
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the required minimum diameter d of the shaft to the nearest millimeter.
Express your answer as an integer.
The shaft is made of A992 steel with the allowable shear
d = 22 mm
stress of Tallow = 75 MPa. Gear B supplies 15 kW of
power, while gears A, C and D withdraw 6 kW, 4 kW
and 5 kW, respectively. The shaft is rotating at 600 rpm.
(Figure 1)
Submit
Previous Answers
v Correct
Part B
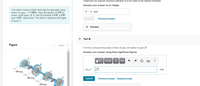
Figure
1 of 1
Find the corresponding angle of twist of gear A relative to gear D.
Express your answer using three significant figures.
It vec
?
B
PA/D = 25
rad
600 mm
600 mm
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
600 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 5 The solid shaft as shown in Figure 5 is made of material that has an allowable stress of [X(45)+20]MPa. Determine the required diameter of the shaft to the nearest mm. Given the value of X=7 and Y=5 15 N-m 25 N-m 30 N-m Figure 5 60 N-m 70 N-marrow_forwardThe shaft is made of A992 steel with the allowable shear stress of Tallow = 75 MPa. Gear B supplies 15 kW of power, while gears A, C and D withdraw 6 kW, 4 kW and 5 kW, respectively. The shaft is rotating at 600 rpm. (Figure 1) Figure 600 mm 600 mm ② 600 mm ▼ Part A Determine the required minimum diameter d of the shaft to the nearest millimeter. Express your answer as an integer. ΠΑΣΦ11 Ivec d= Submit Part B Find the corresponding angle of twist of gear A relative to gear D. Express your answer using three significant figures. VE ΑΣΦΠ Ivec 1 PA/D= Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Request Answer ? www. ? mm radarrow_forwardTorque in = 40nm Holding torque out = 896nm 8.Using your answers from the gear box above, and given that the input shaft has a diameter of 12 mm and the output shaft has a diameter of 15 mm, both shafts are made from aluminium. When this transmission system was operated, it failed. Identify the position where the failure occurred and the reason for this failure. Suggests improvements to the system to overcome the failure mode. The shear strength of aluminium is 207 MPa.arrow_forward
- only Handwritten answer needed please. not typedarrow_forwardThe customised shaft has a diameter of 50 mm. A square parallel key is suggested to be used for mounting a gear into this shaft. The shaft is to be made of SAE 1095 Carbon Steel with a yield stress of 572 MPa. The gear is made from SAE 1045 Carbon Steel with a yield stress of 531 MPa. A key can be made of SAE 1018 Carbon Steel with a yield stress of 372 MPa or SAE 316 Stainless Steel of 241 MPa. The gear transmits torque of 2,000 +P N-m and has a hub length of 100 mm. The design factor is chosen as 3.0 and the width of the key is 12.7 mm. Specify the keys using two materials and explain which material should be recommended in such a design scenario. Key Figure 1: Key, Gear and Shaft You may use the following equations: == T D/2(WL) 4T σ DLH 2T L = TDW 4T L= σDHarrow_forwardThe 60-mm-diameter shaft is made of 6061-T6 aluminum. (Figure 1) Figure 1.20 m 1.20 m 1 of 1 Part A If the allowable shear stress is Tallow = 80 MPa, and the angle of twist of disk A relative to disk C is limited so that it does not exceed 0.060 rad, determine the maximum allowable torque T Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. T = Submit Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY