force has a magnitude of 30N and makes an angle of 40 degrees with the y-axis. What is the magnitude of the vertical component? INCLUDE A DIAGRAM.arrow_forwardFigure Q1a shows two cables attached to a half-ring anchor point as shown in Figure Q1a. Force F1 acts vertically with a force of 2170 N; and F2 acts at an angle 0 relative to the y-axis with a force of 1240 N. y F1 F2 Figure Q1a Cable Anchor Pointarrow_forward
- Two rods and one cable are attached to the supports at O. If two of the forces are as shown, determine the magnitude F and direction of the third force so that the resultant of the three forces is vertically downward with a magnitude of 1160 lb. 1010 lb 45° 35° 430 lbarrow_forwardTwo muscles in the back of the leg pull upward on the Achilles tendon, as shown in the figure below. (These muscles are called the medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle.) F2 = 150 N F1 = 150 N Find the magnitude (in N) and direction (in degrees counterclockwise from the dotted line) of the total force on the Achilles tendon. a) magnitude N b) direction ° counterclockwise from the dotted line c) What type of movement could be caused by this force? This force can raise the heel of the foot. This force can twist the ankle to the left or right. This force can lower the heel of the foot. This force can turn the foot to the left or right.arrow_forwardUsing the method of components, find the resultant of the following concurrent forces. Note: After solving for the Angle of the Resultant, you must then determine the Direction of the Resultant relative to Horizontal (positive x-axis) in a CCW (counter-clockwise direction). Sometimes the Direction of the Resultant may be the same as the Angle of the Resultant. However, you must always calculate both: the Angle of the Resultant (based on the Resultant triangle sketch) and then the Direction of the Resultant based on Horizontal (positive x-axis) in a CCW direction from horizontal.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON