
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
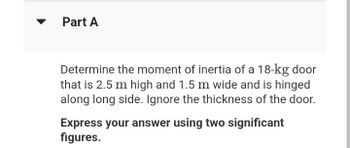
Determine the moment of inertia of a 18-kg door
that is 2.5 m high and 1.5 m wide and is hinged
along long side. Ignore the thickness of the door.
Express your answer using two significant
figures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The meterstick shown is 100 cm long. It is free to pivot around its center of gravity (CG), which is at the 50 cm mark. There is a 24.0 N block hanging from the 80 cm mark. Decide where each of the other blocks should be placed, one at a time, to balance out the 24.0 N block. At what mark on the meter stick would you place a 19.0 N block to balance the 24.0 N block? mark: At what mark on the meter stick would you place a 44.0 N block to balance the 24.0 N block? mark:arrow_forwardTo get up on the roof, a person (mass 62.0 kg) places a 6.80 m aluminum ladder (mass 11.0 kg) against the house on a concrete pad with the base of the ladder 2.00 m from the house. The top of the ladder rests against a plastic rain gutter, which we can assume to be frictionless. The center of mass of the ladder is 2.00 m from the base, as measured along the ladder. The person is standing on the ladder 3.00 m from the base, as measured along the ladder. Find the normal reaction and friction forces (in N) on the ladder at its base. (Enter the magnitudes.) normal reaction force friction forcearrow_forwardplease solve symbolically before using numbersarrow_forward
- The wheels,axle, and handles of a wheelbarrow weigh W=56N. The load chamber and it’s contents weigh WL=635N.the drawing shows these two forces in two different wheelbarrow designs. To support the wheelbarrow in equilibrium, the man’s hands apply a force to the handles that is directed vertically upward.consider a rotational axis at the point where the tire contacts the ground, directed perpendicular to the plane of the paper.find the magnitude of the man’s force for both designs.arrow_forwardA centrifuge rotor rotating at 9300 rpm is shut off and is eventually brought uniformly to rest by a frictional torque of 1.66 m⋅N. If the mass of the rotor is 4.58 kg and it can be approximated as a solid cylinder of radius 0.0440 m, through how many revolutions will the rotor turn before coming to rest? Express your answer to three significant figures. How long will it take? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA hungry bear weighing 85.0 kg walks out on a beam in an attempt to retrieve a basket of food hanging at the end of the beam. The beam is uniform, has a mass of 20.0 kg, is 8.00 m long, and pivoted at the wall; the basket weighs 10.0 kg. If the wire can withstand a maximum tension of 900 N, what is the maximum distance that the bear can walk before the wire breaks? ←x 60.0⁰ Goodiesarrow_forward
- A 4 m long horizontal uniform beam of mass 20 kg is supported by a wire as shown in the figure. The wire makes an angle of 23 degrees with the beam. Attached to the beam 1.2 m from the wall is a ball with a mass of 48 kg. What is the tension in the string? K 0 (m)arrow_forwardMultiple-Concept Example 10 reviews the approach and some of the concepts that are pertinent to this problem. The figure shows a model for the motion of the human forearm in throwing a dart. Because of the force M applied by the triceps muscle, the forearm can rotate about an axis at the elbow joint. Assume that the forearm has the dimensions shown in the figure and a moment of inertia of 0.062 kg-m? (including the effect of the dart) relative to the axis at the elbow. Assume also that the force M acts perpendicular to the forearm. Ignoring the effect of gravity and any frictional forces, determine the magnitude of the force M needed to give the dart a tangential speed of 4.5 m/s in 0.14 s, starting from rest. 0.28 m Axis at elbow joint 0.025 m Number i Unitsarrow_forwardThe meterstick shown is 100 cm long. It is free to pivot around its center of gravity (CG), which is at the 50 cm mark. There is a 23.0 N block hanging from the 80 cm mark. Decide where each of the other blocks should be placed, one at a time, to balance out the 23.0 N block. At what mark on the meter stick would you place a 16.0 N block to balance the 23.0 N block? mark: At what mark on the meter stick would you place a 44.0 N block to balance the 23.0 N block? mark:arrow_forward
- To get up on the roof, a person (mass 82.0 kg) places a 6.60 m aluminum ladder (mass 11.0 kg) against the house on a concrete pad with the base of the ladder 2.00 m from the house. The ladder rests against a plastic rain gutter, which we can assume to be frictionless. The center of mass of the ladder is 2 m from the bottom. The person is standing 3 m from the bottom. What are the magnitudes (in N) of the forces on the ladder at the top and bottom? top N bottom Narrow_forwardAn approximate model for a ceiling fan consists of a cylindrical disk with four thin rods extending from the disk's center, as in the figure below. The disk has mass 2.30 kg and radius 0.200 m. Each rod has mass 0.850 kg and is 0.840 m long. HINT (a) Find the ceiling fan's moment of inertia about a vertical axis through the disk's center. (Enter your answer in kg. m².) kg - m² (b) Friction exerts a constant torque of magnitude 0.113 Nm on the fan as it rotates. Find the magnitude of the constant torque provided by the fan's motor if the fan starts from rest and takes 15.0 s and 16.5 full revolutions to reach its maximum speed. (Enter your answer in N. m.) N.marrow_forwardA 44 kg , 5.2-m-long beam is supported, but not attached to, the two posts in the figure. A 20 kg boy starts walking along the beam. How close can he get to the right end of the beam without it falling over?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON